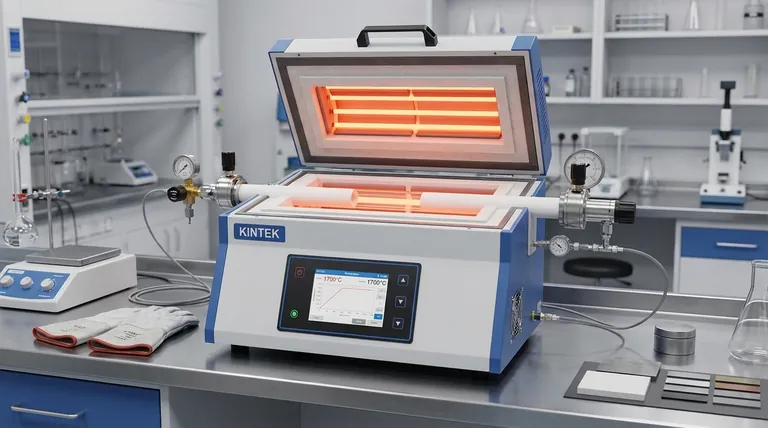
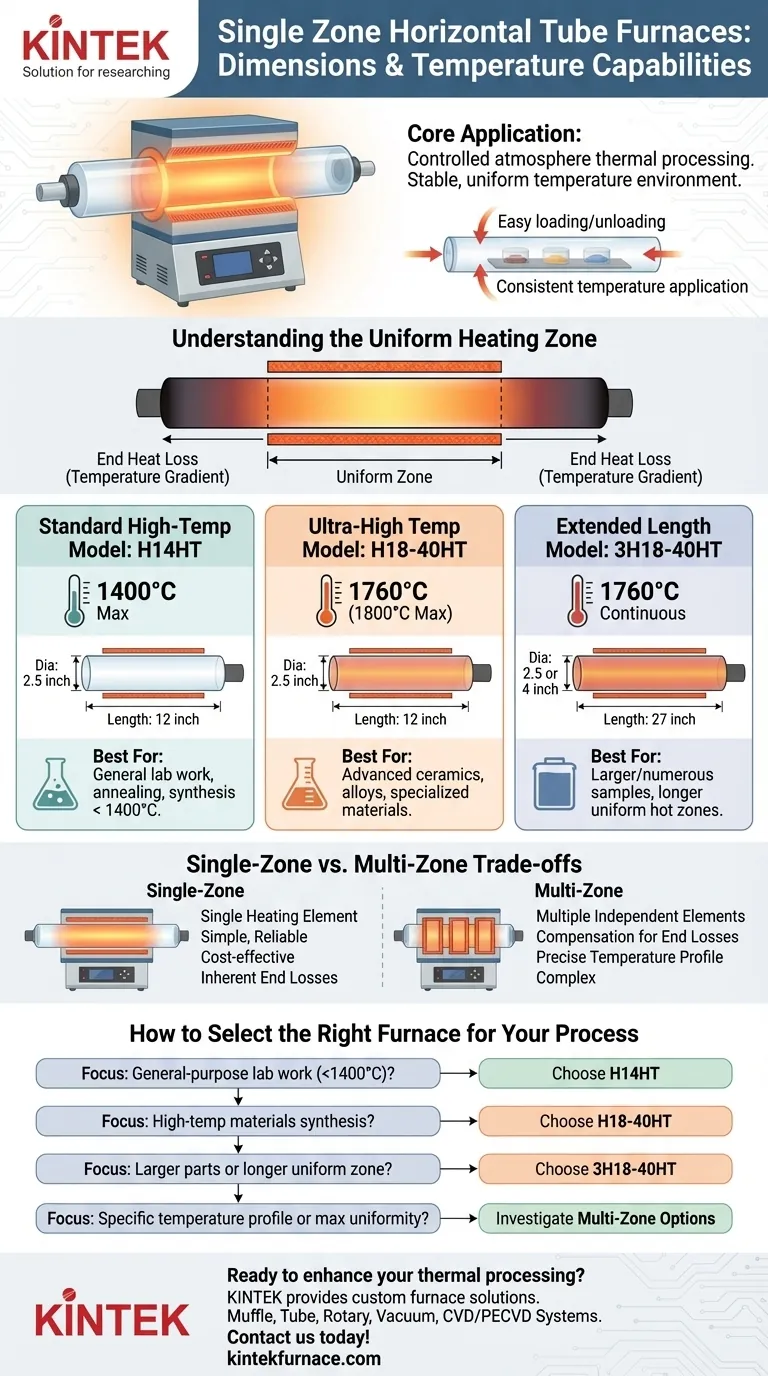
For single-zone horizontal tube furnaces, the key models offer a range from standard to high-temperature capabilities with varying dimensions. The H14HT operates up to 1400°C with a 2.5-inch diameter by 12-inch length. For higher temperatures, the H18-40HT reaches 1760°C (1800°C max) with the same dimensions, while the 3H18-40HT provides similar high-temperature performance but in a longer format (27 inches) with a choice of 2.5 or 4-inch diameters.
