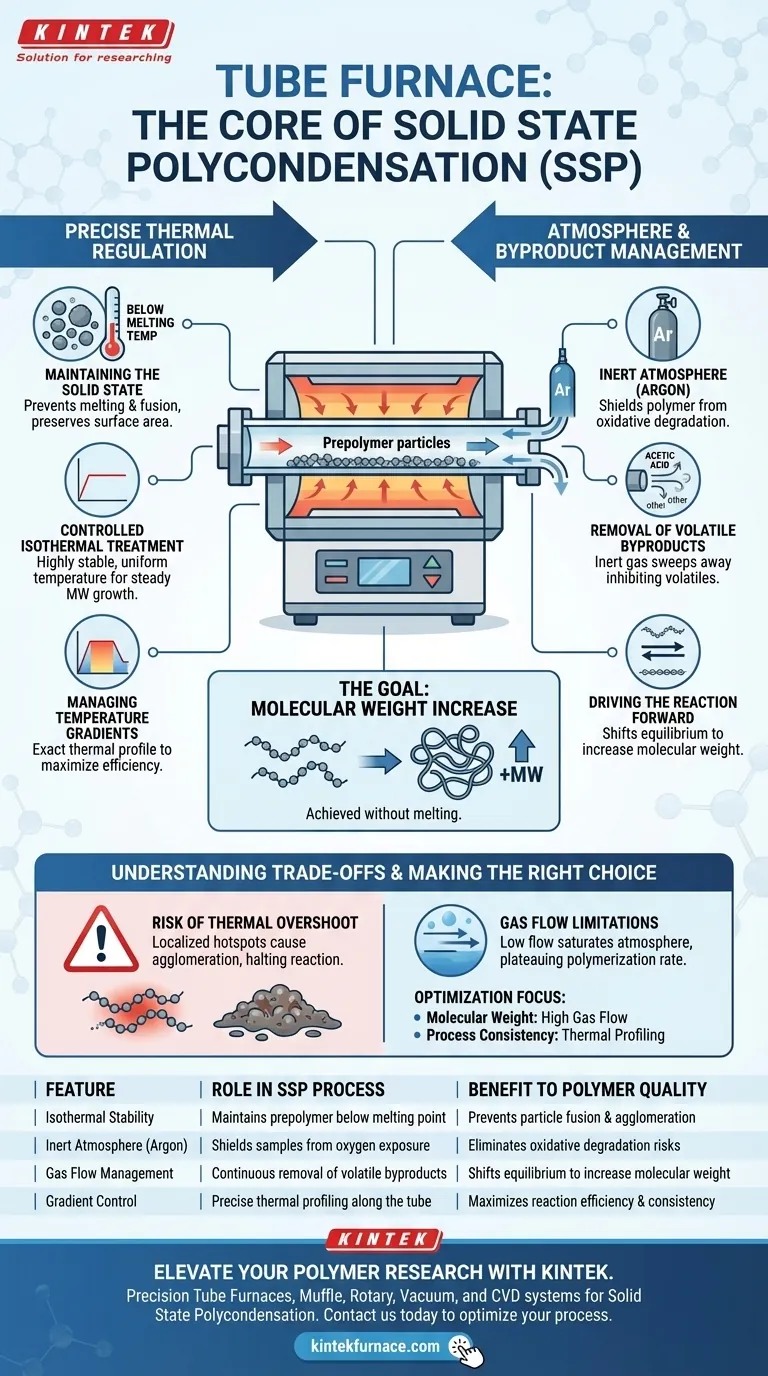
A tube furnace is the preferred apparatus for Solid State Polycondensation (SSP) because it provides the precise environmental control required to increase molecular weight without melting the polymer. It enables long-duration isothermal treatments under a high-purity inert atmosphere, such as argon, ensuring the material remains in a solid state while effectively managing reaction byproducts.
Core Takeaway Successful SSP relies on driving the polymerization reaction forward by removing volatiles while strictly maintaining the polymer below its melting point. The tube furnace is the critical tool that balances these thermal and atmospheric requirements to ensure steady molecular weight growth.

