At its core, a typical muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven defined by a thermally insulated chamber that separates the material being heated from the direct radiation of the heating elements. Key specifications generally include a temperature range from ambient up to 900-1400°C (with models reaching 1800°C), precise digital PID controllers for temperature regulation, heating elements made of durable alloys like Kanthal, and inner chambers constructed from high-purity ceramic to ensure uniform heating and prevent contamination.
A muffle furnace is not just about reaching high temperatures; it's about achieving clean, uniform, and precisely controlled heat. Its specifications are designed to create a stable thermal environment, isolating a sample from combustion byproducts and direct element radiation, which is critical for repeatable results in scientific and industrial applications.

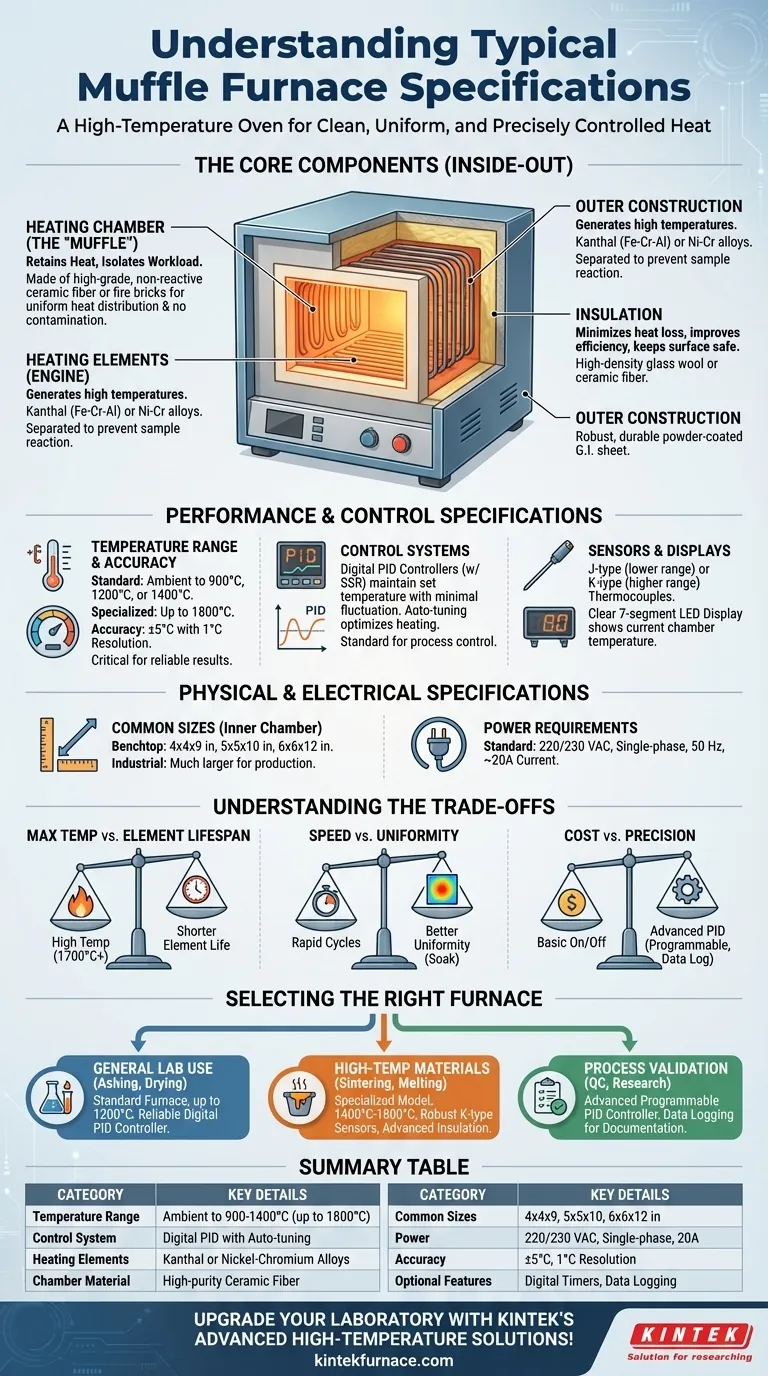
The Core Components: An Inside-Out Look
To understand a muffle furnace's specifications, it is best to examine its construction from the internal chamber outward. Each component serves a distinct purpose related to heat generation, retention, and control.
The Heating Chamber (The "Muffle")
The heart of the furnace is the "muffle"—the inner chamber that holds the sample. It is designed to retain heat and isolate the workload.
Its walls are typically made of high-grade, non-reactive ceramic fiber or fire bricks. This material ensures that the sample is not contaminated by the heating elements and that heat is distributed evenly through convection and radiation.
Heating Elements: The Engine of the Furnace
The heating elements generate the furnace's high temperatures. They are almost always separated from the main chamber to prevent chemical reactions with the sample.
