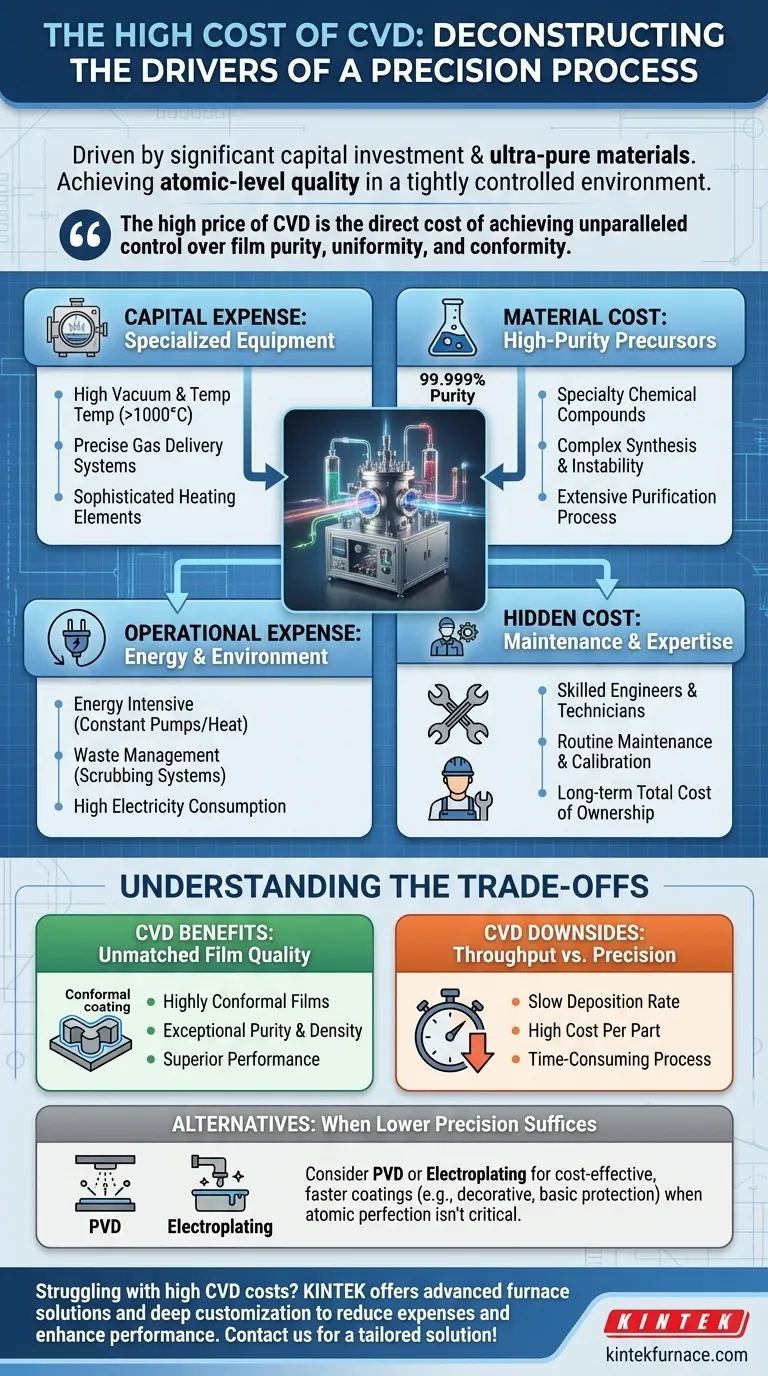
At its core, the high cost of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is driven by two primary factors: the significant capital investment required for highly specialized equipment and the recurring expense of ultra-pure precursor materials. The process demands a tightly controlled environment—high vacuum, extreme temperatures, and precise gas flow—which necessitates complex and expensive machinery to achieve the atomic-level quality required for advanced materials.
The high price of CVD is not an arbitrary expense. It is the direct cost of achieving unparalleled control over film purity, uniformity, and conformity, which are non-negotiable requirements for manufacturing high-performance electronic and optical components.
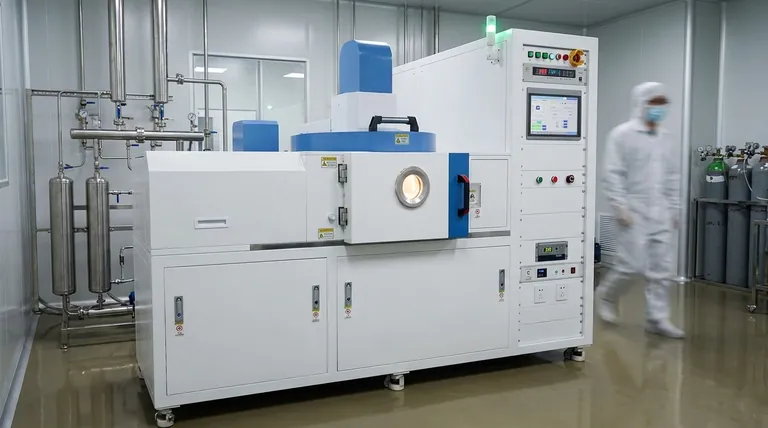

Deconstructing the Core Costs of CVD
To understand the budget for a CVD process, you must break down its costs into four key areas: capital equipment, precursor materials, operational consumption, and human expertise.
