At its core, a vertical fluidized bed tube furnace is a highly specialized tool used for precise, uniform thermal processing of powders and granular materials. Its applications range from drying and sintering common industrial powders to synthesizing advanced materials like graphene and ceramics in controlled-atmosphere environments.
The furnace's true value lies in its unique combination of technologies: it merges the uniform heat transfer of a fluidized bed with the precise temperature and atmospheric control of a sealed tube furnace, solving the common problem of inconsistent heating in static powder processing.
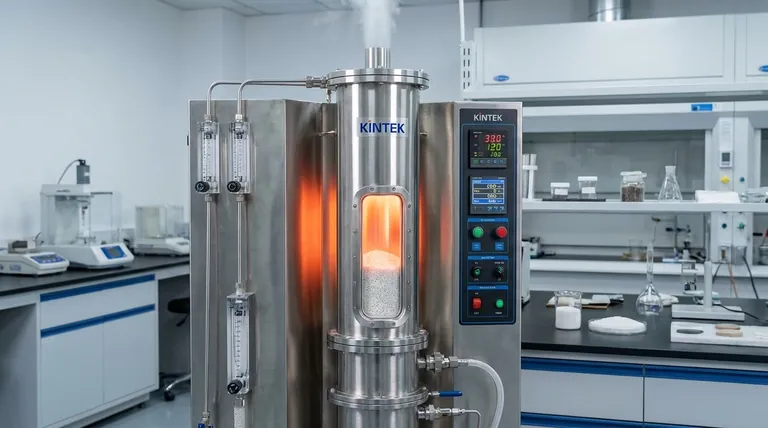

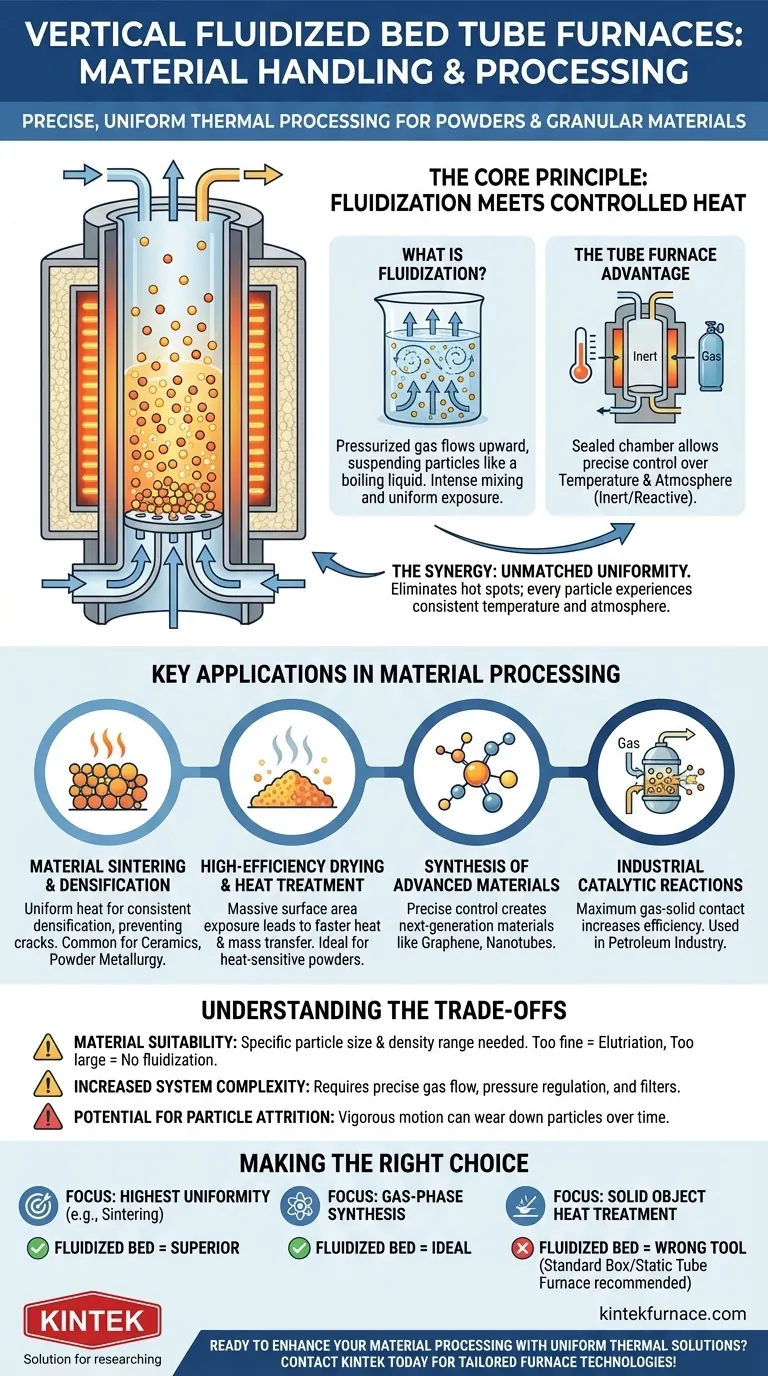
The Core Principle: Fluidization Meets Controlled Heat
To understand its applications, you must first grasp the underlying mechanism. These furnaces don't just heat materials; they fundamentally change how heat interacts with them on a particle-by-particle basis.
