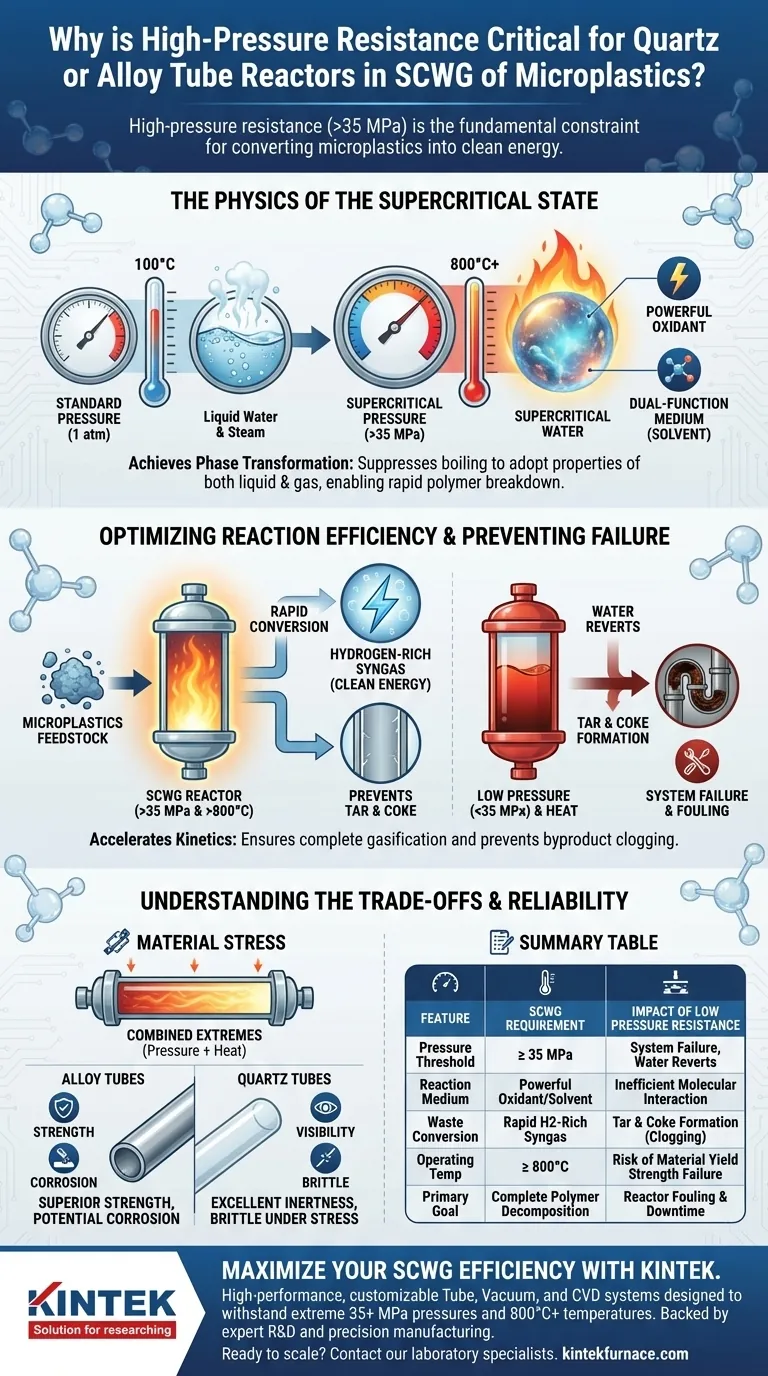
High-pressure resistance is the fundamental constraint that dictates the success or failure of converting microplastics into clean energy. For quartz or alloy tube reactors used in Supercritical Water Gasification (SCWG), the material must withstand internal pressures often exceeding 35 MPa to maintain water in a supercritical state. Without this structural resilience, the system cannot sustain the unique reaction medium required to rapidly decompose polymers into hydrogen-rich syngas.
Core Takeaway The efficiency of SCWG hinges entirely on keeping water in a supercritical phase, which requires maintaining extreme pressure alongside high heat. If the reactor cannot sustain pressures above 35 MPa, water reverts to a standard liquid or steam, halting the oxidation process and allowing the system to clog with tar and coke.

The Physics of the Supercritical State
Achieving Phase Transformation
The primary reason for high-pressure resistance is the physical requirement to transform water. At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C. However, in SCWG, the reactor must suppress boiling to reach the supercritical point.
