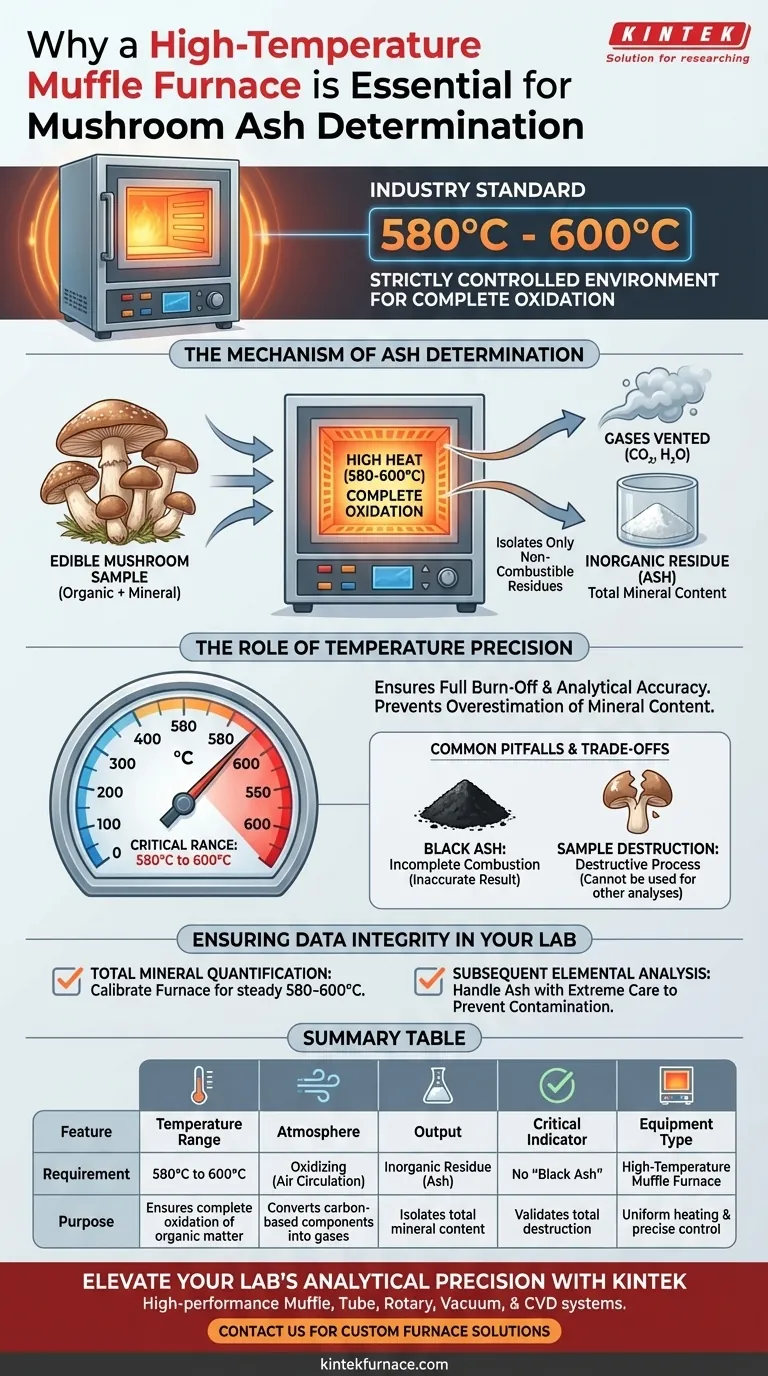
A high-temperature muffle furnace is the industry standard for ash determination because it provides a strictly controlled environment capable of maintaining temperatures between 580°C and 600°C. This specific thermal intensity is required to completely oxidize and decompose all organic matter within the edible mushroom sample, ensuring that only the non-combustible mineral residues remain for analysis.
Accurate ash determination relies on the total destruction of organic material. The muffle furnace isolates the sample's true mineral content by sustaining the extreme heat necessary to incinerate carbon-based components without contaminating the inorganic residue.

