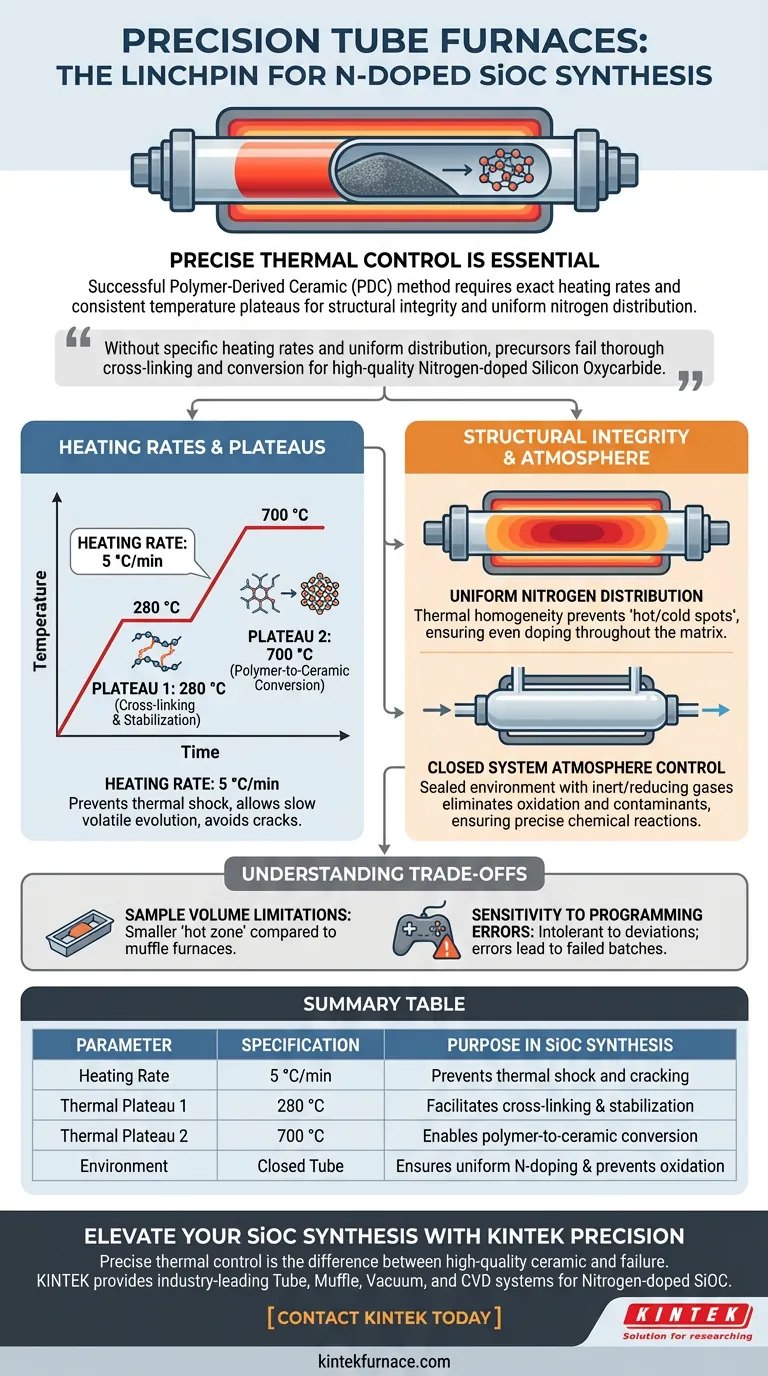
Precise thermal control is the linchpin of successful SiOC synthesis. A precision tube furnace is required because it guarantees a stable heating rate of 5 °C/min and maintains consistent temperature plateaus at critical thresholds, specifically 280 °C and 700 °C. This exactitude is necessary to ensure the structural integrity of the precursor and to achieve a uniform distribution of nitrogen throughout the final material.
The Polymer-Derived Ceramic (PDC) method relies on a precision tube furnace to manage the delicate transition from polymer to ceramic. Without the furnace's ability to maintain specific heating rates and uniform temperature distribution, the precursor cannot undergo the thorough cross-linking and conversion necessary to form high-quality Nitrogen-doped Silicon Oxycarbide.

The Critical Role of Heating Rates and Plateaus
The conversion of a polymer precursor into a ceramic is not merely about reaching a high temperature; it is about the path taken to get there.
Controlling the Rate of Change
The primary reference establishes that a heating rate of 5 °C/min is essential. A precision tube furnace uses programmable controllers to maintain this linear ramp. This controlled rate prevents thermal shock and allows volatile components to evolve slowly, preventing cracks or defects in the material structure.
The Importance of Thermal Plateaus
The process requires holding the material at specific temperatures: 280 °C and 700 °C. These are not arbitrary figures; they correspond to distinct chemical phases.
