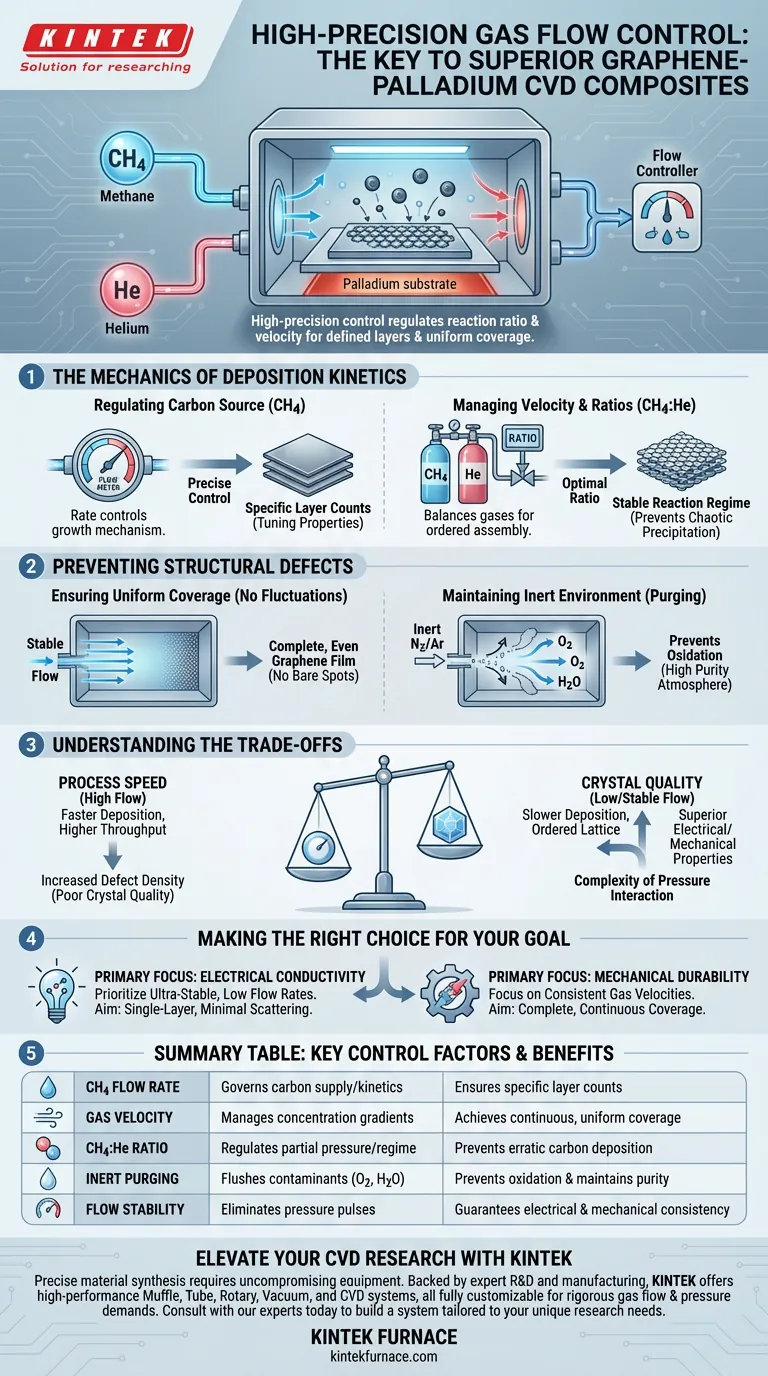
High-precision gas flow control is the governing factor in defining the structural quality of graphene-palladium composites. It acts as the primary regulator for the chemical reaction, strictly managing the ratio and velocity of methane (CH4) and helium (He) to dictate the specific number of graphene layers and ensure continuous, uniform coverage across the palladium substrate.
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the difference between a high-performance composite and a defective material lies in the stability of the gas phase. Precise flow regulation prevents erratic carbon deposition, ensuring the electrical and mechanical consistency required for advanced material applications.
The Mechanics of Deposition Kinetics
Regulating the Carbon Source Supply
In the graphene-palladium CVD process, methane typically serves as the carbon feedstock. The rate at which this carbon is supplied is the direct variable controlling the growth mechanism.
If the flow is too high, carbon atoms may deposit too rapidly, leading to uncontrolled multi-layer growth. Conversely, precision control allows for the synthesis of specific layer counts, which is essential for tuning the material's properties.
