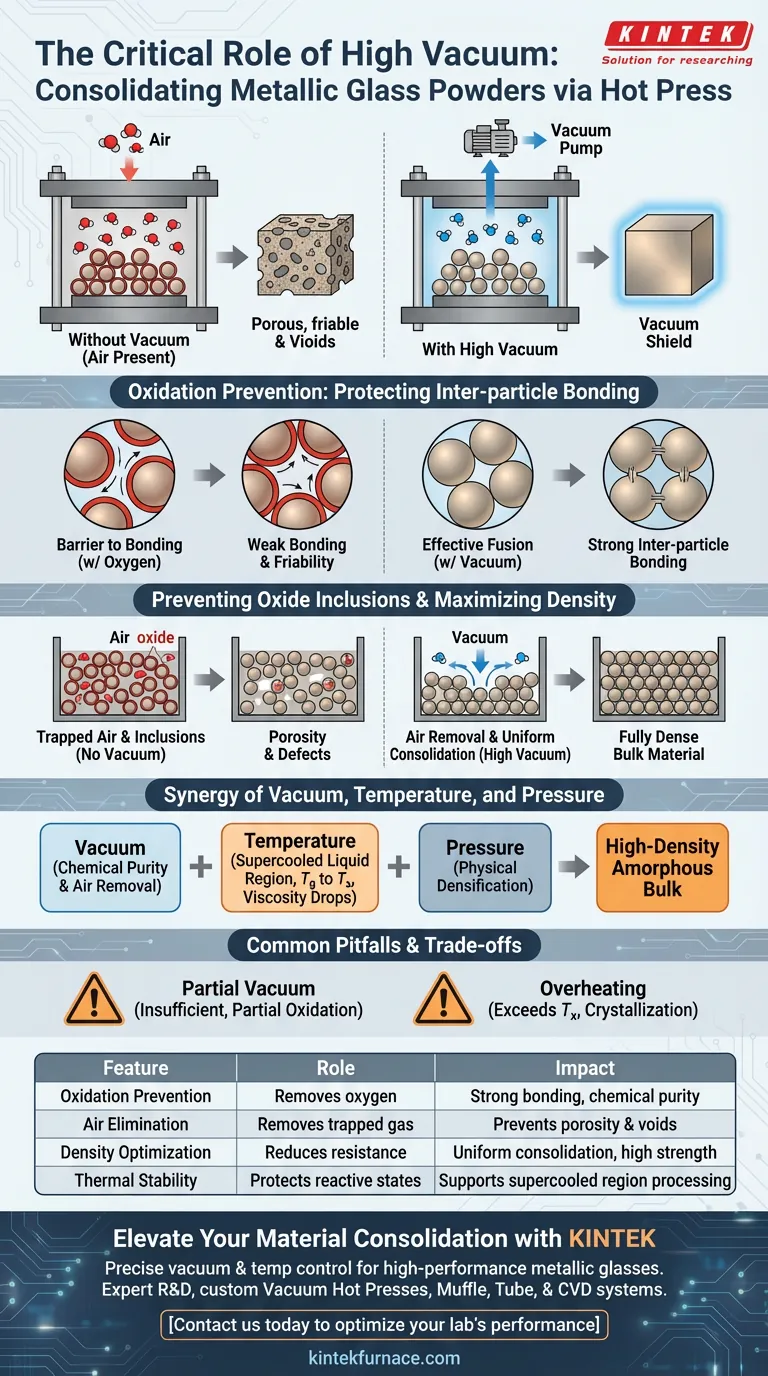
A high-vacuum environment is strictly required within a hot press to eliminate residual air between powder particles and to prevent the oxidation of the metallic glass powder. At elevated temperatures, even trace amounts of oxygen can react with the powder surfaces, compromising the material's integrity and preventing the formation of a solid, cohesive bulk material.
The vacuum acts as a critical shield, preserving the chemical purity of the powder while removing physical barriers to consolidation. By stripping away air and preventing oxide formation, the vacuum ensures the final product retains the high density and mechanical strength characteristic of metallic glass.
The Critical Role of Oxidation Prevention
Protecting Inter-particle Bonding
For metallic glass powders to consolidate into a single solid mass, the particles must bond chemically at their surfaces. Oxidation acts as a barrier to this process.
If oxygen is present during heating, a thin oxide layer forms on the surface of each powder particle. This layer prevents the particles from fusing together effectively, leading to weak inter-particle bonding and a friable final product.
Preventing Oxide Inclusions
Beyond surface issues, oxidation introduces impurities known as oxide inclusions into the bulk material.
These inclusions act as defects within the material's microstructure. They degrade the mechanical performance, often making the material brittle and reducing its thermal stability.
