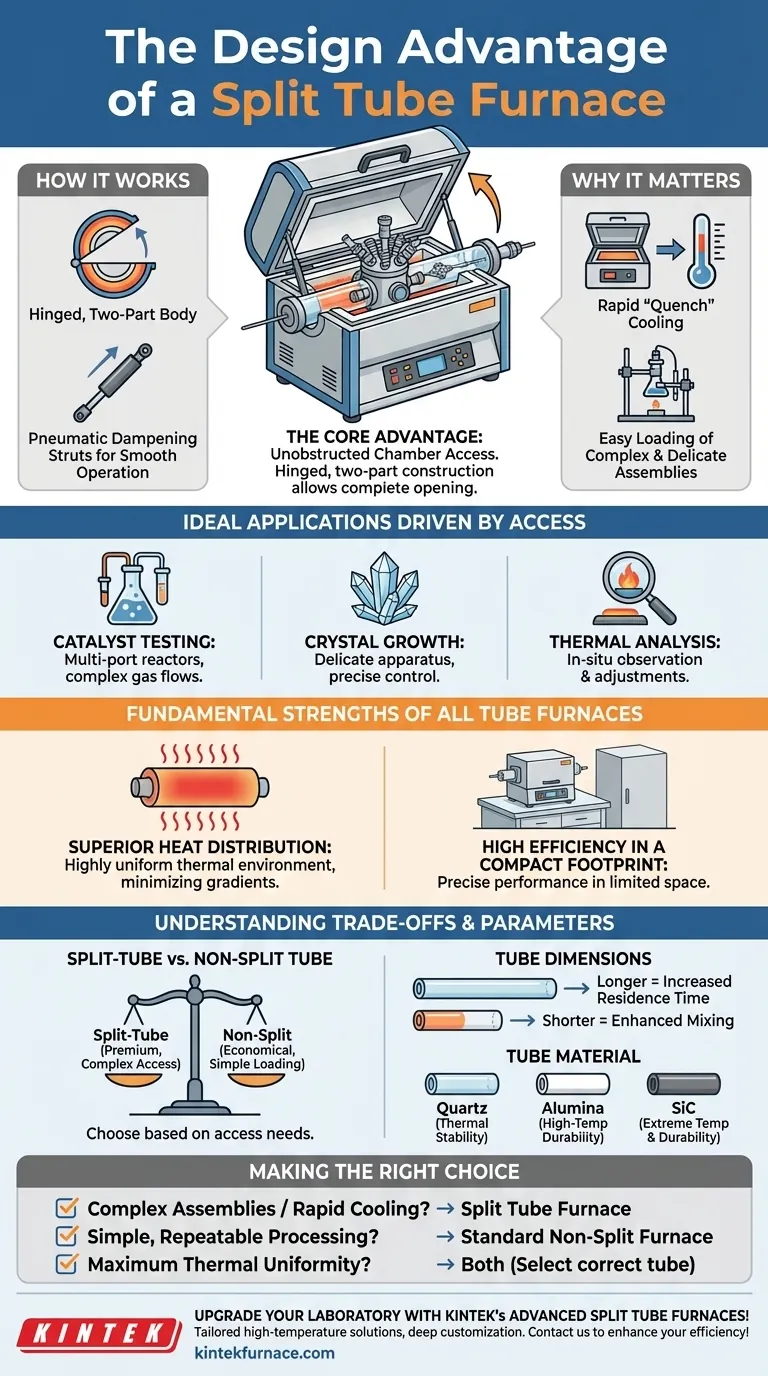
At its core, the principal design advantage of a split tube furnace is the unparalleled access it provides to the internal work tube. This hinged, two-part construction allows the heating chamber to be opened completely, which is a critical feature for specific, demanding applications where loading from the end of a tube is impractical or impossible.
While all tube furnaces excel at providing uniform heating in a compact space, the split-tube design specifically solves the logistical challenge of easily placing, adjusting, and removing complex experimental setups or delicate samples.
The Core Advantage: Unobstructed Chamber Access
The defining feature of a split tube furnace is that its cylindrical heating chamber is divided lengthwise into two halves. These are joined by hinges, allowing the top half to open like a clamshell.
How the Split Mechanism Works
The furnace body is literally "split" along its horizontal axis. These two sections are hinged on one side and latched on the other, enabling the entire furnace to be opened.
Many modern designs incorporate pneumatic dampening struts, which allow the top half to be opened and closed smoothly and safely, protecting both the operator and the fragile tube inside.
Why Rapid Access Matters
This design directly facilitates complex laboratory work. Operators can place an entire pre-assembled reactor, a delicate crystal growth apparatus, or a sample with multiple sensor feeds directly into the furnace's center.
This also allows for rapid cooling. By opening the chamber, the sample can be "quench" cooled in ambient air far more quickly than waiting for a solid furnace to dissipate its heat, which is vital for certain material science processes.
Ideal Applications Driven by Access
The split-tube design is not a universal necessity, but it is indispensable for certain fields.
It is ideal for catalyst testing, where reactors may have multiple inlet and outlet ports, and for crystal growth, where the apparatus can be delicate and complex. It also excels in thermal analysis applications requiring in-situ observation or adjustment.
Fundamental Strengths of All Tube Furnaces
Beyond the split-tube feature, it's important to recognize the inherent benefits of the tube furnace platform itself, which are shared by both split and non-split models.
Superior Heat Distribution
The cylindrical chamber design is naturally suited for creating a highly uniform thermal environment. Heat radiates evenly onto the work tube from all sides, minimizing temperature gradients that could compromise experimental results.
High Efficiency in a Compact Footprint
Compared to larger box furnaces or other industrial heating equipment, tube furnaces deliver precise, high-temperature performance in a much smaller footprint. This makes them a mainstay in research laboratories and development facilities where space is often limited.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Parameters
Choosing a furnace involves weighing the benefits of the split design against other critical factors.
Split-Tube vs. Non-Split Tube
The primary trade-off is often simplicity and cost. A standard, solid-body tube furnace has a simpler construction, which can make it more economical. It is perfectly adequate for processes where samples can be easily slid into the tube from one end.
The split-tube design is a premium feature, justified when the experimental setup demands the access it provides.
The Role of Tube Dimensions
The length and diameter of the work tube are critical design parameters. A longer tube increases the time a sample or gas is exposed to heat (residence time), improving reaction efficiency. A shorter tube, conversely, can enhance gas-solid mixing in certain applications.
The Impact of Tube Material
The material of the work tube itself is crucial. Quartz is common for its thermal stability and transparency at lower temperatures, while materials like alumina or silicon carbide (SiC) are used for their durability and ability to withstand extremely high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is handling complex assemblies or requiring rapid sample cooling: A split tube furnace is the necessary and correct choice.
- If your primary focus is simple, repeatable thermal processing where samples are easily loaded: A standard non-split tube furnace is often the more practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum thermal uniformity: Both designs provide excellent results, but pay close attention to selecting the right tube material and dimensions for your specific temperature and process.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace design begins with a clear understanding of your operational workflow.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Unobstructed Chamber Access | Hinged, clamshell design allows full opening for easy loading of complex setups and rapid cooling. |
| Ideal Applications | Catalyst testing, crystal growth, thermal analysis requiring in-situ adjustments. |
| Key Trade-offs | Premium feature vs. standard tube furnaces; higher cost but essential for specific workflows. |
| Tube Material Options | Quartz for thermal stability, alumina or SiC for high-temperature durability. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced split tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our split tube furnace can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















