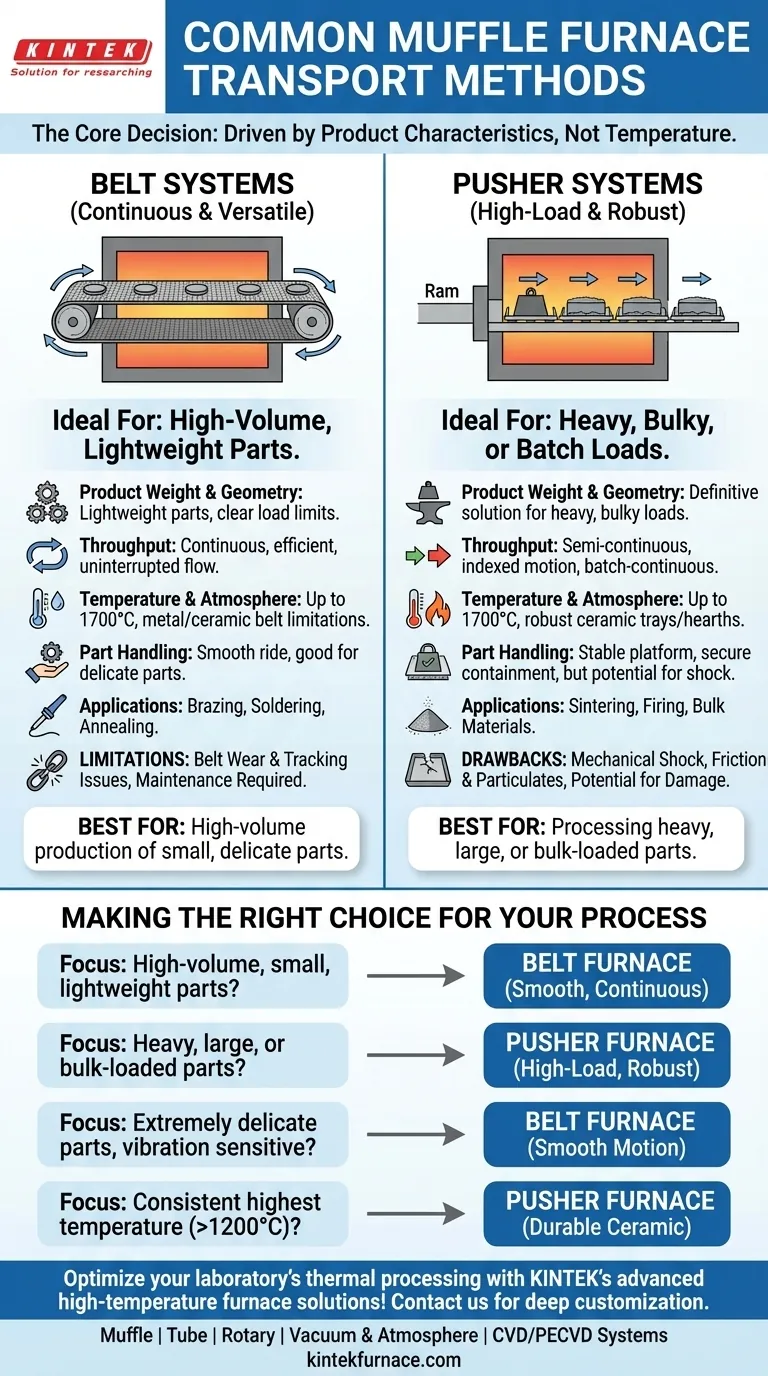
In muffle furnaces, the two most common methods for transporting materials through the heating chamber are belt systems and pusher systems. A belt furnace uses a continuous alloy or ceramic belt to move parts, making it a very common choice for continuous processes under a controlled atmosphere. In contrast, a pusher furnace uses a ram to push trays or "boats" of material through the furnace in a semi-continuous sequence.
The core decision between a belt and a pusher transport system is not about furnace temperature or heating method, but about the physical characteristics of your product. Belts excel at continuous flow for lighter parts, while pushers are engineered to handle heavier, bulkier loads.