The selection of a single-zone horizontal tube furnace is not just about its maximum temperature. It is a critical decision based on the required length of your uniform heating zone and the physical size of your sample, balanced against the inherent simplicity of a single-zone design.

Understanding the Core Application
A horizontal tube furnace is a fundamental tool for thermal processing, designed to heat materials in a controlled atmosphere within a ceramic or quartz tube. Its primary value lies in its ability to create a stable and uniform temperature environment.
The Purpose of a Horizontal Orientation
The horizontal design allows for easy loading and unloading of samples. It is particularly effective for processes like annealing, calcination, and synthesis where a consistent temperature must be applied evenly across the length of the material.
Achieving a Uniform Heating Zone
The "heated length" of a furnace tube is not the same as its "uniform heating zone." A single heating element wraps around the tube, but heat naturally escapes from the ends. The uniform zone is the central portion of the tube where the temperature is most stable and consistent.
Essential Operational Features
Beyond heat, these furnaces are defined by their control and safety systems. Precise temperature control is managed by a thermocouple and a PID controller, while over-temperature protection and safety interlocks ensure safe operation, especially during unattended runs.
Single-Zone Model Specifications
Single-zone models are defined by one heating element and one controller, making them ideal for establishing a single, stable processing temperature.
Standard High-Temperature Model (1400°C)
- Model: H14HT
- Max Temperature: 1400°C (2552°F)
- Tube Dimensions: 2.5-inch diameter by 12-inch length.
- Best For: General-purpose lab work, annealing, and synthesis below 1400°C.
Ultra-High Temperature Model (1800°C)
- Model: H18-40HT
- Max Temperature: 1760°C continuous, 1800°C (3272°F) max.
- Tube Dimensions: 2.5-inch diameter by 12-inch length.
- Best For: Processing advanced ceramics, high-temperature alloys, and specialized materials.
Extended Length, High-Temperature Model
- Model: 3H18-40HT
- Max Temperature: 1760°C continuous.
- Tube Dimensions: 2.5 or 4-inch diameter by 27-inch length.
- Best For: Processing larger or more numerous samples, or when a longer uniform hot zone is required for the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone
Choosing a single-zone furnace is a deliberate engineering decision. Understanding its limitations is key to ensuring it meets your process requirements.
The Advantage of Simplicity
A single-zone furnace is straightforward, reliable, and cost-effective. For a vast range of applications that only require one stable temperature, it is the optimal solution. Operation is simple: set one temperature, and the furnace maintains it.
The Inherent Limitation: End Losses
The primary trade-off of a single-zone furnace is temperature uniformity over length. Due to heat escaping from the tube ends, the temperature will naturally be lower there than in the center. The longer the furnace, the longer the potential uniform zone, but gradients at the ends are unavoidable.
When to Consider a Multi-Zone Furnace
If your process requires an exceptionally long and precise uniform hot zone, or if you need to create a specific temperature gradient along the sample, a multi-zone furnace is necessary. These furnaces use multiple, independently controlled heating elements (e.g., three zones) to compensate for end losses or to intentionally create different temperature profiles.
How to Select the Right Furnace for Your Process
Base your decision on the specific demands of your thermal processing task.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work below 1400°C: The H14HT offers the necessary performance in a standard, compact footprint.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing materials at very high temperatures: The H18-40HT provides the required temperature capability for smaller-scale work.
- If your primary focus is processing larger parts or batches in a longer uniform zone: The extended length of the 3H18-40HT is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific temperature profile or maximizing uniformity over a long length: A single-zone model is not the right tool; you should investigate three-zone furnace options.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's capabilities with your specific process goals is the key to successful and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Model | Max Temperature | Tube Dimensions (Diameter x Length) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| H14HT | 1400°C | 2.5" x 12" | General-purpose lab work, annealing, synthesis below 1400°C |
| H18-40HT | 1760°C continuous, 1800°C max | 2.5" x 12" | Processing advanced ceramics, high-temperature alloys, specialized materials |
| 3H18-40HT | 1760°C continuous | 2.5" or 4" x 27" | Processing larger samples, longer uniform hot zones |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with a custom furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















