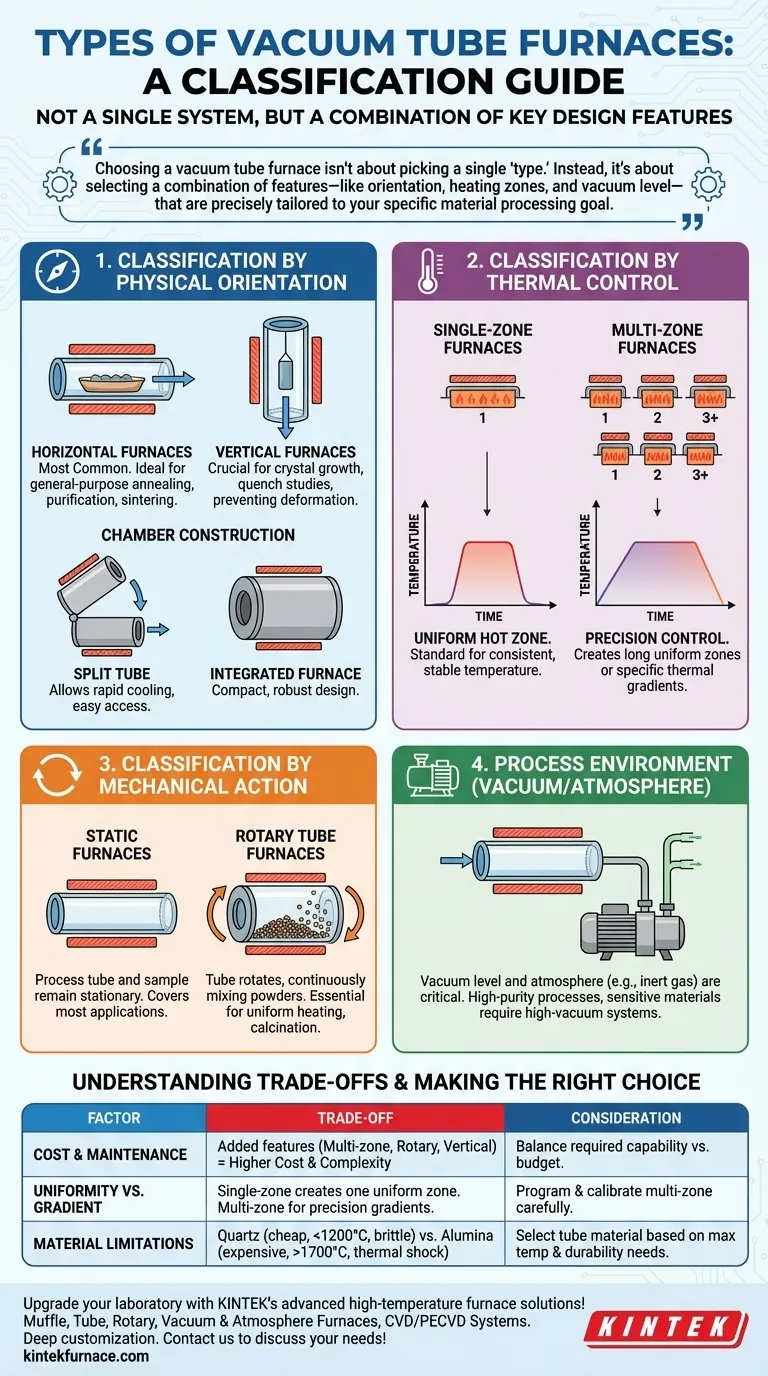
In short, vacuum tube furnaces are not categorized by a single system but are classified based on several key design and functional characteristics. The primary classifications are based on their physical orientation (horizontal, vertical), thermal control (single-zone, multi-zone), mechanical action (static, rotary), and the process environment they create (vacuum level, atmosphere).
Choosing a vacuum tube furnace isn't about picking a single 'type.' Instead, it's about selecting a combination of features—like orientation, heating zones, and vacuum level—that are precisely tailored to your specific material processing goal.
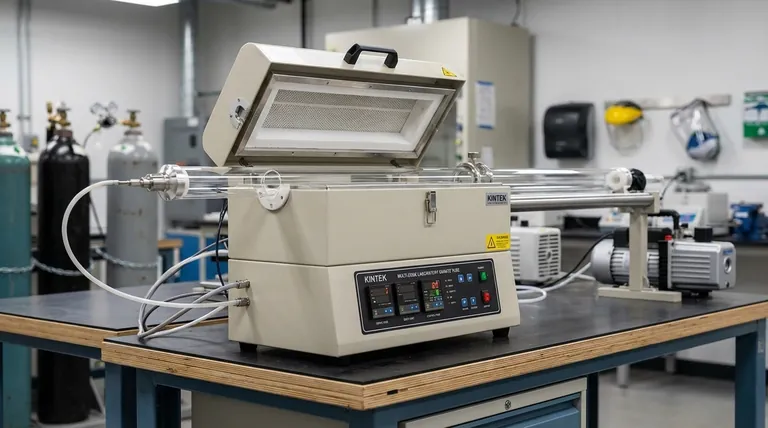

Classification by Physical Orientation
The physical layout of the furnace is the most visible distinction and directly impacts how samples are loaded and how heat and gravity interact with them.