Deconstructing the Transport Mechanisms
To select the right furnace, you must first understand the fundamental operational differences between the primary transport methods. Each is designed to solve a different set of material handling challenges.
The Belt Furnace: Continuous and Versatile
A belt furnace uses a mesh belt, typically made of a high-temperature metal alloy or advanced ceramic, that runs in a continuous loop through the furnace chamber.
Parts are placed directly onto the belt at the entrance and are carried through the heating and cooling zones at a precisely controlled speed. This design is ideal for ensuring that every part receives an identical thermal profile.
Because of their continuous, smooth operation, belt furnaces are the standard for many high-volume applications like brazing, soldering, and annealing of smaller components.
The Pusher Furnace: High-Load and Robust
A pusher furnace operates by using a powerful actuator (the "pusher") to advance a train of trays or containers through the furnace. A new tray is loaded at the entrance, pushing the entire line of trays forward by one position.
This semi-continuous, indexed motion makes it exceptionally well-suited for processing parts that are too heavy, large, or awkwardly shaped for a belt. The trays, often made of robust ceramic or high-temperature alloys, provide a stable platform for the load.
Pusher systems are the go-to choice for applications like sintering large powder metal parts, firing heavy ceramic blocks, or processing bulk materials in batches.
Key Factors Influencing Your Choice
The specifications of your product and process will point you directly toward the optimal transport system. Consider these factors before making a decision.
Product Weight and Geometry
This is the most critical factor. Belt systems have a clear load limit per square foot. If your parts are heavy, they will cause excessive stretching, sagging, and premature wear on a belt. Pusher furnaces are the definitive solution for heavy loads.
Required Process Throughput
For true, uninterrupted high-volume production, a belt furnace offers the most efficient, continuous flow. A pusher furnace is better described as semi-continuous or batch-continuous, as its throughput is dictated by the tray size and the cycle time of the pusher mechanism.
Operating Temperature and Atmosphere
Both systems can operate at very high temperatures (often up to 1700°C) and within controlled atmospheres. However, the transport material itself becomes a key variable. Metal alloy belts have temperature limitations, after which more expensive ceramic belts are required. Pusher furnaces often use thick, durable ceramic trays and hearths that are inherently robust at extreme temperatures.
Part Handling and Placement
Delicate parts that could be damaged by the "shove" of a pusher mechanism are better suited for the smooth ride of a belt furnace. Conversely, parts that might roll or shift on a moving belt can be securely contained within the trays of a pusher furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No system is perfect for every application. Acknowledging the inherent limitations of each method is key to avoiding costly mistakes.
Belt System Limitations
The primary weakness of a belt system is the belt itself. It is a maintenance item that can stretch, distort, or suffer from tracking and alignment problems over time. An unexpected belt failure can lead to significant production downtime.
Pusher System Drawbacks
The indexed motion of a pusher can impart mechanical shock to the product load, which is unacceptable for certain delicate assemblies. Furthermore, friction between trays and the furnace hearth can lead to wear and generate particulates, a potential concern in high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be a direct reflection of your manufacturing requirements. Use the following guidelines to steer your choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, lightweight parts: A belt furnace is the industry standard and will provide the most efficient continuous throughput.
- If your primary focus is processing heavy, large, or bulk-loaded parts: A pusher furnace is specifically designed for the high-load capacity and robustness you require.
- If your primary focus is processing extremely delicate parts sensitive to vibration: The smooth, continuous motion of a belt furnace is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is operating consistently at the highest end of the temperature spectrum (>1200°C): A pusher furnace with a robust ceramic hearth and tray system often provides greater long-term durability.
Understanding these fundamental transport differences empowers you to select a furnace that aligns perfectly with your production goals and material requirements.
Summary Table:
| Transport Method | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Belt System | Lightweight parts, high-volume continuous processes | Smooth operation, ideal for brazing, soldering, annealing |
| Pusher System | Heavy or bulky loads, high-temperature applications | Robust handling, semi-continuous, suitable for sintering, firing |
Optimize your laboratory's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?



