This generally requires pressures exceeding 35 MPa. Only at this intense pressure does water stop behaving like a typical liquid or gas and adopt properties of both.
Water as a Dual-Function Medium
Once the reactor maintains this pressure, the water acts as both a powerful oxidant and a reaction medium. This dual role is critical for breaking down the complex carbon chains found in microplastics.
If the reactor pressure drops, the water loses its solvent properties. This renders it ineffective at interacting with the plastic feedstock at a molecular level.
Optimizing Reaction Efficiency
Accelerating Chemical Conversion
High-pressure environments facilitate the rapid conversion of microplastics. The reference data indicates that when the pressure holds the water in a supercritical state, the reaction kinetics accelerate significantly.
This speed is crucial for converting solid waste into hydrogen-rich syngas. A reactor capable of sustaining high pressure ensures the residence time is sufficient for complete gasification.
Preventing System Failure
Beyond gas production, high pressure is essential for system longevity. In lower-pressure environments, the breakdown of plastics often results in the formation of tar and coke.
These byproducts are sticky and solid, leading to reactor fouling and blockages. By maintaining high pressure (>35 MPa), the supercritical water effectively gasifies these intermediates, preventing them from depositing on the reactor walls.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Stress of Combined Extremes
While pressure is the focus, it cannot be viewed in isolation. These reactors must simultaneously withstand temperatures exceeding 800°C.
This combination creates immense thermal and mechanical stress. A material might handle 35 MPa at room temperature, but its yield strength often drops significantly at 800°C.
Material Selection Limits
Designing for these conditions involves a strict trade-off between durability and chemical inertness.
Alloy tubes generally offer superior strength but may be susceptible to corrosion in the harsh oxidative environment of supercritical water. Quartz tubes offer excellent chemical resistance and visibility but are brittle, making catastrophic failure under pressure a higher risk if handled improperly.
Ensuring Reactor Reliability
To ensure your SCWG project operates safely and efficiently, evaluate your reactor design against your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximum conversion efficiency: Ensure your reactor is rated well above the 35 MPa threshold to guarantee the water remains a potent oxidant throughout the process.
- If your primary focus is operational continuity: Prioritize materials that can withstand the formation of char or coke if pressure fluctuations occur, preventing permanent clogging.
A reactor with adequate high-pressure resistance is not just a vessel; it is the active enabler of the chemical physics required to turn plastic waste into fuel.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Supercritical Water Gasification (SCWG) Requirement | Impact of Low Pressure Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Threshold | ≥ 35 MPa | System failure; water reverts to liquid/steam |
| Reaction Medium | Water acts as a powerful oxidant/solvent | Inefficient molecular interaction; slow kinetics |
| Waste Conversion | Rapid conversion to H2-rich syngas | Formation of tar and coke (clogging) |
| Operating Temp | ≥ 800°C | Risk of material yield strength failure |
| Primary Goal | Complete polymer decomposition | Reactor fouling and system downtime |
Maximize Your SCWG Efficiency with KINTEK
Don't let reactor failure stall your green energy breakthroughs. KINTEK provides high-performance, customizable Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to withstand the extreme 35+ MPa pressures and 800°C+ temperatures required for supercritical water gasification.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our reactors ensure consistent phase transformation and prevent costly tar formation, whether you are using high-strength alloys or chemically inert quartz.
Ready to scale your microplastic conversion? Contact our laboratory specialists today to design a system tailored to your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Dorota Wieczorek, Katarzyna Ławińska. Microplastic Recovery and Conversion Pathways: The Most Recent Advancements in Technologies for the Generation of Renewable Energy. DOI: 10.3390/en18184949
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What additional features might a split tube furnace have? Boost Your Lab's Precision and Control
- What are the core functions of a tube sintering furnace in Fe3C/NC pyrolysis? Master Your Synthesis Process
- What are the benefits of a high-pressure metal tube reactor for CO2 hydrogenation? Achieve Kinetic Precision
- How does a tube furnace ensure uniform heating? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- Why is temperature range important when choosing a tube furnace? It Dictates Cost, Materials, and Performance
- What is a tube furnace and what are its applications? Unlock Precision Heating for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of using a fixed-bed continuous flow tube reaction system? Unlock Precision CO2 Hydrogenation
- What is the operational principle of a 70mm tube furnace? Master Precise Heat and Atmosphere Control



