The Role of Precise Thermal Regulation
Maintaining the Solid State
The fundamental requirement of SSP is processing the prepolymer below its melting temperature. If the temperature spikes, the particles will melt and fuse, ruining the surface area required for the reaction.
Controlled Isothermal Treatment
A tube furnace excels at maintaining a highly stable, uniform temperature over long durations. This stability creates the ideal environment for the slow, steady increase in molecular weight required for high-performance polyesters.
Managing Temperature Gradients
The equipment allows for the precise control of temperature gradients along the tube. This capability ensures the sample experiences the exact thermal profile necessary to maximize reaction efficiency without crossing thermal degradation thresholds.
Atmosphere and Byproduct Management
The Necessity of an Inert Atmosphere
To prevent oxidative degradation during the heating process, the reaction must occur in a non-reactive environment. The tube furnace facilitates the continuous flow of high-purity argon, shielding the polymer from oxygen.
Removal of Volatile Byproducts
The polycondensation reaction generates volatile byproducts, such as acetic acid, which can inhibit the reaction if not removed. The design of the tube furnace allows the inert gas stream to sweep these byproducts away from the sample surface effectively.
Driving the Reaction Forward
By continuously removing these volatiles, the furnace shifts the chemical equilibrium. This forces the reaction to proceed toward polymer chain extension, resulting in the desired increase in molecular weight.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Overshoot
While tube furnaces are precise, improper calibration can lead to localized hotspots. Even a minor overshoot near the melting point can cause particle agglomeration, reducing the surface area available for byproduct diffusion and halting the reaction.
Gas Flow Limitations
The efficiency of byproduct removal is heavily dependent on gas flow rates within the tube. If the flow is too low, the atmosphere becomes saturated with acetic acid or other volatiles, causing the polymerization rate to plateau regardless of the temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your SSP process using a tube furnace, consider the following approach:
- If your primary focus is Molecular Weight Increase: Prioritize high gas flow rates to ensure aggressive removal of volatile byproducts like acetic acid.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Invest in thermal profiling to ensure there are no temperature spikes that could melt the prepolymer surface.
The tube furnace is not just a heating element; it is a mass transfer device that dictates the success of your polymerization.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in SSP Process | Benefit to Polymer Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Isothermal Stability | Maintains prepolymer below melting point | Prevents particle fusion and agglomeration |
| Inert Atmosphere (Argon) | Shields samples from oxygen exposure | Eliminates oxidative degradation risks |
| Gas Flow Management | Continuous removal of volatile byproducts | Shifts equilibrium to increase molecular weight |
| Gradient Control | Precise thermal profiling along the tube | Maximizes reaction efficiency and consistency |
Elevate Your Polymer Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a failed melt and a high-performance polymer. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Tube Furnaces, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of Solid State Polycondensation.
Whether you require aggressive byproduct removal or ultra-stable thermal profiling, our systems are fully customizable to your unique laboratory needs. Contact us today to discover how KINTEK’s advanced heating solutions can optimize your polymerization process and ensure consistent molecular weight growth.
Visual Guide
References
- Pavel A. Mikhaylov, A. Ya. Malkin. Processing of Thermotropic Fully Aromatic Polyesters by Powder Molding Accompanied by Solid-State Post-Polymerization. DOI: 10.3390/polym17101358
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the design advantage of a split tube furnace? Unlock Easy Access for Complex Lab Setups
- What types of atmospheres can a horizontal electric furnace control? Master Material Processing with Precision
- What is the function of a tube reactor during the reduction process of Siderite Ore? Optimize Your Metallization Process
- What maintenance does a horizontal tube furnace require? Ensure Peak Performance and Safety
- What are the features of more elaborate tube furnaces? Precision Control for Advanced Thermal Processing
- What is the maximum temperature for a tube furnace? Unlock the Right Heat for Your Application
- What is the process for using a vacuum tube experimental furnace? Master Precise Control for Your Lab
- Why are a split furnace and a PID temperature controller core in supercritical water gasification? Essential Guide



