Managing Gas Velocity and Ratios
It is not enough to simply introduce gas into the chamber; the velocity and ratio of the gases must be balanced.
The primary reference highlights the critical relationship between methane and helium. Helium often acts as a carrier or diluent, helping to manage the partial pressure of the carbon source. Maintaining an exact ratio ensures that the reaction remains in a regime favorable for ordered atomic assembly rather than chaotic precipitation.
Preventing Structural Defects
Ensuring Uniform Coverage
A palladium substrate requires a consistent supply of reactants to achieve a homogeneous coating. Fluctuations in gas flow create concentration gradients within the furnace.
These gradients lead to uneven deposition, where some areas of the substrate receive too much carbon while others remain bare. High-precision controllers eliminate these pulses, ensuring that the graphene film covers the palladium surface completely and evenly.
Maintaining an Inert Environment
While the primary reaction involves methane and helium, supplementary data suggests the broader importance of excluding contaminants. Precision flow systems are often used to introduce inert gases like nitrogen or argon during heating phases.
This positive flow of inert gas helps flush out oxygen and water vapor. By strictly controlling this "background" flow, you prevent the oxidation of the carbon carrier or the substrate, which would otherwise compromise the purity of the reaction atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Speed vs. Crystal Quality
There is often a tension between the rate of production and the quality of the crystal lattice.
Higher gas flow rates can accelerate the deposition process, increasing throughput. However, this often comes at the cost of increased defect density, as carbon atoms have less time to diffuse and find their ideal lattice positions.
Complexity of Pressure Interaction
Flow control cannot be viewed in isolation; it is intrinsically linked to chamber pressure.
As noted in broader CVD contexts, vacuum systems work in tandem with flow controllers to maintain a stable environment. Changing the gas flow rate inevitably impacts the chamber pressure, requiring a sophisticated control loop to maintain the specific low-pressure conditions needed for uniform film growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your graphene-palladium CVD process, align your flow control strategy with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize ultra-stable, low-flow rates to achieve single-layer graphene with minimal scattering centers.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Durability: Focus on ensuring consistent gas velocities to guarantee complete, continuous coverage of the palladium substrate without gaps.
Ultimately, the reliability of your composite material is a direct reflection of the stability of your gas delivery system.
Summary Table:
| Control Factor | Impact on Graphene-Palladium Composite | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| CH4 Flow Rate | Governs carbon supply and deposition kinetics | Ensures specific layer counts |
| Gas Velocity | Manages concentration gradients in the furnace | Achieves continuous, uniform coverage |
| CH4:He Ratio | Regulates partial pressure and reaction regime | Prevents erratic carbon deposition |
| Inert Purging | Flushes oxygen and water vapor from chamber | Prevents oxidation and maintains purity |
| Flow Stability | Eliminates pressure pulses and fluctuations | Guarantees electrical & mechanical consistency |
Elevate Your CVD Research with KINTEK
Precise material synthesis requires uncompromising equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet the rigorous gas flow and pressure demands of advanced composite development.
Whether you are optimizing electrical conductivity or mechanical durability, our specialized lab high-temp furnaces provide the stability your materials deserve. Consult with our experts today to build a system tailored to your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Kaihao Zhang, Sameh Tawfick. Ultrathin damage-tolerant flexible metal interconnects reinforced by in-situ graphene synthesis. DOI: 10.1038/s41528-024-00300-8
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How does a recirculating chiller influence the quality of polymer films in iCVD? Achieve Superior Surface Smoothness
- What is the high-temperature capability of specialized CVD furnaces? Achieve Up to 1950°C for Advanced Materials
- What is the role of the Quartz Tube CVD Furnace in the synthesis of 2D In2Se3 nanosheets? Expert Synthesis Guide
- What types of coating precursors are used in the CVD deposition process? Essential Classes for Superior Film Quality
- What advantages does a CVD Tube Furnace offer for material research? Unlock Precision and Versatility for Advanced Synthesis
- What are the technical advantages of using a CVD system? Optimize Carbon Nanotube Growth for Thermal Conductivity
- What tasks do ultrasonic cleaning and ion sputtering systems perform in PVD? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Adhesion
- Why is CVT preferred over solid-phase reaction for Janus RhSeCl? Key Advantages in Crystal Growth



















