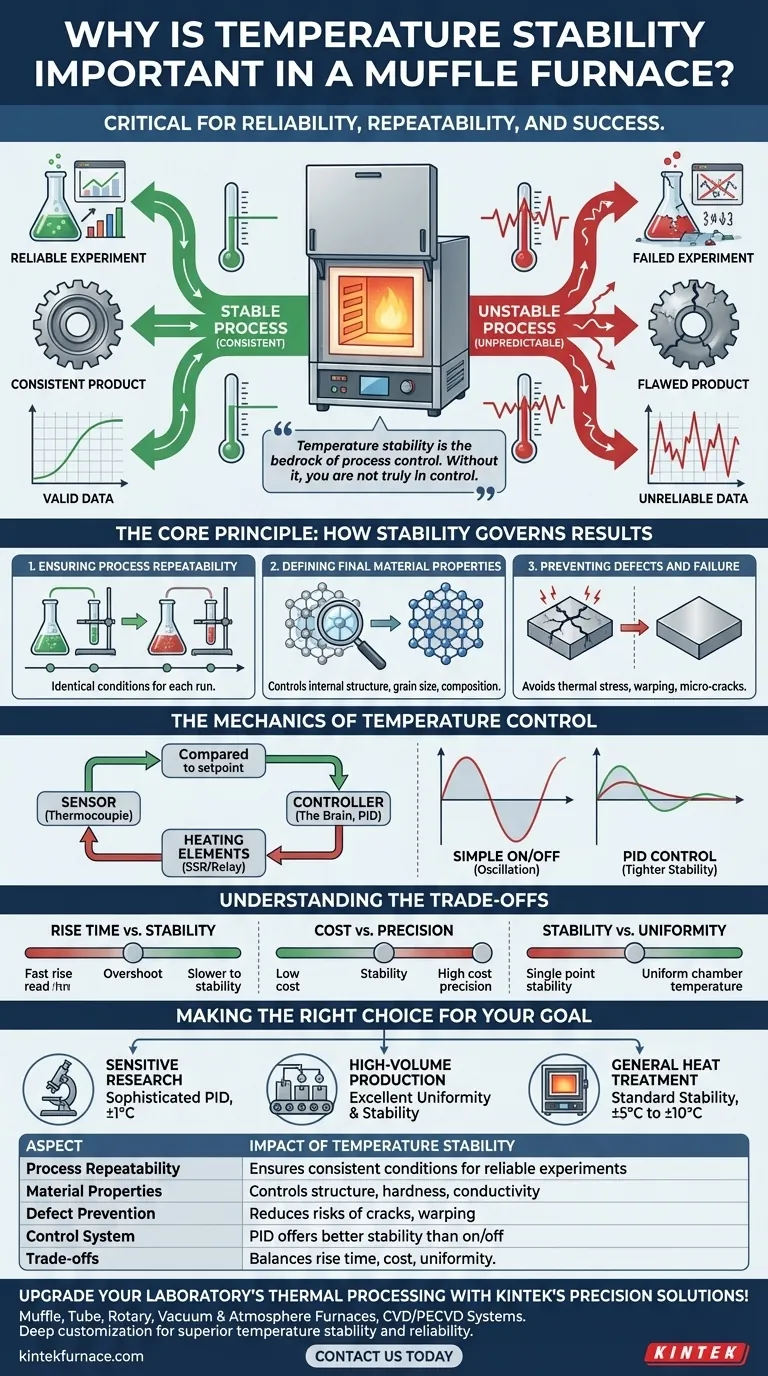
In short, temperature stability is critical because it ensures the reliability, repeatability, and success of any process conducted in a muffle furnace. For materials that are sensitive to thermal variations, even minor fluctuations can drastically alter the final outcome, leading to failed experiments, inconsistent product quality, and unreliable data.
Temperature stability is the bedrock of process control. It dictates whether you achieve the intended material properties consistently or produce unpredictable and flawed results. Without it, you are not truly in control of your thermal process.