- At 280 °C: The furnace allows for thorough cross-linking of the polymer, stabilizing the structure before higher heat is applied.
- At 700 °C: The furnace facilitates the actual conversion from the polymeric phase to the ceramic phase.
Ensuring Structural Integrity and Doping
The quality of Nitrogen-doped Silicon Oxycarbide (SiOC) is defined by its internal structure and chemical composition. The furnace architecture directly influences these outcomes.
Uniform Nitrogen Distribution
A key requirement for this material is nitrogen doping. A precision tube furnace ensures accurate temperature distribution across the entire length of the tube. This thermal homogeneity prevents "hot spots" or "cold spots" that would lead to uneven doping, ensuring that nitrogen is distributed uniformly throughout the ceramic matrix.
The Polymer-to-Ceramic Conversion
The Polymer-Derived Ceramic (PDC) method relies on the integrity of the precursor during pyrolysis. If the temperature fluctuates, the cross-linking process may fail. The tube furnace provides the stable thermal environment required to preserve the structural integrity of the material as it undergoes significant chemical changes.
Atmosphere Control and Environment
While temperature is the primary factor, the physical configuration of a tube furnace offers secondary benefits essential for this synthesis.
Closed System Thermodynamics
Unlike open-air furnaces, a tube furnace creates a sealed environment. This allows for the precise control of the thermodynamic environment, often involving the use of inert or reducing gases.
Eliminating Contaminants
By purging oxygen and maintaining a controlled atmosphere, the furnace prevents unwanted oxidation reactions. This ensures that the organic ligands decompose strictly according to the synthesis plan, rather than reacting unpredictably with ambient air.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a precision tube furnace is the optimal tool for this application, it is important to understand the operational constraints.
Sample Volume Limitations
Tube furnaces generally have a smaller "hot zone" compared to muffle furnaces. While they offer superior precision and atmosphere control, they are often limited in the volume of material they can process in a single batch.
Sensitivity to Programming Errors
Because the SiOC synthesis relies on specific ramp rates (5 °C/min) and hold times, the process is intolerant of programming errors. A deviation in the heating program can result in incomplete cross-linking or structural collapse, rendering the batch useless.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the best results with Nitrogen-doped SiOC precursors, align your furnace settings with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Ensure your heating ramp does not exceed 5 °C/min to prevent rapid outgassing and cracking.
- If your primary focus is Uniform Doping: Verify that your sample is positioned exactly in the center of the uniform temperature zone (the "flat zone") of the tube to guarantee consistent nitrogen distribution.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Strictly adhere to the dwell times at the 280 °C and 700 °C plateaus to allow complete cross-linking and ceramic conversion.
Ultimately, the precision tube furnace is not just a heat source; it is a reaction vessel that dictates the chemical and structural destiny of your SiOC material.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Purpose in SiOC Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | 5 °C/min | Prevents thermal shock and cracking during outgassing |
| Thermal Plateau 1 | 280 °C | Facilitates thorough polymer cross-linking and stabilization |
| Thermal Plateau 2 | 700 °C | Enables successful conversion from polymeric to ceramic phase |
| Environment | Closed Tube | Ensures uniform nitrogen doping and prevents oxidation |
Elevate Your SiOC Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal control is the difference between a high-quality ceramic and a failed precursor. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically designed for the delicate requirements of Nitrogen-doped SiOC production.
Our expert R&D and manufacturing teams offer fully customizable solutions to ensure your lab achieves perfect heating rates and atmosphere control. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our specialized lab high-temperature furnaces can optimize your material research and manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Berta Pérez‐Román, Fernando Rubio‐Marcos. Synergistic Effect of Nitrogen Doping and Textural Design on Metal-Free Carbide-Derived Carbon Electrocatalysts for the ORR. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5c10307
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of pre-treating quartz tube reactors? Achieve High-Purity CVT Crystal Growth with Precision
- What are the main industries where tube furnaces are used? Essential for Semiconductor, Battery, and Materials R&D
- Why must a programmable vacuum tube furnace with a nitrogen atmosphere be used for Bi2Se3? Optimize Your Thin Films
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace for REBCO tapes? Find Critical 175°C Thresholds
- How does a high-temperature tube atmosphere furnace contribute to nitrogen-doping of graphene oxide? Enhance Your R&D
- Why are vacuum-sealed high-purity fused quartz tubes utilized as reaction vessels for PTI/Cu complex synthesis?
- Why is a tube furnace required for the calcination of TiO2 in an H2/Ar mixed atmosphere? Engineering TiO2-X Defects
- How does a tube furnace generate high temperatures? Efficient, Precise Heating for Your Lab



















