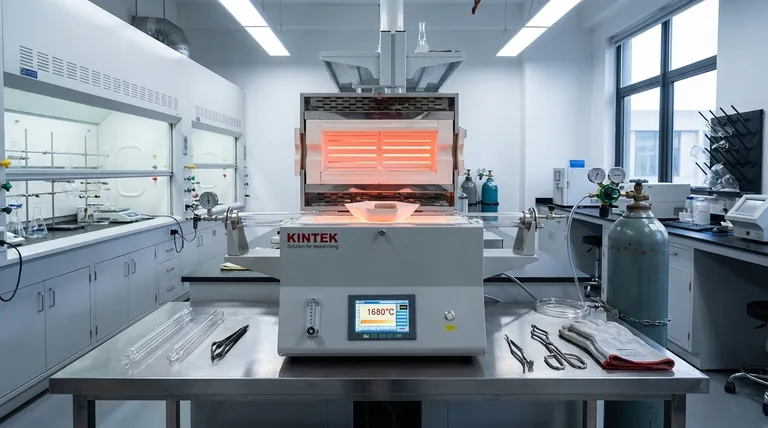
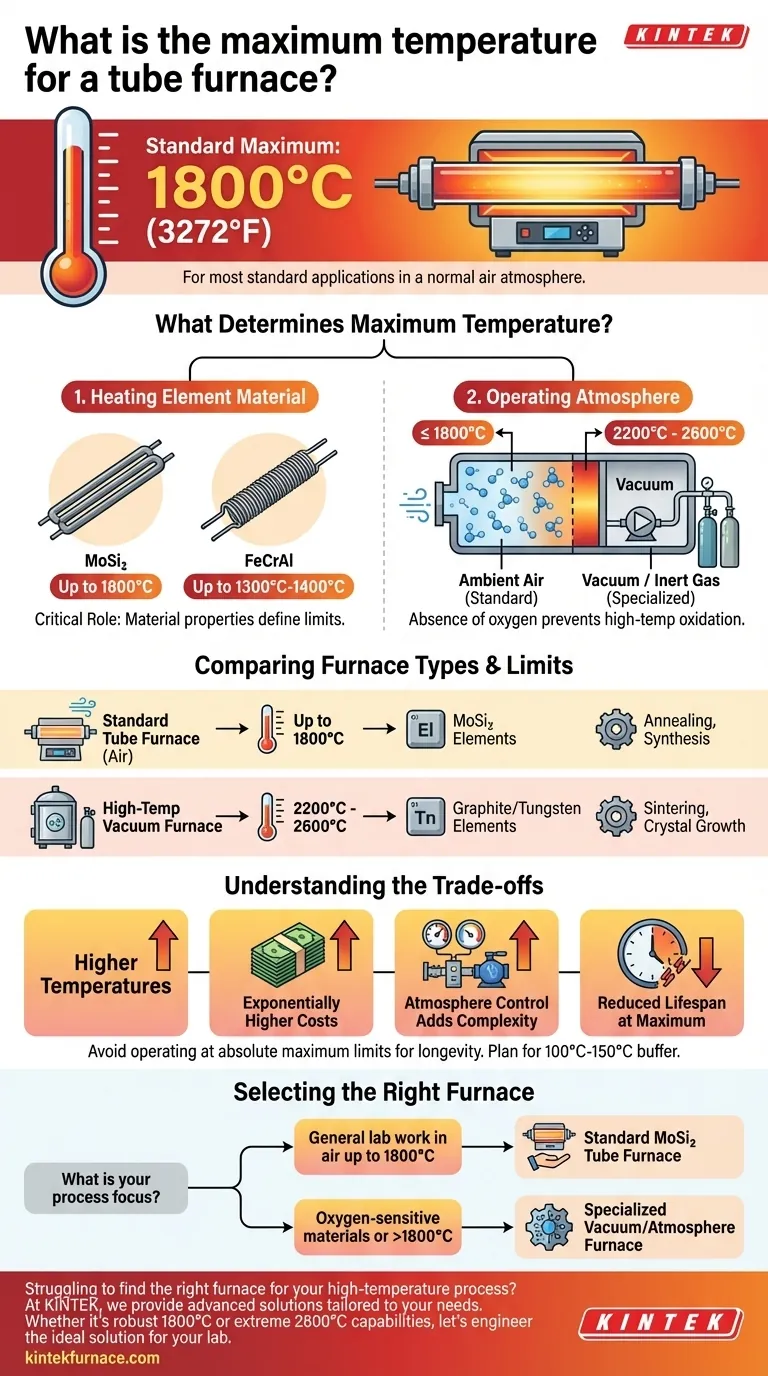
For most standard applications, the maximum operating temperature of a tube furnace is 1800°C (3272°F). This limit is primarily dictated by the material of the heating elements and the furnace's design for operation in a normal air atmosphere.
