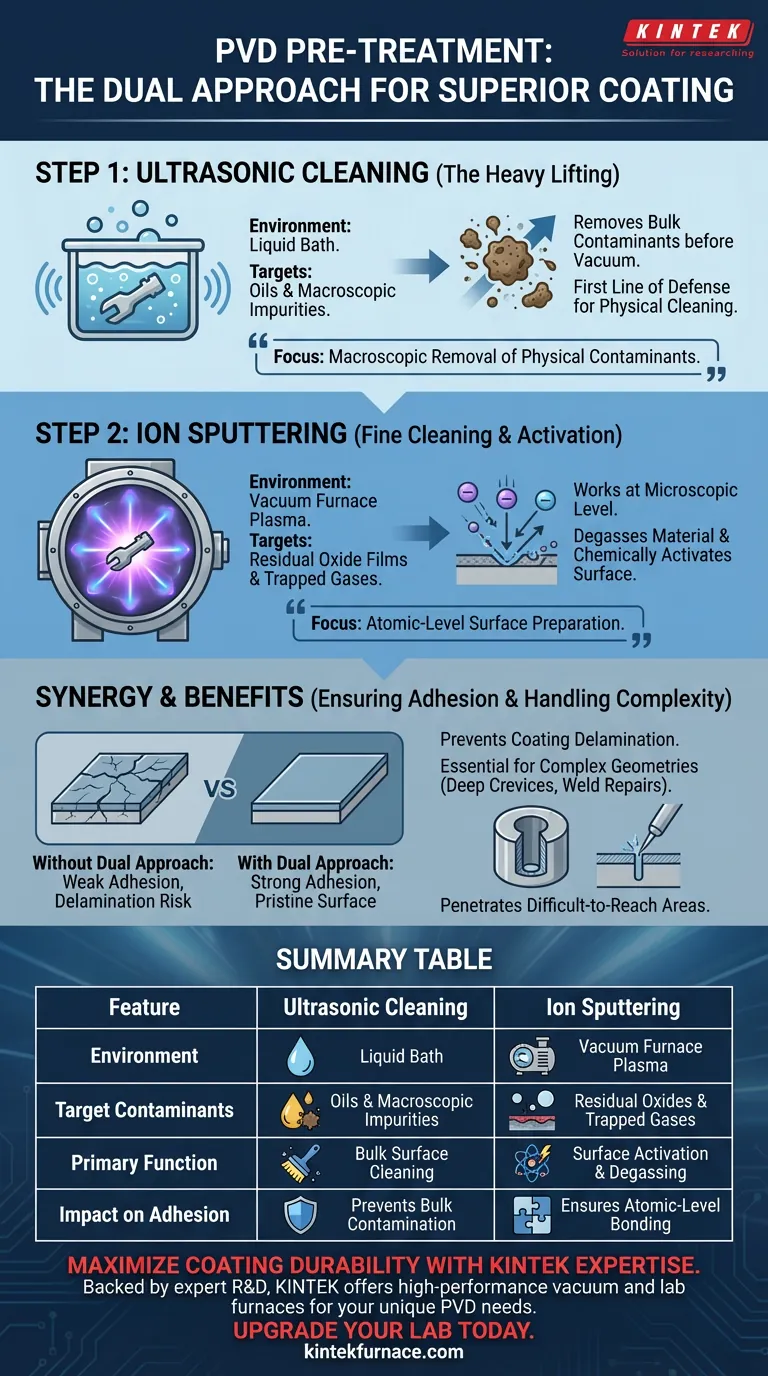
Two distinct cleaning technologies operate in sequence to prepare surfaces for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). First, ultrasonic cleaning performs the heavy lifting by removing oils and macroscopic impurities before the part undergoes coating. Subsequently, ion sputtering takes place within the vacuum furnace to strip away residual oxide films, degas the material, and chemically activate the surface for bonding.
Effective PVD pre-treatment requires a dual approach: macroscopic removal of physical contaminants followed by atomic-level surface preparation. The synergy between ultrasonic cleaning and ion sputtering is the defining factor in achieving strong coating adhesion, particularly for complex geometries like deep crevices or weld repairs.

The Mechanics of PVD Pre-Treatment
Step 1: Ultrasonic Cleaning
The first line of defense in the pre-treatment phase is the ultrasonic cleaning system.
This process is tasked with removing larger, tangible contaminants from the workpiece. It specifically targets oils and macroscopic surface impurities that accumulate during manufacturing or handling.
