At their core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces provide significant environmental benefits primarily because they use gas-phase reactants. This approach drastically reduces the liquid and solid waste streams associated with traditional wet-chemical or solid-phase fabrication methods, leading to a cleaner, more efficient process. Furthermore, their design intrinsically promotes high energy efficiency and precise material use.
The primary environmental advantage of a CVD furnace is its fundamental efficiency. By building thin films atom by atom from a gas, it minimizes material waste, energy consumption, and the generation of difficult-to-treat industrial byproducts.

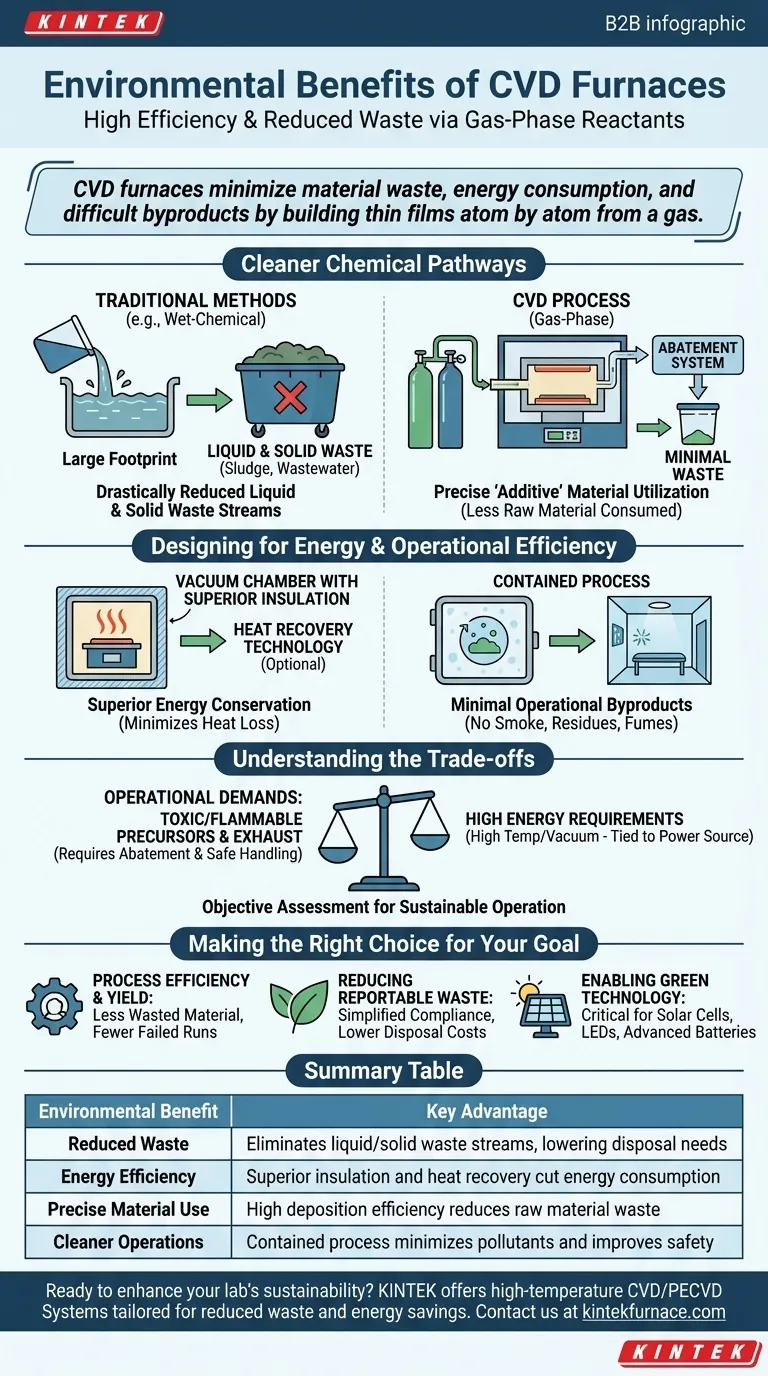
The Foundation: Cleaner Chemical Pathways
The most direct environmental benefit of CVD comes from the very nature of its chemical process, which stands in stark contrast to many alternative manufacturing techniques.
Drastically Reduced Liquid and Solid Waste
CVD processes build materials from gaseous precursors. This virtually eliminates the large volumes of wastewater or solid waste sludge that are common byproducts of liquid-phase preparation methods like electroplating or sol-gel processing.
This shift from liquid or solid reactants to gases results in a fundamentally cleaner operation with a much smaller waste-management footprint.
Precise Material Utilization
The CVD process allows for exceptionally precise control over film thickness and uniformity. Because you are depositing material directly onto a substrate with high conformity, you use only the material you need.
This "additive" approach is far more resource-efficient than "subtractive" methods, where a bulk material is etched away, creating significant waste. Higher deposition efficiency means less raw material is consumed per product.
Designing for Energy and Operational Efficiency
Modern furnaces, including CVD systems, are engineered to minimize energy loss and operational byproducts, contributing to a more sustainable footprint.
Superior Energy Conservation
CVD furnaces, particularly those operating under vacuum, feature excellent thermal insulation and controlled atmospheres. This design minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment, ensuring that the energy consumed is used effectively to drive the reaction.
Some advanced systems even incorporate waste heat recovery technology, capturing exhaust heat to further improve overall energy utilization in an industrial setting.
Minimal Operational Byproducts
During operation, a well-maintained CVD system does not produce pollutants like smoke, waste gas, or residues directly from the chamber. The process is self-contained.
Unlike processes involving open flames or chemical baths, the contained nature of CVD improves the immediate work environment by reducing noise and eliminating exposure to fumes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While CVD offers clear advantages, a complete environmental assessment requires acknowledging its operational demands and inputs. True objectivity means understanding the full picture.
Precursor and Exhaust Gas Management
The gaseous precursors used in CVD can be toxic, flammable, or possess a high global warming potential (GWP). Safe handling and storage are critical environmental and safety mandates.
Furthermore, unreacted gases and reaction byproducts in the exhaust stream must be captured and treated in an abatement system before being released. These abatement systems consume energy and have their own maintenance requirements.
High Energy Requirements for Operation
Achieving the high temperatures and high-vacuum conditions necessary for many CVD processes is energy-intensive. The overall "green" credential of a CVD process is therefore tied to the source of its electricity. A facility powered by renewable energy will have a much lower carbon footprint than one powered by fossil fuels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The environmental benefits of CVD are best leveraged when aligned with a specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and yield: The precise material control of CVD directly translates to less wasted raw material and fewer failed runs, which is a powerful economic and environmental advantage.
- If your primary focus is reducing reportable waste: CVD's near-elimination of liquid and solid waste streams simplifies environmental compliance and reduces disposal costs compared to wet-chemical methods.
- If your primary focus is enabling green technology: CVD is an indispensable manufacturing tool for products like high-efficiency solar cells, solid-state lighting (LEDs), and advanced battery components, making it a critical enabler of the broader green economy.
Ultimately, adopting CVD is a step toward a more precise, efficient, and sustainable approach to advanced material fabrication.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Benefit | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Reduced Waste | Eliminates liquid/solid waste streams, lowering disposal needs |
| Energy Efficiency | Superior insulation and heat recovery cut energy consumption |
| Precise Material Use | High deposition efficiency reduces raw material waste |
| Cleaner Operations | Contained process minimizes pollutants and improves safety |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced CVD furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for reduced waste and energy savings. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your environmental goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis



















