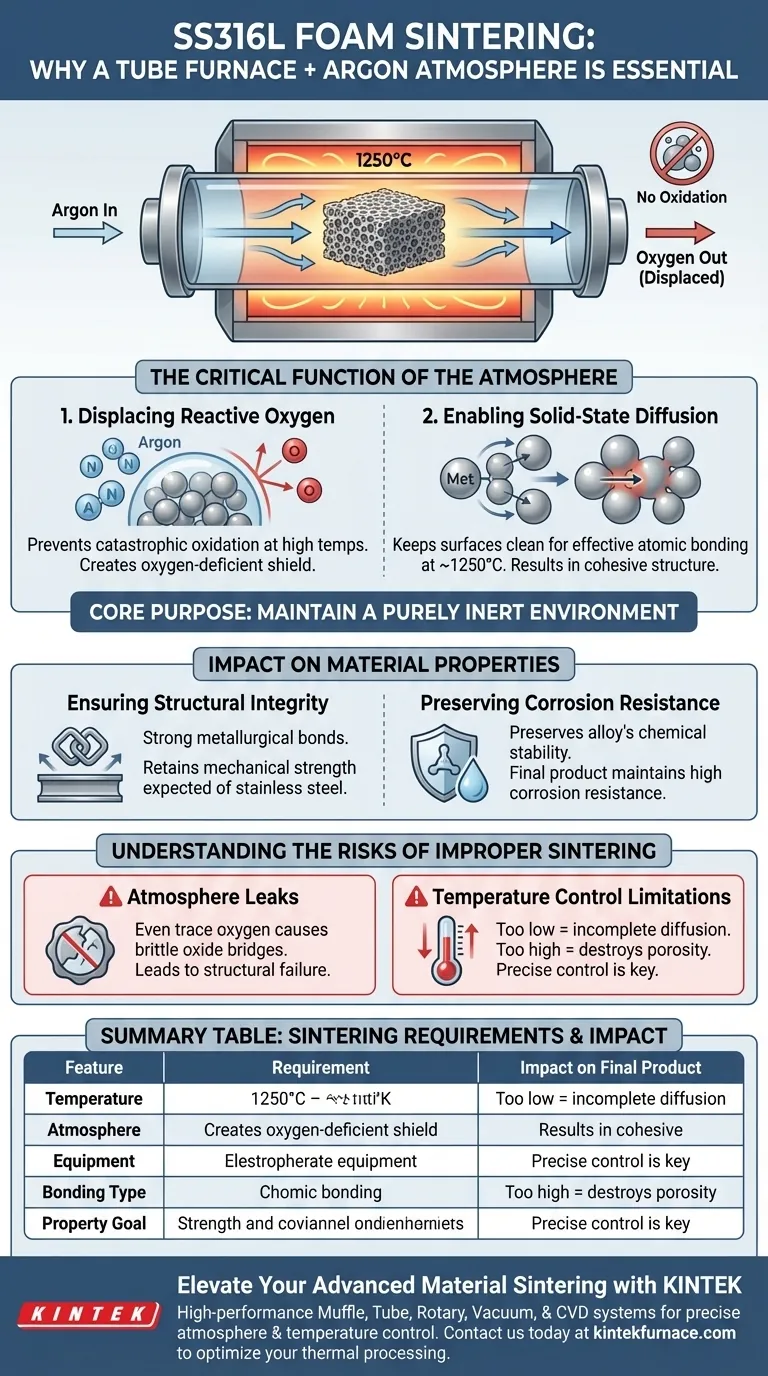
A tube furnace coupled with an argon atmosphere is strictly required for sintering SS316L foam to prevent catastrophic oxidation during the heating process. This specific setup allows the material to reach the necessary 1250°C for bonding while ensuring the stainless steel powder fuses through solid-state diffusion rather than reacting chemically with the air.
The core purpose of this configuration is to maintain a purely inert environment during the thermal cycle. By displacing oxygen with argon, you ensure that the metal particles undergo metallurgical bonding, which is the only way to secure the high strength and corrosion resistance inherent to 316L stainless steel.

The Critical Function of the Atmosphere
Displacing Reactive Oxygen
At elevated temperatures, stainless steel is highly reactive to oxygen. If exposed to standard air during sintering, the metal would rapidly oxidize.