By eliminating these bulk contaminants early, the system ensures the part is physically clean before entering the delicate vacuum environment.
Step 2: Ion Sputtering
Once the workpiece is secured inside the vacuum furnace, ion sputtering performs a "fine cleaning" function.
This process involves bombarding the workpiece with plasma under high vacuum.
Unlike ultrasonic cleaning, which targets surface dirt, sputtering works at a microscopic level to remove residual oxide films.
Surface Activation and Degassing
Beyond simple cleaning, ion sputtering fundamentally changes the surface state of the material.
The bombardment process effectively degasses the material, releasing trapped gases that could otherwise compromise the vacuum or the coating.
Simultaneously, it activates the surface, creating a highly reactive state that is chemically primed to accept the coating.
The Necessity of a Dual Approach
Ensuring Coating Adhesion
The primary goal of combining these two systems is to guarantee strong coating adhesion.
Neither method is sufficient on its own; ultrasonic cleaning cannot remove atomic-level oxides, and ion sputtering is not designed to handle heavy grease or bulk debris.
Using them in tandem ensures the substrate is pristine and reactive, preventing coating delamination (peeling).
Handling Complex Geometries
This two-step protocol is particularly vital when coating parts with intricate features.
Workpieces featuring deep holes, narrow slits, or weld repairs present significant cleaning challenges.
The combination of fluid-based ultrasonic penetration and gas-based plasma bombardment ensures that even these difficult-to-reach areas are thoroughly prepared.
Critical Considerations and Constraints
The Risk of Process Isolation
A common pitfall is assuming that one cleaning method can compensate for the other.
If ultrasonic cleaning is skipped, the ion sputtering process will likely fail to remove heavy surface oils, leading to immediate contamination of the vacuum chamber.
Conversely, relying solely on ultrasonic cleaning leaves behind invisible oxide layers, which acts as a barrier to adhesion and results in weak coatings.
Geometry-Dependent Efficiency
While this combination is effective for complex parts, the efficiency of ion sputtering can be influenced by "line of sight" limitations in extreme geometries.
However, the plasma environment is generally effective at reaching into deep holes and slits that mechanical wiping or simple rinsing cannot touch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the lifespan and performance of your PVD coatings, you must verify that your pre-treatment protocol aligns with the complexity of your parts.
- If your primary focus is Adhesion Strength: Ensure your process includes ion sputtering to fully remove oxide films and activate the surface prior to deposition.
- If your primary focus is Complex Part Geometry: Rely on the combination of ultrasonic cleaning and plasma bombardment to clean deep holes, slits, and weld repairs that standard cleaning misses.
A PVD coating is only as strong as the surface preparation that precedes it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ultrasonic Cleaning | Ion Sputtering |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Liquid Bath | Vacuum Furnace Plasma |
| Target Contaminants | Oils & Macroscopic Impurities | Residual Oxides & Trapped Gases |
| Primary Function | Bulk Surface Cleaning | Surface Activation & Degassing |
| Impact on Adhesion | Prevents Bulk Contamination | Ensures Atomic-Level Bonding |
Maximize Coating Durability with KINTEK Expertise
Don't let poor surface preparation compromise your product quality. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance vacuum systems and lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique PVD and heat treatment needs.
Whether you are handling complex geometries with deep crevices or require high-strength adhesion for industrial tools, our team is ready to provide the precision equipment you need.
Upgrade your lab today—contact our specialists here!
Visual Guide
References
- André Paulo Tschiptschin. PROCESSOS SOB VÁCUO USADOS PARA TRATAMENTOS TÉRMICOS E DE SUPERFÍCIE DE AÇOS E LIGAS ESPECIAIS. DOI: 10.17563/rbav.v43i1.1262
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
People Also Ask
- Why use Argon and Hydrogen for MnS Nanosheet CVD? Achieve High-Purity Synthesis Results
- What are the characteristics of freestanding monolithic materials produced by CVD furnaces? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance
- How does a CVD system facilitate in-situ graphene synthesis? High-Quality Coatings for Flexible Electronics
- How is the CVD process environment created? Master Precise Control for Superior Thin Films
- What is the typical thickness range for CVD coatings? Optimize Performance for Your Application
- What are the advantages of CVD furnaces in preparing high-quality thin films? Achieve Superior Thin Films with High Purity and Uniformity
- What is the primary function of a sputtering deposition system in graphene growth? Expert Catalyst Engineering
- Why is Ar/H2 necessary for copper selenide CVD? Ensure High Purity and Uniform Synthesis



















