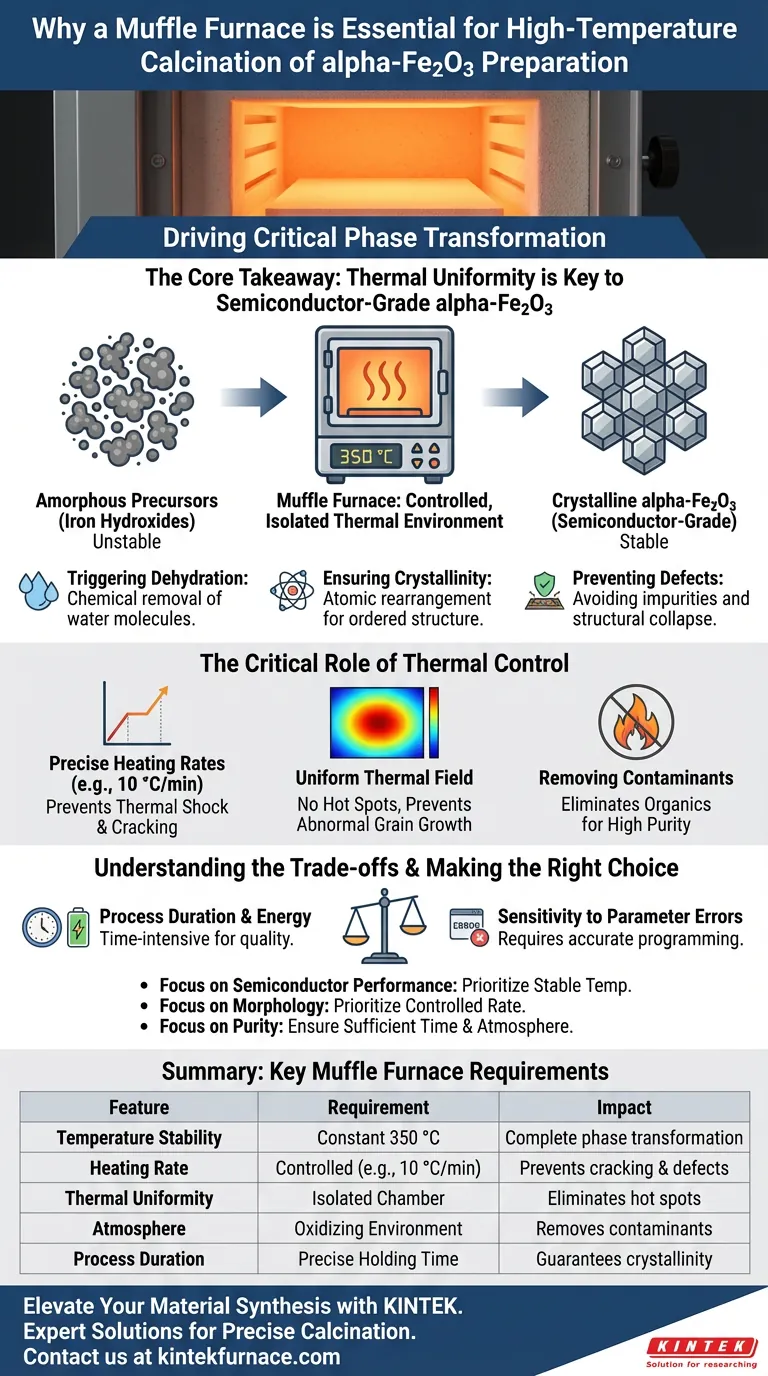
A muffle furnace is strictly required to drive the critical phase transformation from amorphous precursors to crystalline alpha-Fe2O3. It provides a stable, isolated thermal environment—typically maintaining a constant 350 °C with a controlled heating rate—that triggers the dehydration of iron hydroxide precursors to create a pure, semiconductor-grade metal oxide.
The Core Takeaway Achieving high-performance alpha-Fe2O3 is not merely about heating the material; it is about thermal uniformity. A muffle furnace ensures a precise temperature field that converts unstable precursors into a stable crystalline phase, preventing the structural defects and impurities that commonly result from uneven heating methods.
The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
Converting Amorphous Precursors
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this context is to alter the state of the material. Hydrothermal products often exist as amorphous iron hydroxides or unstable precursors.