Maximizing Density and Structural Integrity
Eliminating Residual Air
Metallic glass powders are often packed loosely before pressing, leaving significant gaps filled with air.
A high-vacuum environment physically removes this trapped air before the consolidation process begins. If this air were not removed, it would be trapped inside the material during pressing, creating voids and porosity that significantly lower the density of the final component.
Ensuring Uniform Consolidation
By removing air resistance and surface oxides, the vacuum allows the powder particles to rearrange and deform more easily under pressure.
This facilitates a smoother consolidation process, resulting in a fully dense bulk material that accurately reflects the properties of the original amorphous alloy.
The Synergy of Vacuum, Temperature, and Pressure
Supporting the Supercooled Liquid Region
Consolidation typically occurs in the supercooled liquid region—the temperature range between the glass transition ($T_g$) and crystallization ($T_x$) temperatures.
In this range, the material viscosity drops, allowing for excellent flow. The vacuum ensures that while the material is in this highly reactive, semi-fluid state, it remains chemically stable and does not degrade due to environmental exposure.
Enhancing Pressure Efficiency
While the vacuum handles chemical purity and air removal, the high-pressure loading system handles the physical mechanics of densification.
The vacuum works in tandem with high pressure to close voids and overcome the resistance of hard powders. This combination allows for high-density bonding at lower temperatures, which is crucial for avoiding unwanted crystallization.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
The Risk of Partial Vacuum
A "rough" vacuum is often insufficient for metallic glass consolidation.
If the vacuum level is not high enough, trace oxygen will still cause partial oxidation. This may result in a material that looks solid but possesses internal weak points and reduced fatigue life.
Vacuum Cannot Fix Overheating
While vacuum prevents oxidation, it does not prevent crystallization caused by excessive heat.
Even in a perfect vacuum, if the temperature exceeds the crystallization point ($T_x$), the amorphous structure will be lost. The vacuum must be paired with precise temperature control to maintain the unique properties of the metallic glass.
Ensuring Process Success
Recommendations for Optimization
To achieve the best results when hot pressing metallic glass powders, consider your specific goals:
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Ensure the deepest possible vacuum to eliminate all oxide inclusions that could act as stress concentrators.
- If your primary focus is maximum density: Combine the high vacuum with a high-pressure loading system to mechanically force voids closed.
- If your primary focus is maintaining the amorphous state: Monitor temperature rigorously to stay within the supercooled region, as vacuum alone cannot prevent thermal crystallization.
Success in hot pressing metallic glass relies on the absolute elimination of air to preserve the material's purity and potential.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Vacuum Hot Pressing | Impact on Metallic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Removes oxygen molecules | Ensures strong inter-particle bonding and chemical purity. |
| Air Elimination | Vacuums out trapped gas | Prevents porosity and internal voids in the final bulk material. |
| Density Optimization | Reduces surface resistance | Facilitates uniform consolidation for high-strength components. |
| Thermal Stability | Protects reactive states | Safely supports processing within the supercooled liquid region. |
Elevate Your Material Consolidation with KINTEK
Precise control over vacuum and temperature is non-negotiable for high-performance metallic glasses. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Vacuum Hot Presses, Muffle, Tube, and CVD systems designed to meet the most rigorous lab requirements.
Whether you need custom high-temp furnaces or advanced sintering solutions, our engineering team is ready to tailor a system to your unique research needs. Contact us today to optimize your lab's performance and ensure the structural integrity of your advanced materials.
Visual Guide
References
- Pee‐Yew Lee, Chung‐Kwei Lin. Synthesis of Nanocrystal-Embedded Bulk Metallic Glass Composites by a Combination of Mechanical Alloying and Vacuum Hot Pressing. DOI: 10.3390/ma18020360
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a Vacuum Hot Pressing (VHP) furnace facilitate the preparation of highly dense Mg3Sb2? Expert Densification
- What role does a vacuum hot press furnace play in the densification of nanocomposites? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace compared to explosive cladding? Get Precision Results
- What are the primary functions of high-strength graphite molds? Optimize GNPs-Cu/Ti6Al4V Hot-Pressing Sintering
- What is the necessity of low-temperature degassing in vacuum hot pressing? Ensure Superior Diamond Tool Quality
- What is hot pressing and what does it involve? Unlock Superior Material Density and Strength
- What is the purpose of applying vibration to the loaded graphite mold? Enhance TiAl-SiC Composite Sintering Performance
- What is the purpose of performing high-temperature degassing in a vacuum furnace before the hot pressing of Al-Cu alloy powders? Ensure Maximum Density and Strength



















