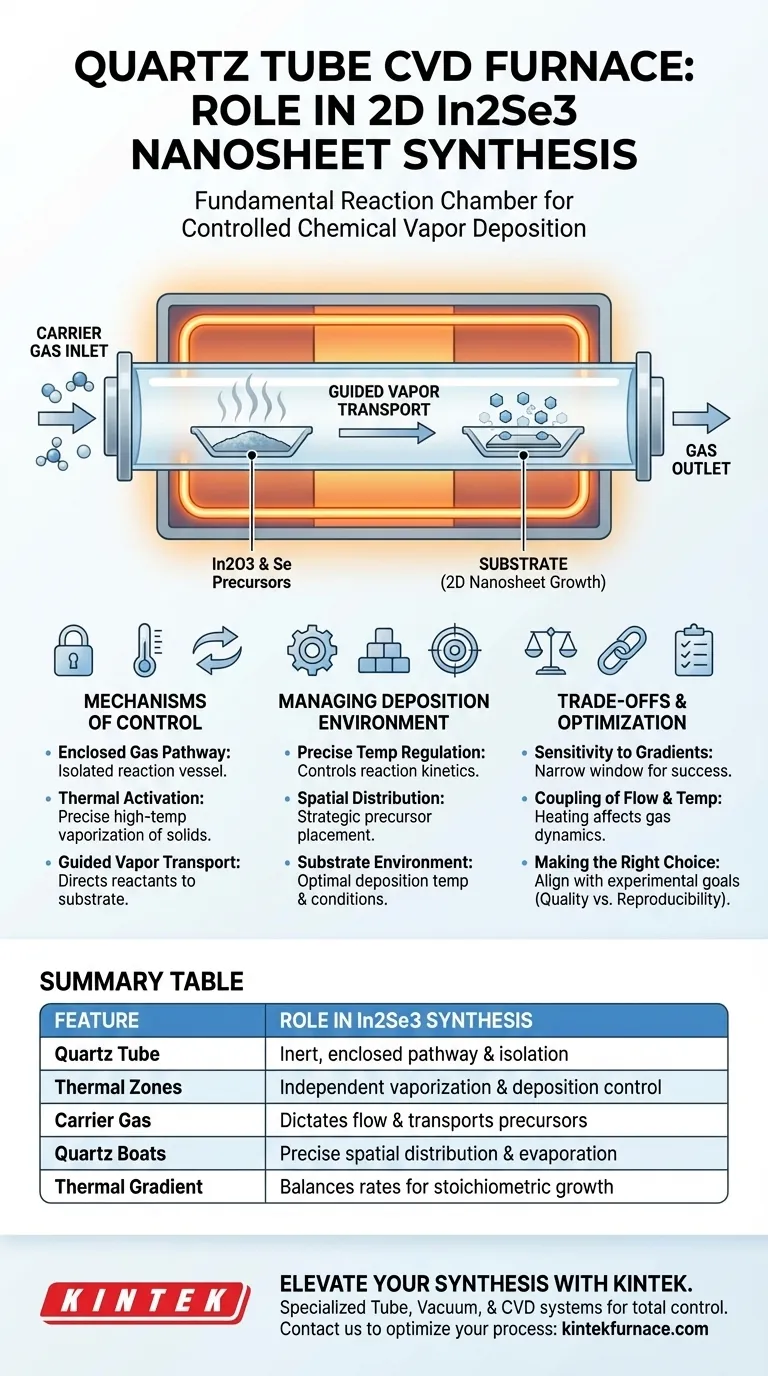
The Quartz Tube CVD Furnace acts as the fundamental reaction chamber for the synthesis of 2D In2Se3 nanosheets, providing the strictly controlled environment necessary for chemical vapor deposition. It facilitates the precise heating required to vaporize solid precursors—specifically In2O3 and Selenium (Se) powder—and maintains an enclosed pathway for a carrier gas to transport these vapors to a downstream substrate for growth.
Core Takeaway The furnace is not merely a heating source; it is a flow reactor that synchronizes the sublimation of solids with gas transport dynamics. Its primary function is to establish a stable thermal gradient that allows precursors to vaporize at different rates while ensuring reaction and deposition occur exclusively on the target substrate.

The Mechanisms of Control
The Enclosed Gas Pathway
The quartz tube serves as an isolation vessel, separating the reaction from the outside atmosphere.