Horizontal Furnaces
This is the most common configuration. The tube is oriented horizontally, and samples are typically placed in a ceramic "boat" and pushed to the center of the heated zone.
They are ideal for general-purpose applications like annealing, purification, and sintering where the sample's orientation to gravity is not critical.
Vertical Furnaces
In this design, the tube is oriented vertically. This is crucial for processes where gravity plays a role.
Vertical furnaces are used for crystal growth, experiments where you need to drop a sample into a quench bath, or to prevent flat samples from sagging or deforming at high temperatures.
Split Tube vs. Integrated Furnaces
This refers to the construction of the heating chamber itself. A split tube furnace has hinges that allow the heating chamber to be opened, which is useful for rapid cooling or inserting a sealed process tube.
An integrated furnace is a single, solid cylinder, offering a more compact and often more robust design.
Classification by Thermal Control
The number and control of heating zones determine the furnace's ability to create a uniform temperature or a specific thermal gradient.
Single-Zone Furnaces
These furnaces have one set of heating elements and one controller. They are designed to create a single, uniform hot zone in the center of the tube.
This is the standard for most laboratory applications where a consistent, stable temperature is the primary requirement.
Multi-Zone Furnaces
These furnaces have two, three, or even more independent heating zones, each with its own thermocouple and controller.
Their purpose is either to create a much longer and more precise uniform temperature zone than a single-zone furnace can achieve, or to deliberately create a temperature gradient along the tube for processes like chemical vapor transport.
Classification by Mechanical Action
Some processes require the sample to be moved or agitated during heating to ensure uniformity.
Static Furnaces
In a standard or static furnace, the process tube and the sample within it remain stationary during the heating cycle. This covers the vast majority of applications.
Rotary Tube Furnaces
In this specialized design, the entire process tube is slowly rotated during operation. This tumbling action continuously mixes powders or granular materials.
Rotary furnaces are essential for applications like calcination or when synthesizing materials from powders, as they ensure every particle is exposed to the same temperature profile, preventing hot spots and improving reaction uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Complexity vs. Control
Each design choice represents a trade-off between capability, cost, and complexity. Acknowledging these is critical for making an informed decision.
Cost and Maintenance
Added features directly increase cost and complexity. A multi-zone, rotary, vertical furnace is significantly more expensive and requires more maintenance than a standard single-zone, horizontal model.
Uniformity vs. Gradient
A single-zone furnace is optimized for creating one uniform hot zone. While a multi-zone furnace can create a longer uniform zone, it requires careful programming and calibration. Its primary advantage is the ability to create controlled temperature gradients, which are unnecessary for many applications.
Material Limitations
The process tube itself—often quartz or alumina—is a critical component. Quartz tubes are cost-effective but have a lower maximum temperature (~1200°C) and can become brittle. Alumina tubes can withstand much higher temperatures (>1700°C) but are more expensive and less resistant to thermal shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific process dictates the ideal furnace configuration. There is no single "best" type.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work like annealing or purification: A single-zone, horizontal furnace offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is uniform powder processing or calcination: A rotary tube furnace is necessary to ensure consistent heating throughout the sample.
- If your primary focus is creating specific thermal profiles or very long uniform hot zones: A multi-zone furnace is required for this level of precise thermal control.
- If your primary focus is preventing sample deformation at high temperatures: A vertical furnace configuration is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive materials or thin-film deposition: A furnace equipped with a high-vacuum pump system is non-negotiable to ensure process purity.
Ultimately, understanding these classifications transforms the question from "what type?" to "which combination of features best serves my process?"
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Orientation | Horizontal, Vertical | Annealing, crystal growth, preventing deformation |
| Thermal Control | Single-zone, Multi-zone | Uniform heating, temperature gradients |
| Mechanical Action | Static, Rotary | General lab work, powder processing, calcination |
| Process Environment | Vacuum level, Atmosphere | High-purity processes, sensitive materials |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for enhanced efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations
- What steps are involved in the installation of a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety for Your Lab
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering



