The term "maximum temperature" is not a single value but is instead determined by two key factors: the furnace's heating element material and its operating atmosphere (air versus vacuum or inert gas).

What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
To understand why different furnaces have different temperature limits, you must look at their core components and intended operating environment. The answer lies in the physics of the materials used.
The Critical Role of the Heating Element
The heart of any furnace is its heating element. The material used for this element is the single biggest factor in determining its maximum temperature.
Elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) are required to reach temperatures up to 1800°C in air without degrading. Lower-temperature furnaces often use more common alloys like Kanthal (FeCrAl), which typically max out around 1300°C - 1400°C.
The Impact of the Operating Atmosphere
The second critical factor is the atmosphere inside the furnace tube. Most standard tube furnaces operate in ambient air.
However, specialized furnaces that operate under a vacuum or with an inert gas (like Argon) can reach much higher temperatures, often between 2200°C and 2600°C. This is because the absence of oxygen prevents the high-temperature oxidation and failure of both the heating elements and the material being processed.
Comparing Furnace Types and Their Limits
The references you've seen for different temperatures are not contradictory; they are referring to different classes of furnaces designed for different tasks.
Standard Tube Furnaces (Up to 1800°C)
These are the workhorses of many research and production labs. They are designed for processes like thermal annealing, material synthesis, and quality control testing in an air atmosphere. Their 1800°C limit is a function of using robust heating elements that can withstand long-term exposure to oxygen at high temperatures.
High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces (2200°C - 2600°C)
When you see temperatures exceeding 2000°C, the equipment is almost always a vacuum furnace. These are highly specialized systems for applications like sintering advanced ceramics, brazing refractory metals, or growing crystals.
By removing the air, these furnaces can use heating elements (often graphite or tungsten) that would instantly burn up in an oxygen environment, allowing them to achieve extreme temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is not just about finding the highest temperature. Higher performance comes with significant trade-offs in cost, complexity, and maintenance.
Higher Temperatures Mean Exponentially Higher Costs
The specialized materials required for extreme temperatures—from the heating elements to the ceramic insulation and control systems—are significantly more expensive. A 2200°C vacuum furnace can cost many times more than a standard 1800°C tube furnace.
Atmosphere Control Adds Complexity
Operating a vacuum or inert gas furnace requires a complex system of pumps, gauges, seals, and gas flow controllers. This increases not only the initial cost but also the operational knowledge required to run the equipment safely and effectively.
Reduced Lifespan at Maximum Limits
Consistently operating any furnace at its absolute maximum rated temperature will drastically shorten the lifespan of its heating elements. For longevity and reliability, it is standard practice to select a furnace with a maximum temperature at least 100°C-150°C higher than your required operating temperature.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be guided entirely by the specific requirements of your process, not by the maximum temperature figure alone.
- If your primary focus is general lab work in air up to 1800°C: A standard MoSi₂-element tube furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials or requires temperatures above 1800°C: You must select a specialized vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace designed for those conditions.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific material and process goals is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Factor | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Tube Furnace (Air) | Up to 1800°C | MoSi₂ Heating Elements | Annealing, Synthesis |
| High-Temp Vacuum Furnace | 2200°C - 2600°C | Vacuum/Inert Gas Atmosphere | Sintering, Crystal Growth |
Struggling to find the right furnace for your high-temperature process? At KINTEK, we understand that the 'maximum temperature' is just the beginning. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing allows us to provide advanced solutions—from Muffle and Tube Furnaces to specialized Vacuum & Atmosphere systems—perfectly tailored to your unique experimental needs. Whether you require robust 1800°C performance or extreme 2600°C capabilities, our deep customization ensures your furnace matches your material and process goals precisely. Let's engineer the ideal solution for your lab. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