The Capital Expense: Specialized Equipment
The initial setup for a CVD system represents the largest upfront cost. This isn't just any furnace; it's a precision instrument.
The vacuum chamber must be capable of reaching high or ultra-high vacuum to eliminate atmospheric contaminants. Any stray oxygen or water molecule can create defects in the final film, so the integrity of the chamber, pumps, and seals is critical and expensive.
Furthermore, high-temperature furnaces are needed to provide the thermal energy required to drive the chemical reactions. These systems must maintain exceptionally stable and uniform temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C, which demands sophisticated heating elements and control systems.
Finally, a precise gas delivery system, using mass flow controllers (MFCs), is essential for feeding precursor gases into the chamber at exact rates. This control is what ensures the final film is uniform across the entire substrate.
The Material Cost: High-Purity Precursors
The raw materials for CVD, known as precursors, are a major recurring cost. These are not standard industrial gases; they are specialty chemical compounds.
The cost is directly tied to purity. For semiconductor applications, precursors must be "five nines" (99.999%) pure or better. Removing that last fraction of a percentage of impurities requires extensive and costly chemical purification processes.
Certain precursors, like the metal-organic compounds (e.g., TMGa, TMIn) used in manufacturing LEDs and high-speed transistors, are exceptionally expensive due to their complex synthesis and instability.
The Operational Expense: Energy and Environment
A CVD reactor is energy-intensive. The vacuum pumps run constantly, and the high-temperature furnaces consume a significant amount of electricity to maintain their setpoints for hours at a time.
Beyond energy, there is the cost of waste management. Many CVD processes produce hazardous or toxic byproduct gases that cannot be vented into the atmosphere. These require exhaust gas scrubbing systems, which add to the operational complexity and cost.
The Hidden Cost: Maintenance and Expertise
These complex systems do not run themselves. They require highly skilled engineers and technicians for operation, process development, and routine maintenance.
The cost of replacing vacuum components, cleaning the chamber of residual deposits, and calibrating the control systems contributes to the total cost of ownership over the lifetime of the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Pay the Premium for CVD?
The high cost of CVD is a barrier, but it's accepted in many industries because the process delivers results that less expensive methods cannot match.
The Benefit: Unmatched Film Quality
CVD excels at producing films that are highly conformal, meaning they can coat complex, three-dimensional topographies with a perfectly uniform thickness. This is something alternative methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) struggle with.
The process also yields films that are dense, have low defect counts, and possess exceptional purity, leading to superior electrical, optical, or mechanical properties.
The Downside: Throughput vs. Precision
A significant trade-off with CVD is its often slow deposition rate. The chemical reactions must be managed carefully to ensure quality, which can make the process time-consuming.
This low throughput means the cost per wafer or part can be high, making it less suitable for applications where speed and volume are more important than ultimate film quality.
When Alternatives Make Sense
For applications that do not require atomic-level perfection, other methods are more economical. PVD (sputtering or evaporation) is often faster and cheaper for applying simple metal or ceramic coatings. For thick, non-critical conductive layers, electroplating can be a far more cost-effective solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use CVD requires aligning its capabilities and costs with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge performance (semiconductors, advanced optics, wear-resistant tooling): The high cost of CVD is a necessary investment to achieve the required purity, conformity, and material properties that define product performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating (decorative finishes, basic corrosion protection): You should first evaluate lower-cost, higher-throughput alternatives like PVD, electroplating, or spray pyrolysis before committing to the expense of CVD.
Ultimately, understanding these cost drivers empowers you to justify the investment in CVD when precision is paramount or to pivot to more economical alternatives when it is not.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Key Components | Impact on Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Equipment | Vacuum chambers, high-temperature furnaces, gas delivery systems | High upfront investment |
| Precursor Materials | Ultra-pure gases, metal-organic compounds | Major recurring expense |
| Operational Expenses | Energy consumption, waste management systems | Ongoing costs |
| Maintenance & Expertise | Skilled labor, system upkeep | Long-term ownership costs |
Struggling with the high costs of CVD processes? KINTEK can help! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Reduce expenses and enhance performance—contact us today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















