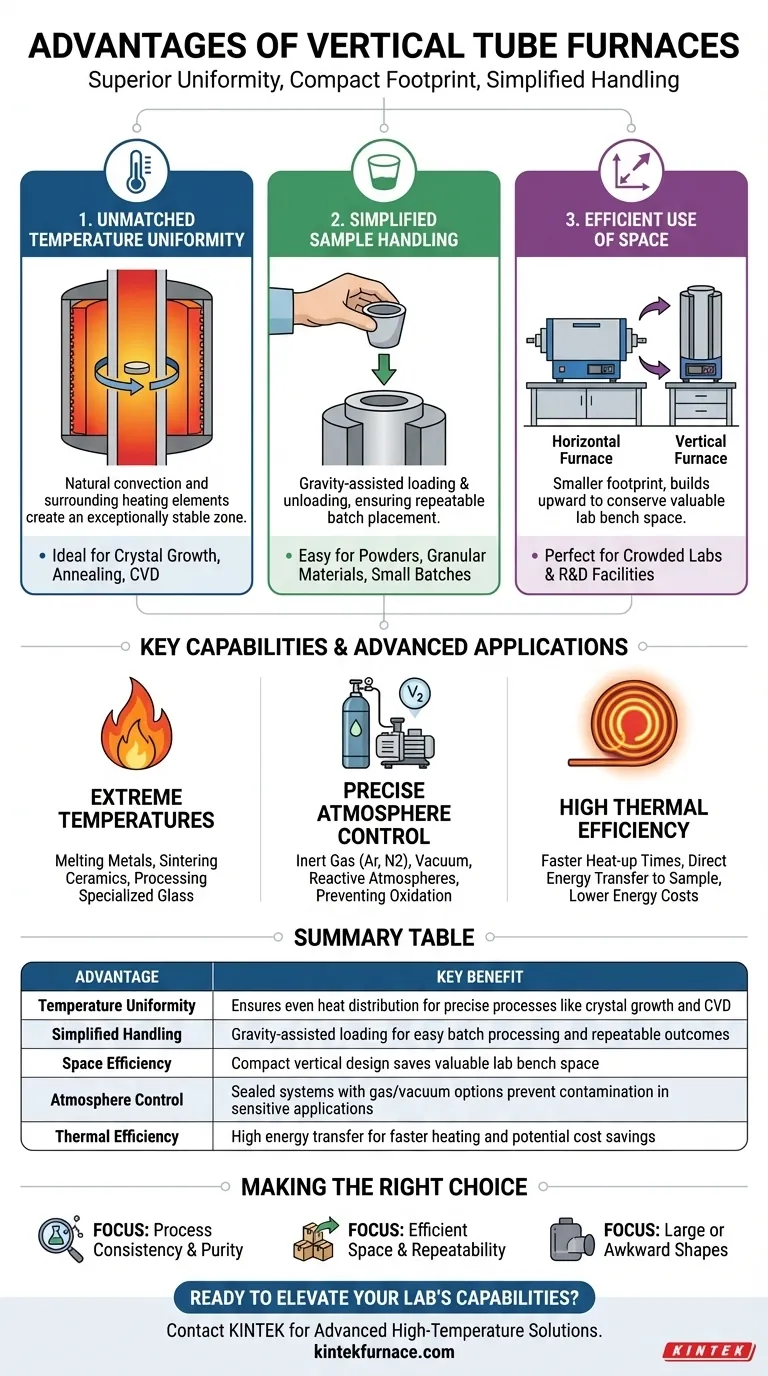
In short, vertical tube furnaces offer superior temperature uniformity, a smaller physical footprint, and simpler sample handling compared to their horizontal counterparts. These advantages stem directly from their vertical orientation, which optimizes heat distribution and simplifies the loading and unloading of materials, particularly for batch processing.
The decision to use a vertical tube furnace is not merely about saving space. It is a strategic choice for processes where thermal consistency, atmospheric purity, and repeatable results are paramount, as the vertical design inherently minimizes thermal gradients and simplifies material management.

The Core Principle: How Vertical Orientation Drives Performance
A vertical tube furnace operates by placing a material inside a vertically oriented heating chamber. This simple change in orientation from a horizontal furnace creates a distinct set of operational advantages.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The vertical alignment, combined with surrounding heating elements, promotes natural convection. This allows heat to be distributed evenly throughout the tube, creating an exceptionally stable and uniform temperature zone.
This high degree of uniformity is critical for processes like crystal growth, annealing, and chemical vapor deposition, where even minor temperature fluctuations can compromise the final product.
Simplified Material Handling
Loading and unloading samples, especially powders, granular materials, or small batches, is significantly easier. Gravity assists in positioning the sample crucible in the center of the heat zone.
This simplifies batch processing, ensuring that each batch is placed in the exact same thermal environment, which leads to highly consistent and repeatable outcomes.
Efficient Use of Laboratory Space
Vertical furnaces have a much smaller footprint than horizontal models of similar capacity. By building upward instead of outward, they conserve valuable bench space.
This makes them an ideal choice for crowded research and development labs or quality control facilities where space is at a premium.
Key Capabilities for Advanced Applications
Beyond the fundamental design benefits, vertical tube furnaces are engineered for demanding, high-temperature processes that require precise control.
Achieving Extreme Temperatures
These furnaces are often designed to reach very high temperatures, making them suitable for melting metals, sintering advanced ceramics, and processing specialized glass.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Many vertical tube furnaces can be sealed and integrated with vacuum pumps and gas delivery systems. This allows for processing materials in a controlled inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) or reactive gas atmosphere.
This capability is essential for preventing oxidation and contamination in sensitive materials science and semiconductor applications.
High Thermal Efficiency
The design of a vertical tube furnace, with its encompassing heating elements and robust insulation, typically results in high thermal efficiency.
This means that more of the energy consumed is transferred directly to the sample, leading to faster heat-up times and potentially lower long-term energy costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vertical tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Initial Cost and Complexity
High-performance vertical tube furnaces, especially those with advanced atmosphere and temperature controls, can represent a significant capital investment compared to simpler box or horizontal furnaces.
Maintenance Considerations
The components required for high-temperature and vacuum operation, such as seals, gaskets, and heating elements, require regular inspection and periodic replacement, contributing to the overall cost of ownership.
Limitations on Sample Size
The diameter of the process tube inherently limits the size and geometry of the sample. For large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects, a chamber or box furnace may be a more practical alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the specific requirements of your application and your primary goals.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and material purity: The superior temperature uniformity and atmosphere control of a vertical tube furnace make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is efficient lab space and repeatable batch processing: The small footprint and gravity-assisted loading of a vertical model offer clear advantages.
- If your primary focus is processing large or awkwardly shaped parts: A box or chamber furnace will likely provide the necessary capacity and flexibility that a tube furnace cannot.
Ultimately, choosing a vertical tube furnace is an investment in precision, repeatability, and control for your most critical thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Ensures even heat distribution for precise processes like crystal growth and CVD |
| Simplified Handling | Gravity-assisted loading for easy batch processing and repeatable outcomes |
| Space Efficiency | Compact vertical design saves valuable lab bench space |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed systems with gas/vacuum options prevent contamination in sensitive applications |
| Thermal Efficiency | High energy transfer for faster heating and potential cost savings |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom vertical tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior thermal processing with precision and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















