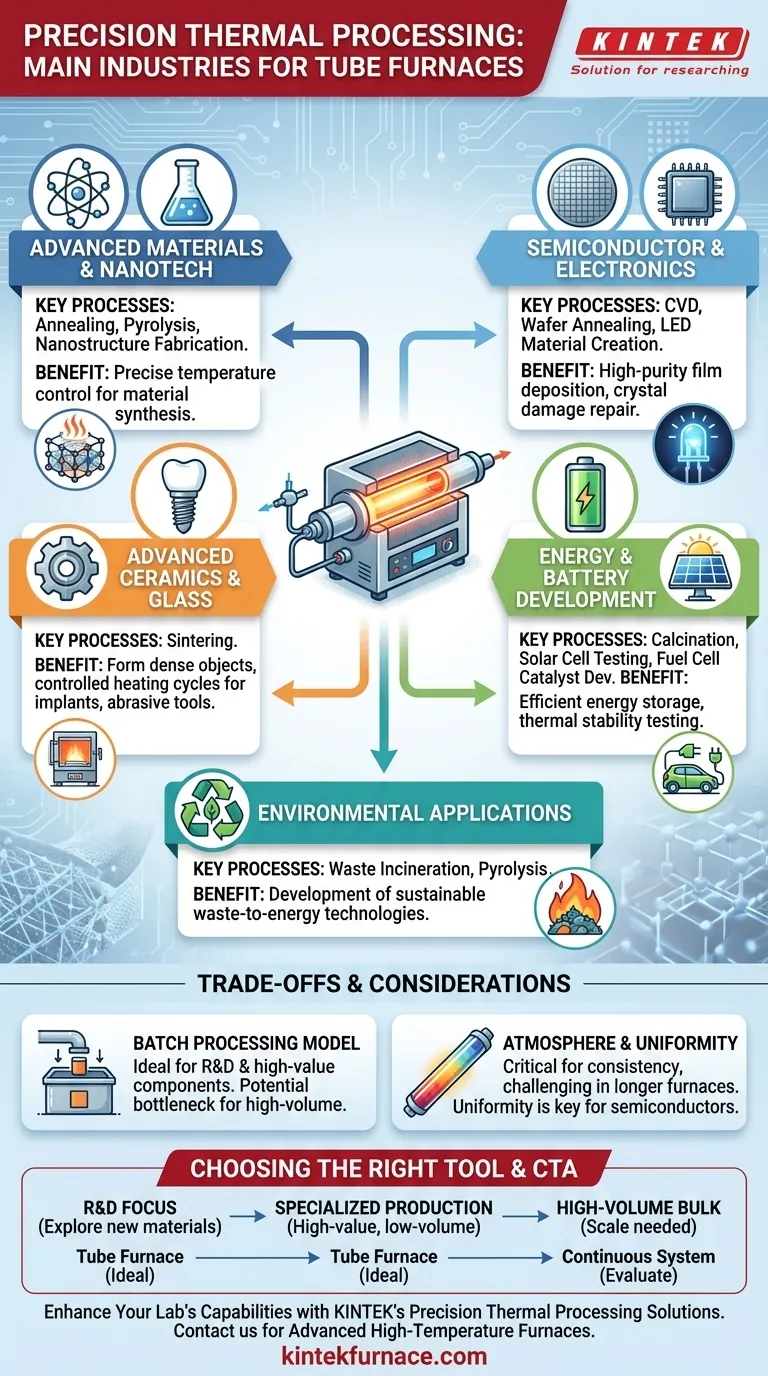
At their core, tube furnaces are tools for precision thermal processing. They are critical in any industry where creating or modifying advanced materials requires absolute control over temperature and atmospheric conditions. Key sectors include semiconductor manufacturing, advanced materials research, metallurgy, and the development of new energy technologies like lithium-ion batteries.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its capacity to create a tightly controlled, uniform, and repeatable thermal environment. This precision is what enables the synthesis of materials that are foundational to modern technology.

The Foundation: Advanced Materials Synthesis & Research
The most widespread use of tube furnaces is in the creation and testing of new materials. Their precise control over the process environment makes them indispensable for research and specialized production.
