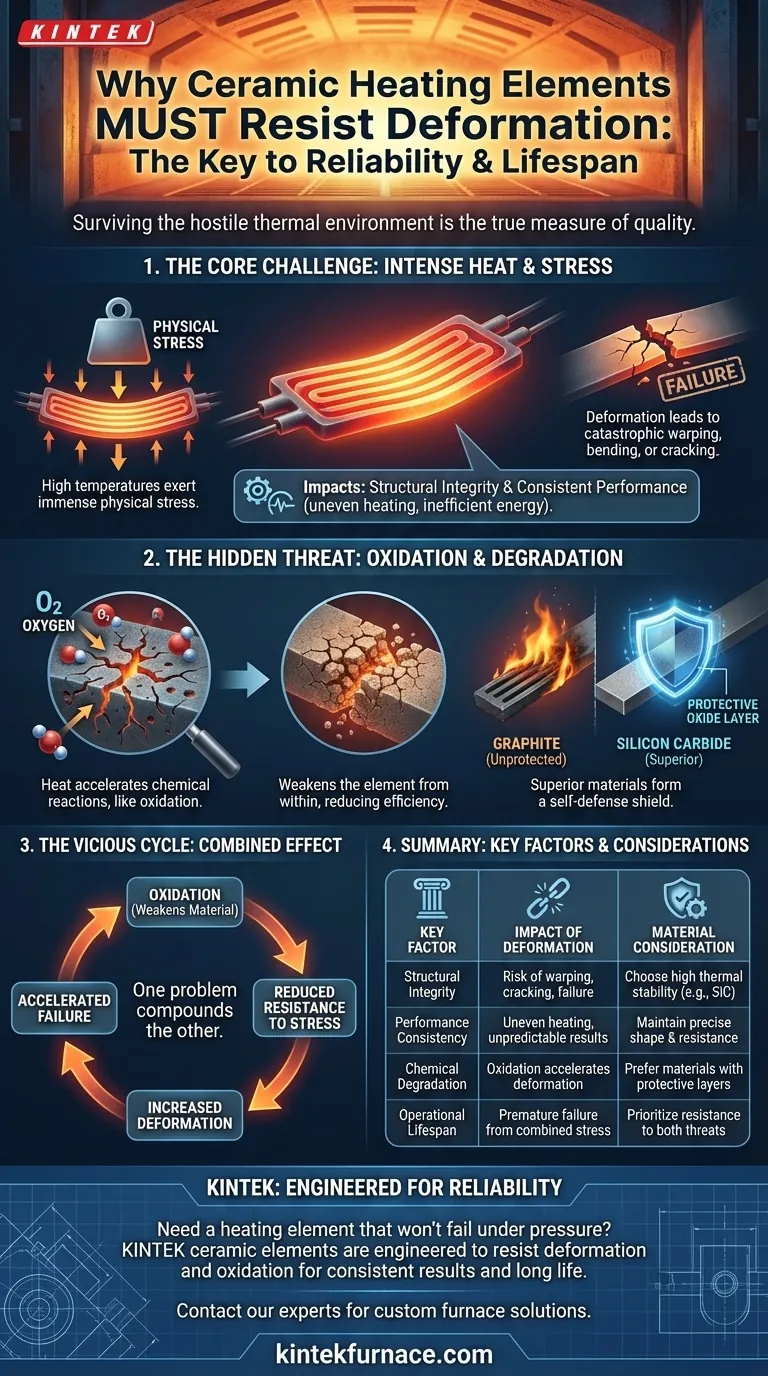
A ceramic heating element's resistance to deformation is critical because it directly determines its structural integrity and operational lifespan. At the very high temperatures required for operation, materials are prone to warping, bending, or breaking, which would cause immediate failure and compromise the entire system.
The true measure of a ceramic heating element is not just its ability to generate heat, but its capacity to survive the hostile thermal environment it creates. Resisting both physical deformation and chemical degradation are the twin pillars of its long-term reliability and performance.