The Mechanism of Ash Determination
To understand why this equipment is non-negotiable, one must look at the chemical requirements of isolating minerals from organic tissue.
Complete Oxidation of Organic Matter
Edible mushrooms consist largely of organic compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
To measure the mineral content, these organic components must be physically removed. The muffle furnace achieves this through complete oxidation, converting organic matter into gases (such as carbon dioxide and water vapor) that vent away from the sample.
Isolation of Non-Combustible Residues
Once the organic matter is decomposed, what remains is the inorganic residue, commonly referred to as ash.
This residue represents the total mineral content of the mushroom. By isolating this material, researchers can accurately weigh the minerals and perform subsequent analyses to determine the specific elemental composition.
The Role of Temperature Precision
The muffle furnace is not just about heat; it is about sustained, precise thermal control.
The 580°C to 600°C Requirement
The primary reference specifies a distinct temperature window between 580°C and 600°C for edible mushrooms.
This range is critical. Temperatures below this threshold may fail to fully burn off the organic material, leading to an overestimation of mineral content.
Ensuring Analytical Accuracy
The consistency of the muffle furnace ensures that the oxidation process is uniform throughout the sample.
This reliability allows for the precise calculation of mineral percentages. It serves as the foundational step for determining the nutritional quality and elemental safety of the mushroom samples.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is the definitive tool for this task, operators must be aware of the procedural limitations.
Risk of Incomplete Combustion
If the furnace does not maintain adequate air circulation or fails to reach the target temperature, organic carbon may remain in the crucible.
This results in "black ash," which indicates incomplete oxidation and renders the weight measurement inaccurate.
Sample Destruction
The process is destructive by nature.
Because the organic structure is incinerated, the sample cannot be used for other types of organic analysis (such as vitamin or protein testing) after the ash determination is complete.
Ensuring Data Integrity in Your Lab
To ensure your ash determination yields valid results, align your equipment settings with your specific analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is total mineral quantification: Ensure the furnace is calibrated to hold a steady temperature between 580°C and 600°C to guarantee the total removal of organic mass.
- If your primary focus is subsequent elemental analysis: Handle the resulting ash with extreme care to prevent contamination, as this residue is the purified baseline for identifying specific mineral elements.
Precision in temperature control is the only way to turn a biological sample into reliable chemical data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for Mushroom Ash Determination | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 580°C to 600°C | Ensures complete oxidation of organic matter |
| Atmosphere | Oxidizing (Air circulation) | Converts carbon-based components into ventable gases |
| Output | Inorganic Residue (Ash) | Isolates total mineral content for quantification |
| Critical Indicator | No "Black Ash" (Carbon-free) | Validates total destruction of organic material |
| Equipment Type | High-Temperature Muffle Furnace | Provides uniform heating and precise thermal control |
Elevate Your Lab's Analytical Precision with KINTEK
Don't let incomplete combustion compromise your research data. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of ash determination and material science.
Whether you are analyzing edible mushrooms or advanced ceramics, our customizable laboratory high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal stability and precision you need for reliable results.
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing capabilities? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Arowora Kayode Adebisi, Isaac John Umaru. Comparative Study on the Proximate and Amino Acids Levels in Selected Edible Mushroom Species. DOI: 10.58578/ajbmbr.v2i2.5892
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature muffle furnace utilized to determine the ash content of asphalt samples? Guide to Lab Success
- What are the common transport methods used in Muffle Furnaces? Choose the Right System for Your Lab
- What were the outcomes of using the muffle furnace for environmental sample analysis? Boost Purity and Accuracy in Your Lab
- Why are muffle furnaces not suitable for low-temperature applications? Discover the High-Temperature Design Limits
- How does muffle furnace temperature control affect copper(II) orthoperiodate synthesis? Master Phase Purity
- What precautions should be taken when placing items into the muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in High-Temp Operations
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the calcination modification of clinoptilolite? Optimize Zeolite Performance
- What safety measures should be observed regarding the surroundings of a muffle furnace? Ensure a Secure Lab Setup



