Common materials include Kanthal (iron-chromium-aluminium) alloys or nickel-chromium. Kanthal A1 wire is frequently used for its durability and ability to produce uniform temperature distribution in models operating up to 1400°C.
Construction and Insulation: Containing the Heat
The outer body is typically built from a robust material like powder-coated G.I. (galvanized iron) sheet for durability.
Between the inner chamber and the outer body lies critical insulation, such as a high-density imported glass wool blanket or ceramic fiber filling. This minimizes heat loss, improves energy efficiency, and keeps the external surface safe to the touch.
Performance and Control Specifications
These specifications define how the furnace operates, how accurately it performs, and how the user interacts with it. They are the most critical factors for ensuring reliable experimental or process outcomes.
Temperature Range and Accuracy
Standard benchtop muffle furnaces often operate from ambient temperature up to 900°C, 1200°C, or 1400°C. Specialized, high-temperature models can reach 1700°C or 1800°C.
A typical accuracy specification is ±5°C, with a resolution or least count of 1°C. This level of precision is essential for most laboratory applications.
Control Systems: Precision and Automation
Modern furnaces rely on digital PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers. These sophisticated systems continuously adjust the power to the heating elements (often via a Solid State Relay, or SSR) to maintain the set temperature with minimal fluctuation.
Many controllers feature auto-tuning, which allows the furnace to "learn" the thermal properties of the workload to optimize heating and prevent temperature overshoot. While manual controls exist on older models, PID systems are now the standard for process control.
Sensors and Displays: Monitoring the Process
Temperature is measured using a thermocouple. J-type thermocouples are common for lower ranges (up to ~750°C), while K-type thermocouples are used for higher temperatures (up to ~1250°C).
The temperature is typically shown on a simple and clear 7-segment LED display, providing an at-a-glance reading of the current chamber temperature.
Physical and Electrical Specifications
These practical details are crucial for installation and fitting the furnace into a specific workspace.
Common Sizes
Muffle furnaces are available in a wide range of sizes. Common inner chamber dimensions for benchtop laboratory models include:
- 4 x 4 x 9 inches
- 5 x 5 x 10 inches
- 6 x 6 x 12 inches
Much larger industrial models are also available for production-scale processes.
Power Requirements
A standard benchtop muffle furnace typically requires a dedicated circuit providing 220/230 VAC, single-phase, 50 Hz power, with a current rating of approximately 20A.
Optional Features
Many furnaces can be equipped with optional features to suit specific needs. A common option is a digital timer, which can be programmed to run for extended periods (e.g., up to 999 hours) and automatically shut off the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a muffle furnace involves balancing performance, longevity, and cost. Understanding the inherent trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Maximum Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
Operating a furnace consistently at its maximum rated temperature will significantly shorten the lifespan of the heating elements. Furnaces designed for extremely high temperatures (1700°C+) use more exotic and expensive elements and insulation, increasing the initial cost.
Speed vs. Uniformity
Some models are designed for rapid heating and cooling cycles. While efficient, this can sometimes come at the cost of perfect temperature uniformity across the entire chamber compared to a furnace that heats more slowly and allows the temperature to "soak" and stabilize.
Cost vs. Precision
A basic furnace with a simple on/off controller is inexpensive but offers poor temperature stability. An advanced, programmable PID controller with data logging capabilities adds significant cost but provides the precision and repeatability required for certification, research, and quality control.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
The ideal specifications depend entirely on your intended use. Match the furnace's capabilities to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general lab use (e.g., ashing, heat treating, drying): A standard furnace with a range up to 1200°C and a reliable digital PID controller is the most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials science (e.g., sintering ceramics, melting glass): You must invest in a specialized model rated for 1400°C to 1800°C, which will have robust K-type (or other high-temp) sensors and advanced insulation.
- If your primary focus is process validation and repeatability (e.g., quality control, sensitive research): Prioritize a furnace with an advanced, programmable PID controller and consider models with data logging to document your thermal cycles.
Ultimately, understanding these specifications empowers you to select a tool that is not just a hot box, but a precise instrument for your specific task.
Summary Table:
| Specification Category | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Ambient to 900-1400°C (up to 1800°C for high-temp models) |
| Control System | Digital PID controllers with auto-tuning for precision |
| Heating Elements | Kanthal or nickel-chromium alloys for durability |
| Chamber Material | High-purity ceramic fiber or fire bricks for uniform heating |
| Common Sizes | Benchtop models: 4x4x9 in, 5x5x10 in, 6x6x12 in |
| Power Requirements | 220/230 VAC, single-phase, 20A typical |
| Accuracy | ±5°C with 1°C resolution |
| Optional Features | Digital timers, data logging for extended automation |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can meet your specific requirements and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