Argon acts as a protective shield. By introducing argon gas into the tube furnace, you physically displace the oxygen and create an oxygen-deficient environment. This prevents the formation of oxide layers on the surface of the metal particles.
Enabling Solid-State Diffusion
Sintering is not melting; it is the fusing of particles below their melting point. For SS316L foam, this occurs around 1250°C.
Effective sintering relies on solid-state diffusion, where atoms move across particle boundaries to create a bond. This process is significantly hindered by surface oxides. By using an argon atmosphere to keep particle surfaces clean, the metal atoms can diffuse freely, resulting in a cohesive, unified structure.
Impact on Material Properties
Ensuring Structural Integrity
The strength of the final metal foam depends entirely on the quality of the bonds between particles.
Without the protection of an inert atmosphere, the bonds between particles would be weak or non-existent. The argon environment ensures that metallurgical bonding takes place, resulting in a foam product that retains the mechanical strength expected of stainless steel.
Preserving Corrosion Resistance
One of the primary reasons for selecting SS316L is its resistance to corrosion.
Oxidation during the sintering process changes the chemical composition of the steel's surface, potentially degrading these properties. Processing the foam in a tube furnace with argon preserves the alloy's chemical stability, ensuring the final product maintains high corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Sintering
The Consequence of Atmosphere Leaks
If the tube furnace is not perfectly sealed or if the argon flow is interrupted, the environment ceases to be inert.
Even trace amounts of oxygen at 1250°C can compromise the sintering batch. This results in a "brittle" foam where particles are stuck together by weak oxide bridges rather than fused metal, leading to structural failure under load.
Temperature Control Limitations
While the atmosphere is critical, the temperature profile is equally important.
The tube furnace must reliably maintain 1250°C. If the temperature fluctuates too low, diffusion will be incomplete regardless of the argon atmosphere. Conversely, excessive heat could melt the structure, destroying the foam's porosity. The tube furnace provides the controlled high-temperature environment necessary to balance these factors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure successful fabrication of SS316L foam, consider the following regarding your equipment setup:
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Ensure your furnace can maintain a continuous flow of argon to facilitate pure solid-state diffusion without oxide interference.
- If your primary focus is chemical stability: Prioritize a completely sealed tube environment to prevent oxidation, which is critical for retaining the material's corrosion resistance.
The synergy between the thermal control of the tube furnace and the chemical inertness of argon is the defining factor in producing high-quality metal foam.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for SS316L Sintering | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Stable 1250°C | Enables solid-state diffusion for particle bonding |
| Atmosphere | Inert Argon Gas | Displaces oxygen to prevent brittle oxide formation |
| Equipment | Sealed Tube Furnace | Ensures a controlled, leak-proof thermal environment |
| Bonding Type | Metallurgical Bonding | Guarantees high mechanical strength and porosity preservation |
| Property Goal | Corrosion Resistance | Maintains the chemical stability of the 316L alloy |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Sintering with KINTEK
Precision matters when your material's structural integrity is on the line. At KINTEK, we understand the rigorous demands of sintering SS316L foam and other reactive alloys.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our laboratory high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research or production needs, ensuring perfect atmosphere control and temperature uniformity every time.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact us today to discover how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and material quality.
Visual Guide
References
- Fazimah Mat Noor, Joko Sedyono. Effect of Using Different Types of Solvents in SS316L Slurry Preparation on the SS316L Foam Properties. DOI: 10.37934/aram.136.1.110119
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace with programmable temperature control necessary for graphene? Ensure High-Quality Graphene on Silver
- What are the key features of a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Precise, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- In what scenarios are laboratory high-temperature tube furnaces or muffle furnaces utilized? Study MgTiO3-CaTiO3 Ceramics
- What are the advantages of vertical tube furnaces? Achieve Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What are the types of vacuum tube furnaces based on? Key Classifications for Your Lab
- What are the dimensions and temperature capabilities of single zone horizontal tube furnace models? Explore Key Specs for Your Lab
- How are vertical fluidized bed tube furnaces utilized in material handling and processing? Achieve Uniform Thermal Processing for Powders
- What is the primary role of a vacuum vertical tube furnace in the process of producing magnesium via carbothermal reduction? Enabling Efficient, High-Purity Metal Production



