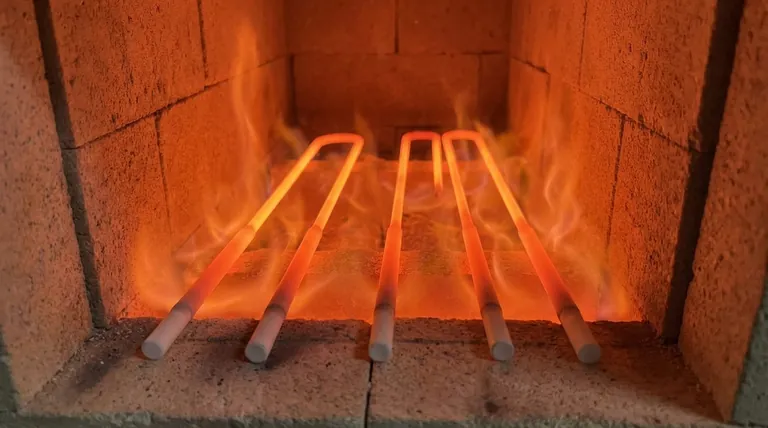

The Core Challenge: Surviving Intense Heat
Any material's physical properties are tested under extreme temperatures. For a heating element, which operates in this state by design, stability is the most fundamental requirement for it to function correctly and safely.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
High temperatures exert immense physical stress on a material's structure. An element that cannot withstand this stress will deform.
This deformation can manifest as warping, bending, or even cracking. Such a failure is often catastrophic, leading to a complete breakdown of the heating system.
Ensuring Consistent Performance
The shape and dimensions of a heating element are precisely engineered to deliver a specific heating profile and electrical resistance.
If the element warps or changes shape, its performance becomes unpredictable. This can lead to uneven heating, inefficient energy use, and a failure to meet process requirements.
Beyond Shape: The Threat of Chemical Degradation
While physical deformation is a primary concern, it is closely linked to the chemical stability of the material. Intense heat is a powerful catalyst for chemical reactions, most notably oxidation.
The Inevitable Attack of Oxidation
Oxidation is a process where a material reacts with oxygen, and this process is massively accelerated by heat. Over time, it can literally destroy the heating material.
This chemical degradation weakens the element from within, reducing its efficiency and dramatically shortening its operational lifespan. A weakened material is also far more susceptible to physical deformation.
How Materials Defend Themselves
Superior ceramic heating elements, such as those made from silicon carbide, have a natural defense mechanism. They form a protective oxide layer on their surface that prevents further degradation.
In contrast, materials like graphite lack this property and will rapidly burn away in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. They can only be used in protected environments, like a vacuum furnace.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the failure modes of a heating element is key to selecting the right one. The two primary threats—deformation and oxidation—are often interconnected.
When Deformation Occurs
The immediate risk of deformation is mechanical failure. The element can break, make contact with other components causing a short circuit, or shift out of position, creating dangerous hot spots.
The Slow Burn of Oxidation
Oxidation is a more gradual failure mode. The first sign is often a loss of heating efficiency, requiring more power to achieve the same temperature. This is followed by eventual burnout and element failure.
The Combined Effect
These two issues compound each other. As an element is weakened by oxidation, its ability to resist physical stress decreases, making deformation more likely. A high-quality element must be robust against both forces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of heating element should be guided by its ability to withstand the specific conditions of your process over the long term.
- If your primary focus is longevity and reliability: Prioritize materials like silicon carbide known for excellent high-temperature stability and inherent resistance to both deformation and oxidation.
- If you are operating in a protected atmosphere (like a vacuum): You may have a wider range of material options, but you must ensure the environment strictly prevents exposure to oxygen to avoid rapid degradation.
Ultimately, a heating element's ability to resist both physical and chemical change under heat is the true measure of its quality and value.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact of Deformation | Material Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Integrity | Risk of warping, cracking, or catastrophic failure | Choose materials with high thermal stability (e.g., silicon carbide) |
| Performance Consistency | Uneven heating, inefficient energy use, unpredictable results | Maintain precise shape and electrical resistance |
| Chemical Degradation | Oxidation weakens material, accelerating deformation | Prefer materials that form protective oxide layers |
| Operational Lifespan | Combined physical and chemical stress leads to premature failure | Prioritize resistance to both deformation and oxidation |
Need a heating element that won't fail under pressure?
At KINTEK, we understand that your lab's success depends on reliable, high-performance equipment. Our ceramic heating elements are engineered to resist deformation and oxidation, ensuring consistent results and a long operational life—even in the most demanding thermal environments.
Let us help you select the perfect heating solution for your unique application. Contact our experts today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems can be customized to meet your specific needs, backed by our expert R&D and manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications
- What ceramic materials are commonly used for heating elements? Discover the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision



















