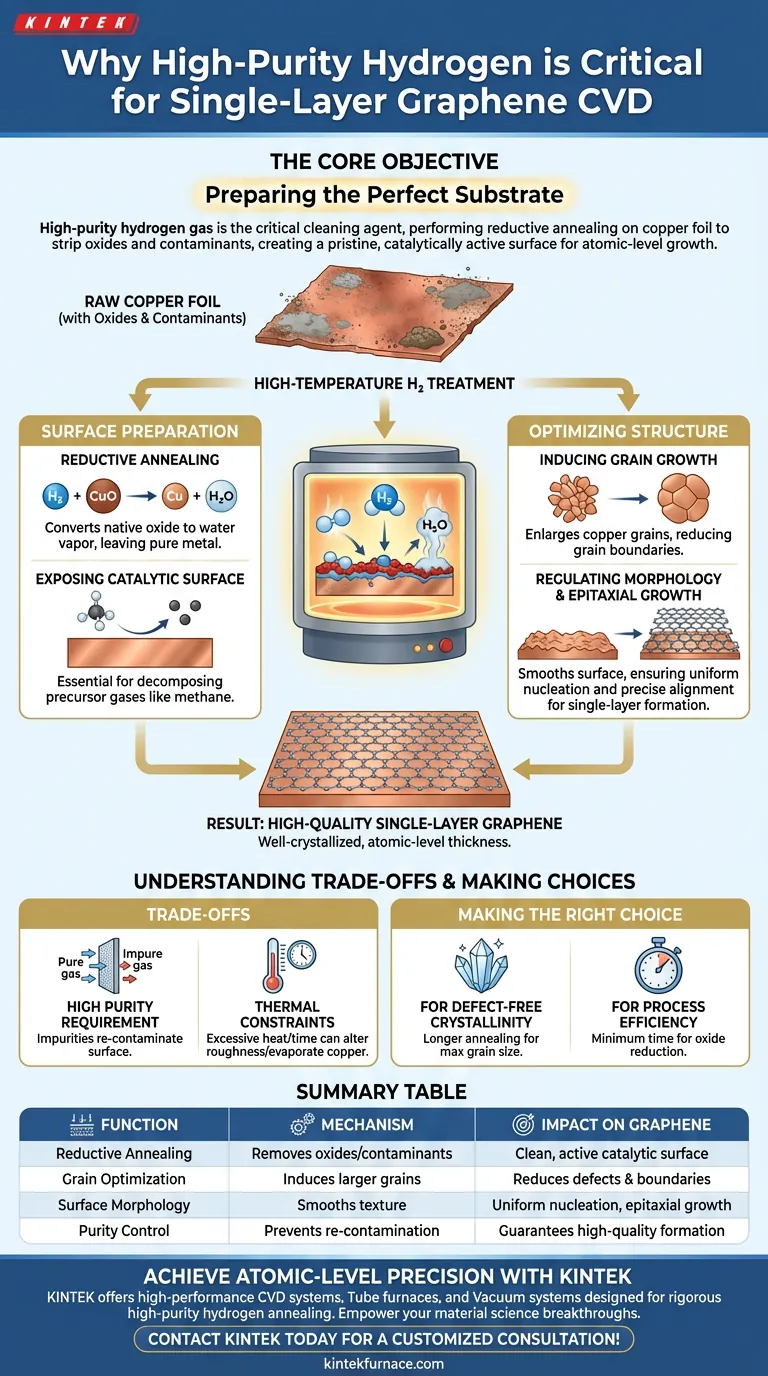
High-purity hydrogen gas is the critical cleaning agent that prepares the substrate for successful synthesis. Introduced during the high-temperature treatment phase, it performs reductive annealing on the copper foil, stripping away native oxides and organic contaminants to expose a pristine, catalytically active surface. Without this step, the subsequent chemical reactions required to form graphene cannot proceed correctly.
The Core Objective Producing high-quality, single-layer graphene requires a substrate that is both chemically pure and structurally optimized. Hydrogen annealing serves as the foundational preparation step, removing surface barriers (oxides) and restructuring the copper grains to create an ideal template for atomic-level growth.
The Mechanics of Surface Preparation
To understand why hydrogen is non-negotiable, you must look at the condition of raw copper foil. It is rarely ready for the delicate process of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Reductive Annealing
The primary function of hydrogen at high temperatures is reductive annealing. Copper naturally forms a native oxide layer when exposed to air.