Triggering Dehydration
By maintaining a specific high temperature (e.g., 350 °C), the furnace facilitates the chemical removal of water molecules from the structure. This dehydration process is the chemical bridge that transforms the precursor into the final alpha-Fe2O3 oxide.
Ensuring Crystallinity
For the material to function as a semiconductor, it must be highly crystalline. The stable heat of the muffle furnace drives the atomic rearrangement necessary to achieve a complete phase transformation, resulting in the ordered crystal structure required for electronic applications.
The Critical Role of Thermal Control
Precise Heating Rates
Temperature is not just about the final number; it is about how you get there. A muffle furnace allows for a programmable ramp rate, such as 10 °C per minute.
Preventing Structural Damage
Controlling the heating rate is essential to manage nucleation and growth kinetics. A controlled ramp prevents thermal shock, which can lead to film cracking, morphological non-uniformity, or the structural collapse of nanosheets.
Uniform Thermal Field
Unlike open-flame or direct heating methods, a muffle furnace envelopes the sample in a uniform heat source. This prevents "hot spots" that cause abnormal grain growth. Uniform heat ensures that active components interact strongly and evenly with the support structure.
Removing Contaminants
Elimination of Organics
The preparation of alpha-Fe2O3 often involves organic surfactants or solvents during the precursor stage. High-temperature calcination provides a continuous oxidizing environment that burns off these residual organics.
Achieving High Purity
Complete removal of these residues is critical. If organic solvents or surfactants remain, they act as impurities that degrade the final material's electrical performance and stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Duration and Energy
While a muffle furnace guarantees quality, it is a time-intensive process. Calcination often requires holding times ranging from several hours (e.g., 5.5 hours) to a full day (24 hours) to ensure complete reaction. This makes the process energy-intensive compared to rapid thermal processing techniques.
Sensitivity to Parameter Errors
The precision of a muffle furnace is a double-edged sword. If the heating program is set incorrectly—for example, a ramp rate that is too aggressive—the material can suffer irreversible defects. The quality of the output is entirely dependent on the accuracy of the thermal program.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your alpha-Fe2O3 preparation, align your furnace settings with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is Semiconductor Performance: Prioritize a stable holding temperature (e.g., 350 °C) to ensure high crystallinity and complete phase purity.
- If your primary focus is Morphological Integrity: Prioritize a slow, controlled heating rate (e.g., 10 °C/min) to prevent cracking and ensure uniform nanosheet growth.
- If your primary focus is Purity: Ensure sufficient holding time and an oxygen-rich atmosphere to fully oxidize and remove any residual organic surfactants.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is not just a heating tool; it is a precision instrument that dictates the structural destiny of your final material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for alpha-Fe2O3 | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Stability | Constant 350 °C | Ensures complete phase transformation from precursors |
| Heating Rate | Controlled (e.g., 10 °C/min) | Prevents film cracking and morphological defects |
| Thermal Uniformity | Isolated Chamber | Eliminates hot spots and abnormal grain growth |
| Atmosphere | Oxidizing environment | Removes organic contaminants and surfactants |
| Process Duration | Precise holding time | Guarantees high crystallinity and electrical stability |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Achieving high-performance alpha-Fe2O3 requires more than just heat; it demands the absolute thermal precision found in KINTEK’s advanced laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your exact calcination parameters.
Whether you need custom programmable ramp rates or superior temperature uniformity for semiconductor-grade oxides, our furnaces are built to deliver repeatable excellence. Don't let thermal instability compromise your research—Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace for your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Renjie Wang, Sankui Xu. Polypyrrole/α-Fe2O3 Hybrids for Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing Performance towards Uric Acid. DOI: 10.3390/coatings14020227
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications of a typical muffle furnace? Key Details for Precise High-Temp Control
- What temperature range do Box Furnaces operate at? From 1100°F to 3300°F for Precision Heat Treatment
- What conditions does a muffle furnace provide for ceramic bricks? Precision Heat for Hedenbergite Synthesis
- How do sample characteristics affect muffle furnace selection? Ensure Accurate and Safe High-Temperature Processing
- How does a muffle furnace differ from a pusher furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- Why is temperature stability important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results and Process Control
- What materials can crucible furnaces melt? A Guide to Metals, Glass & Advanced Materials
- What are the energy efficiency considerations for muffle furnaces? Cut Costs with Smart Design



