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
Tube furnaces are the workhorses of materials science labs. They are used for a variety of processes that form or alter materials at a molecular level.
This includes processes like annealing, which modifies a material's microstructure to improve its properties, and pyrolysis, which thermally decomposes organic materials in the absence of oxygen. They are also fundamental for fabricating novel nanostructures and new alloys.
Semiconductor and Electronics Fabrication
The entire electronics industry is built on materials processed with extreme precision. Tube furnaces play a vital role in semiconductor manufacturing.
They are used for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a process where gases react to deposit a thin, high-purity film onto a substrate like a silicon wafer. They are also used for annealing wafers to repair crystal damage and for creating the specialized LED luminescent materials found in modern displays and lighting.
Advanced Ceramics and Glass
Creating high-performance ceramics and specialized glass requires carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Tube furnaces are used for sintering, where powdered materials like ceramics or metals are heated below their melting point until their particles bond together, forming a solid, dense object. This method is used to create everything from dental implants to industrial abrasive tools.
Powering the Future: Energy and Battery Development
As the world transitions to new energy sources, the materials enabling that shift are often born inside a tube furnace.
Lithium-Ion Battery Materials
The performance of a lithium-ion battery is dictated by the chemical purity and physical structure of its anode and cathode materials.
Tube furnaces are essential for the calcination and synthesis of these positive and negative battery materials. The process involves heating precursor powders in a controlled atmosphere to create the precise crystalline structure required for efficient energy storage and release.
New Energy and Environmental Applications
Beyond batteries, tube furnaces are used across the new energy landscape. Researchers use them to test the thermal stability of new solar cell materials or to develop catalysts for more efficient fuel cells.
In environmental science, they are used for research into processes like the incineration or pyrolysis of solid waste, helping to develop more effective waste-to-energy technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly versatile, the design of a tube furnace comes with inherent operational trade-offs that are critical to understand.
The Batch Processing Model
The majority of tube furnaces operate on a batch processing model. A sample or a set of samples is loaded, processed, and then unloaded before the next batch can begin.
This is ideal for laboratory research, process development, and the production of high-value, low-volume components. However, it can become a bottleneck for high-volume, continuous manufacturing where other furnace types, like conveyor or rotary kilns, might be more efficient.
Atmosphere and Uniformity Challenges
Achieving perfect temperature and atmospheric uniformity across the entire length of the process tube can be a significant engineering challenge, especially in longer furnaces.
While modern controllers and multi-zone heating elements mitigate this, any slight variation can impact the consistency of sensitive materials. For processes like semiconductor fabrication, ensuring this uniformity is a primary operational concern.
How This Applies to Your Objective
Choosing the right thermal processing tool depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is research and development (R&D): A tube furnace is an essential and versatile tool for exploring new materials and processes due to its unparalleled control.
- If your primary focus is specialized, low-to-medium volume production: Tube furnaces are ideal for manufacturing high-value components such as semiconductor wafers, advanced ceramics, or battery precursors where precision outweighs throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, bulk material processing: You should evaluate if a batch-based tube furnace is efficient enough or if a continuous furnace system would better suit your need for scale.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is an enabling technology, providing the precise environment required to turn raw elements into the advanced materials that define innovation.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Key Processes | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science & Nanotechnology | Annealing, Pyrolysis, Nanostructure Fabrication | Precise temperature control, uniform heating for material synthesis |
| Semiconductor & Electronics | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Wafer Annealing, LED Material Creation | High-purity film deposition, crystal damage repair |
| Advanced Ceramics & Glass | Sintering for dental implants, abrasive tools | Dense object formation, controlled heating cycles |
| Energy & Battery Development | Calcination for battery materials, Solar cell testing, Fuel cell catalyst development | Efficient energy storage, thermal stability testing |
| Environmental Applications | Waste incineration, Pyrolysis for waste-to-energy | Development of sustainable technologies |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision thermal processing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like semiconductor, battery, and materials research. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your innovation forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