Hydrogen reacts chemically with this oxide layer, converting it into water vapor that is pumped out of the system. This leaves behind a pure metallic surface essential for the process.
Exposing the Catalytic Surface
CVD growth relies on the metal substrate acting as a catalyst to decompose precursor gases like methane.
By removing oxides and organic impurities, hydrogen exposes the clean metallic catalytic surface. If the surface remains contaminated, the carbon atoms cannot interact properly with the copper, leading to failed or patchy growth.
Optimizing the Substrate Structure
Beyond chemical cleaning, hydrogen annealing physically alters the copper foil to support better graphene formation.
Inducing Grain Growth
At high temperatures, hydrogen annealing promotes the enlargement of copper grains.
Larger copper grains are desirable because they reduce the number of grain boundaries on the substrate. Fewer boundaries in the substrate typically lead to higher quality, more continuous graphene films.
Regulating Surface Morphology
The annealing process helps smooth the surface texture of the foil.
This regulation of surface morphology establishes a uniform foundation. A consistent surface is vital for controlling graphene nucleation, ensuring the film grows evenly across the substrate.
Enabling Epitaxial Growth
The ultimate goal of this pre-treatment is to facilitate epitaxial growth.
By organizing the copper lattice and cleaning the surface, hydrogen creates a template that allows carbon atoms to align precisely. This results in the formation of well-crystallized single-layer graphene with atomic-level thickness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While hydrogen annealing is essential, it introduces specific process sensitivities that must be managed.
The Requirement for High Purity
The system is extremely sensitive to the quality of the gas used. High-purity hydrogen is mandatory; any impurities in the gas stream can re-contaminate the hot copper surface, negating the cleaning effect.
Thermal Constraints
The process requires high temperatures to be effective. This thermal load can lead to copper evaporation if not carefully controlled, potentially altering the surface roughness in undesirable ways if the annealing time is excessive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The duration and intensity of the hydrogen treatment should be tuned based on your specific requirements for the final material.
- If your primary focus is Defect-Free Crystallinity: Prioritize a longer annealing phase to maximize copper grain size and reduce substrate grain boundaries.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Optimize the minimum time required to achieve full oxide reduction without extending into prolonged morphological restructuring.
A pristine, well-structured catalyst is the single most important factor in determining the quality of CVD graphene.
Summary Table:
| Function | Mechanism | Impact on Graphene |
|---|---|---|
| Reductive Annealing | Removes copper oxides and organic contaminants | Provides a clean, active catalytic surface |
| Grain Optimization | Induces growth of larger copper grains | Reduces defects and grain boundaries |
| Surface Morphology | Smooths and regulates substrate texture | Ensures uniform nucleation and epitaxial growth |
| Purity Control | High-purity gas prevents re-contamination | Guarantees high-quality single-layer formation |
Achieve Atomic-Level Precision in Your CVD Research
High-quality graphene synthesis starts with the right environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance CVD systems, Tube furnaces, and Vacuum systems designed to handle the rigorous demands of high-purity hydrogen annealing. Whether you need precise thermal control or customizable systems for unique lab requirements, our high-temperature solutions empower your material science breakthroughs.
Ready to optimize your thin-film growth? Contact KINTEK today for a customized consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Songsong Yao, Tongxiang Fan. Effect of Copper Surface Roughness on the High-Temperature Structural Stability of Single-Layer-Graphene. DOI: 10.3390/ma17071648
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics and uses of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings? Enhance Durability and Efficiency in Your Applications
- What are the environmental benefits of using CVD furnaces? Reduce Waste and Boost Efficiency
- What is the process for synthesizing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) using CVD tube furnaces? Master High-Quality Thin Film Growth
- How is doped silicon dioxide created using CVD? Master Planarization with Doped Glass Techniques
- What are the structural advantages of a customized AP-SCVD system? High-Throughput WO3 Thin Film Production
- What is the function of the high-purity quartz furnace tube in LP-CVD? Enhance Your SLG Synthesis Quality
- What factors contribute to the high cost of CVD processes? Uncover Key Drivers and Cost-Saving Insights
- What is the primary function of a sputtering deposition system in graphene growth? Expert Catalyst Engineering



