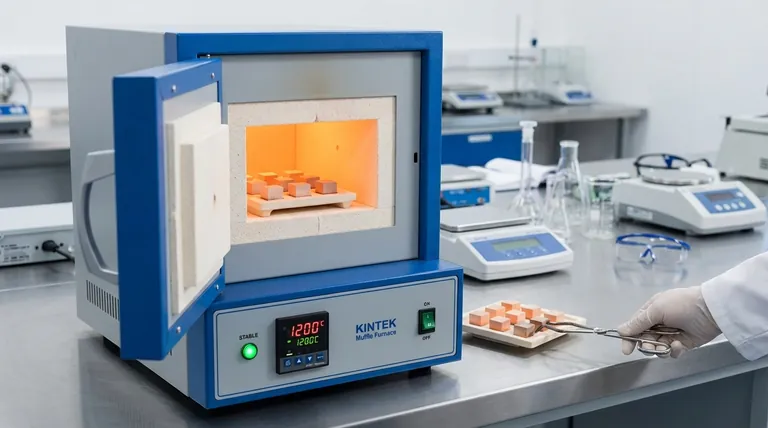

The Core Principle: How Stability Governs Results
Temperature stability refers to the furnace's ability to maintain a set temperature over a specific period with minimal fluctuation. This is distinct from temperature uniformity (consistency across the chamber) and accuracy (how close the average temperature is to the setpoint), but all are vital for process control.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
Scientific research and industrial production rely on repeatability. If a furnace's temperature fluctuates unpredictably between runs, you cannot guarantee that you are subjecting each sample to the identical conditions.
This lack of control makes it impossible to isolate variables or produce consistent products, undermining the validity of research and the quality of manufactured goods.
Defining Final Material Properties
Many thermal processes, such as annealing, sintering, and tempering, are designed to manipulate a material's internal structure. Precise temperature control is what guides this transformation.
Even small deviations can lead to unintended changes in crystal structure, grain size, or chemical composition. This directly impacts the material's final properties, including its hardness, ductility, and conductivity.
Preventing Defects and Failure
Temperature instability can introduce thermal stress in a material, especially during heating and cooling phases. Fluctuations can cause uneven expansion or contraction, leading to micro-cracks, warping, or complete structural failure.
In processes like curing or drying, unstable temperatures can result in incomplete chemical reactions, leaving you with a subpar or unusable final product.
The Mechanics of Temperature Control
Achieving stability is an active process managed by the furnace's control system. Understanding this system clarifies why instability can occur.
The Control Loop Explained
A muffle furnace maintains temperature through a constant feedback loop:
- Sensor (Thermocouple): A thermocouple measures the current temperature inside the chamber and sends a signal to the controller.
- Controller: This is the brain of the system. It compares the actual temperature from the thermocouple to the desired setpoint.
- Heating Elements: Based on the controller's logic, an electromagnetic relay or a more advanced solid-state relay (SSR) switches the heating elements on or off to adjust the temperature.
Simple on/off control creates a natural temperature oscillation around the setpoint. More sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers can predict and dampen these oscillations, providing much tighter stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Perfect temperature control involves balancing competing factors. Recognizing these trade-offs is key to selecting and operating a furnace effectively.
Rise Time vs. Stability
Rise time is the speed at which the furnace reaches its target temperature. A very fast rise time often leads to temperature overshoot, where the furnace exceeds the setpoint before settling down.
Achieving high stability often requires a more controlled, slower heating rate to prevent this initial volatility.
Cost vs. Precision
A simple on/off controller is inexpensive but provides lower stability. A furnace equipped with a sophisticated PID controller and high-quality thermocouples will maintain temperature with far greater precision but comes at a higher cost.
The level of precision you require is directly tied to the cost of the equipment.
Stability vs. Uniformity
A furnace can have excellent stability (consistent temperature at one point over time) but poor uniformity (different temperatures in different parts of the chamber).
For processing large parts or multiple samples at once, temperature uniformity is just as critical as stability to ensure every item receives the same thermal treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating a muffle furnace, consider how its temperature stability aligns with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is sensitive research or material science: Prioritize a furnace with a sophisticated PID controller and documented stability specifications (e.g., ±1°C) to ensure your data is valid and repeatable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Demand excellent temperature uniformity across the chamber in addition to stability to guarantee consistent quality for every part in a batch.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or ashing: A furnace with standard stability (e.g., ±5°C to ±10°C) and a reliable on/off or basic PID controller is often sufficient and more cost-effective.
Ultimately, understanding the role of temperature stability empowers you to select the right tool and master your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Temperature Stability |
|---|---|
| Process Repeatability | Ensures consistent conditions for reliable experiments and production |
| Material Properties | Controls crystal structure, hardness, and conductivity outcomes |
| Defect Prevention | Reduces risks of cracks, warping, and incomplete reactions |
| Control System | PID controllers offer better stability than on/off systems |
| Trade-offs | Balances rise time, cost, and uniformity for optimal performance |
Upgrade your laboratory's thermal processing with KINTEK's precision solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for superior temperature stability and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process control and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