This enclosed environment allows for the introduction of a specific carrier gas. The gas dictates the flow direction, ensuring reactants move predictably from the source zone to the deposition zone.
Thermal Activation of Precursors
Synthesis cannot occur until the solid source materials are converted into a vapor phase.
The furnace applies precise high-temperature heat to vaporize In2O3 and Se powder. Without this thermal energy, the precursors would remain inert solids, unable to participate in the deposition process.
Guided Vapor Transport
Once vaporized, the In2Se3 components must be transported to the substrate without reacting prematurely.
The furnace geometry and gas flow guide these vapors downstream. This transport mechanism ensures that the chemical reaction occurs on the substrate surface rather than on the tube walls or in the gas phase.
Managing the Deposition Environment
Precise Temperature Regulation
The quality of the final 2D nanosheets depends heavily on the stability of the reaction temperature.
The furnace chamber maintains specific set points to control reaction kinetics. This ensures the precursors decompose and recombine into In2Se3 at a rate that favors 2D sheet growth over bulk crystal formation.
Spatial Distribution of Precursors
The placement of source materials within the tube is as critical as the temperature itself.
Quartz boats holding In2O3 and Se are positioned at specific intervals, often with Selenium placed upstream. This spatial arrangement utilizes the furnace's temperature profile to independently manage the evaporation rates of chemically distinct precursors.
Substrate Environment
The final stage of the process occurs downstream where the substrate is located.
The furnace maintains a specific deposition temperature in this zone. This temperature must be low enough to allow condensation and crystallization of the In2Se3, but high enough to ensure high-quality, crystalline nanosheets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gradients
The reliance on thermal gradients creates a narrow window for success.
If the temperature profile across the tube is not perfectly calibrated, the Selenium may evaporate too quickly before the Indium source is active. This leads to non-stoichiometric growth or incomplete reactions.
Coupling of Flow and Temperature
In a standard tube furnace, changing the temperature often impacts the gas flow dynamics (convection).
Adjusting the heat to increase precursor vaporization might inadvertently alter the flow profile near the substrate. This coupling makes independent control of variables difficult, requiring rigorous calibration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the synthesis of In2Se3, you must align your furnace operation with your specific experimental needs.
- If your primary focus is crystal quality: Prioritize a furnace with multi-zone control to decouple the precursor vaporization temperature from the substrate deposition temperature.
- If your primary focus is reproducibility: strictly standardize the spatial positioning of your quartz boats, as slight shifts in location can drastically change the vapor concentration.
Mastering the thermal gradient is the single most important factor in transitioning from random growth to controlled 2D synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in In2Se3 Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Quartz Tube | Provides an inert, enclosed reaction pathway and atmospheric isolation. |
| Thermal Zones | Independently regulates vaporization of In2O3/Se and substrate deposition. |
| Carrier Gas | Dictates flow direction and transports vaporized precursors downstream. |
| Quartz Boats | Ensures precise spatial distribution and evaporation rates of source materials. |
| Thermal Gradient | Balances sublimation rates to ensure stoichiometric 2D crystal growth. |
Elevate Your 2D Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal gradients are the difference between random growth and high-quality 2D In2Se3 nanosheets. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to give you total control over your reaction environment.
Whether you need multi-zone temperature regulation or a fully customizable furnace for unique lab requirements, our team is ready to help you achieve reproducible results.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your CVD process
Visual Guide
References
- Dasun P. W. Guruge, Dmitri Golberg. Thermal Phase‐Modulation of Thickness‐Dependent CVD‐Grown 2D In<sub>2</sub>Se<sub>3</sub>. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202514767
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the three main advantages of CVD diamond chips? Unlock Unmatched Power & Efficiency
- What are the logistical challenges associated with CVD? Overcome Off-Site, Disassembly, and Waste Issues
- How does a dual-zone CVD furnace facilitate ISG of alpha-In2Se3? Optimize Thin Film Synthesis with Dual-Zone Control
- What is the significance of the cold wall CVD technique in graphene research? Unlock Precision Growth for High-Quality Graphene
- Why are high-purity hydrogen and argon necessary for hBN thin film LPCVD? Master Gas Roles for Superior Growth
- What industries commonly use CVD furnaces and for what purposes? Discover Precision Coating Solutions
- What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and what industries benefit from it? Unlock Atomic-Level Material Engineering
- What factors should be considered when choosing a CVD furnace? Key Tips for Optimal Thin-Film Synthesis



