What is Fluidization?
Fluidization is the process of making a bed of solid particles behave like a fluid. This is achieved by passing a pressurized gas upward through the granular material.
As the gas flow increases, it counteracts gravity, causing the particles to become suspended and move around vigorously. This creates a state of intense mixing, similar to a boiling liquid.
The Tube Furnace Advantage: Precise Control
The "tube furnace" component provides a sealed, high-temperature chamber. This design allows for exceptional control over two critical variables: temperature and atmosphere.
The atmosphere can be replaced with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation or with reactive gases to induce specific chemical changes in the material.
The Synergy: Unmatched Processing Uniformity
When combined, these two principles create a uniquely effective processing environment. The fluidization ensures that every single particle is constantly moving and exposed to the same temperature and gas atmosphere.
This eliminates hot spots and temperature gradients common in static furnaces, where powders at the bottom of a crucible heat differently than those on top. The result is a highly consistent and predictable final product.
Key Applications in Material Processing
This unique combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes the vertical fluidized bed tube furnace ideal for several demanding applications.
Material Sintering and Densification
Sintering is the process of forming a solid, dense mass from a powder using heat without melting it. This is a common step in producing ceramics and parts for powder metallurgy.
The furnace's uniform heat transfer is critical for achieving consistent densification and avoiding cracks or weak spots in the final component.
High-Efficiency Drying and Heat Treatment
For processes like drying heat-sensitive powders or performing heat treatments like annealing (softening) and quenching (hardening), fluidization offers a major speed advantage.
The massive surface area exposed by the moving particles leads to dramatically faster heat and mass transfer compared to heating a static pile of powder.
Synthesis of Advanced Materials
The furnace provides the ideal reaction chamber for creating next-generation materials. This includes the synthesis of nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes and graphene.
Precise control over the temperature and the composition of the reactive gases is essential for growing these materials with the desired structure and properties.
Industrial Catalytic Reactions
On a larger industrial scale, the principles of fluidization are used in processes like catalytic cracking in the petroleum industry.
The fluidized bed ensures that reactant gases have maximum contact with the surface area of the solid catalyst particles, dramatically increasing the efficiency and speed of the chemical reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology is not a universal solution. Its specialized nature comes with specific limitations.
Material Suitability is Key
The process only works for particles within a specific range of size and density.
Very fine powders may be blown out of the furnace bed entirely (a problem known as elutriation), while particles that are too large or dense will not fluidize effectively.
Increased System Complexity
A fluidized bed system is inherently more complex than a standard box or tube furnace. It requires precise gas flow control, pressure regulation, and often includes filters to manage dust and particle loss.
Potential for Particle Attrition
The constant, vigorous motion of particles can cause them to rub against each other and the furnace walls. This can lead to attrition, where the particles wear down over time, which may be undesirable for certain materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Ultimately, selecting a vertical fluidized bed tube furnace depends entirely on the specific material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible uniformity in a powder: A fluidized bed furnace is superior for tasks like sintering or annealing where consistency is paramount.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing new materials via gas-phase reactions: This furnace offers an ideal environment with its combination of uniform heat and precise atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is heat treating a solid, non-powder object: This is the wrong tool; a standard box furnace or a static tube furnace would be the appropriate choice.
Choosing the correct thermal processing technology begins with a clear understanding of how heat needs to interact with your specific material.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sintering | Uniform densification, prevents cracks | Ceramics, Powder Metallurgy Parts |
| Drying & Heat Treatment | Fast heat/mass transfer, efficient processing | Heat-Sensitive Powders |
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Precise temperature and atmosphere control | Graphene, Carbon Nanotubes, Nanomaterials |
| Industrial Catalytic Reactions | High efficiency, maximum gas-solid contact | Catalysts in Petroleum Industry |
Ready to enhance your material processing with uniform thermal solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace technologies can optimize your sintering, drying, or synthesis processes for superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















