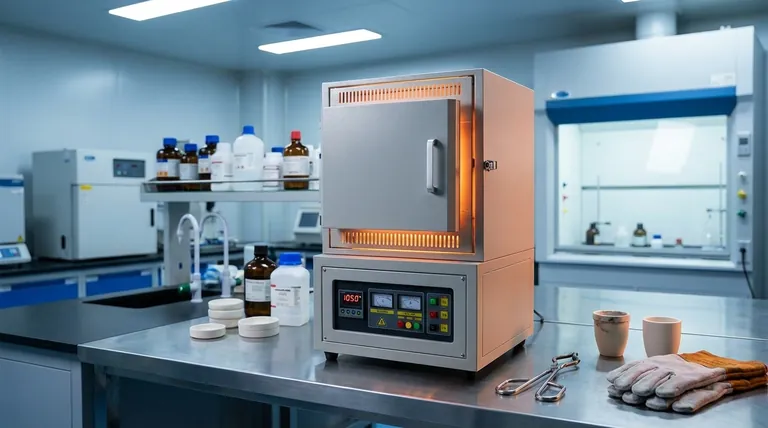
At its core, a muffle furnace is unsuitable for low-temperature applications because its heating elements are fundamentally designed for high-intensity output. Below approximately 300°C to 400°C, these elements fail to emit sufficient or stable radiant heat, making them both ineffective and difficult to control for processes requiring gentle, precise warming.
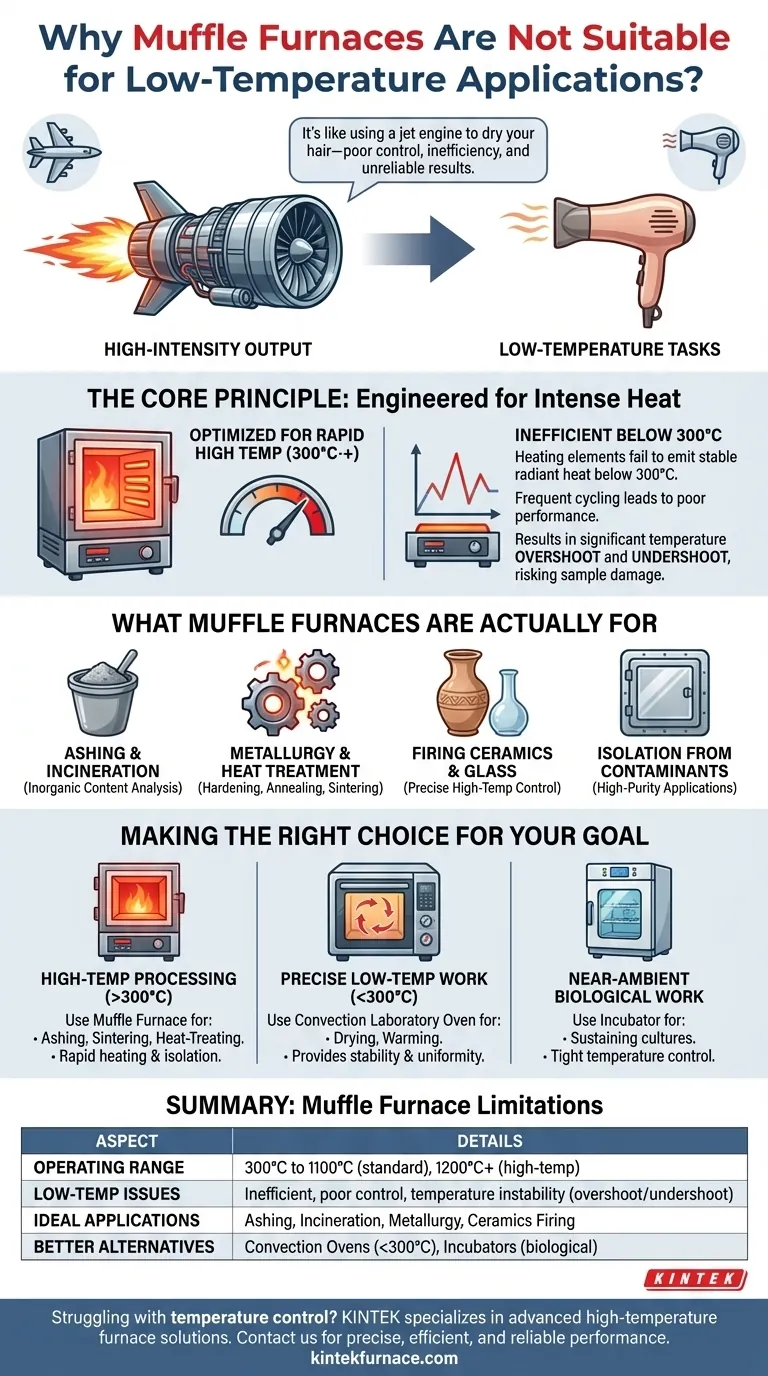
A muffle furnace is a specialized, high-power tool engineered for intense heat. Attempting to use it for low-temperature tasks is like using a jet engine to dry your hair—it's the wrong instrument, leading to poor control, inefficiency, and unreliable results.

The Core Principle: Engineered for Intense Heat
A muffle furnace's design is optimized for reaching and maintaining very high temperatures quickly and uniformly. This specialization is precisely what makes it a poor choice for work below its intended operating range.
Inefficient Heating at Low Temperatures
The heating elements in a muffle furnace are designed to glow red-hot, transferring energy primarily through thermal radiation. At temperatures below 300°C, this radiative output drops significantly.
The furnace's control system must cycle the high-power elements on and off frequently to maintain a low setpoint, leading to poor performance.
Standard Operating Range Defines Its Purpose
Standard muffle furnaces are built to operate reliably from 300°C up to 1100°C. High-temperature models are designed for even higher ranges, starting at 1200°C or more.
Their entire construction, from the heating elements to the insulation, is selected to handle and contain extreme heat, not to delicately manage low temperatures.
Inevitable Temperature Instability
Forcing a muffle furnace to operate near the bottom of its capability results in significant temperature overshoot and undershoot.
The system will inject a large amount of heat to reach the setpoint, likely surpassing it, and then cool down too far before the elements kick back on. This lack of stability can easily ruin sensitive samples.
What Muffle Furnaces Are Actually For
Understanding a muffle furnace's intended applications clarifies why it is not a general-purpose oven. It excels at processes that require intense, isolated heat.
Ashing and Incineration
One of its primary uses is to completely burn away organic or volatile materials to determine the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample. This process, known as ashing, requires consistently high temperatures.
Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
Muffle furnaces are critical for metallurgical processes that alter a material's physical properties. This includes hardening, annealing, sintering, and brazing, all of which occur at hundreds or thousands of degrees Celsius.
Firing Ceramics and Glass
The production of ceramics, glass, and enamel coatings demands precise control at very high temperatures. The furnace's ability to provide uniform heat ensures the material is fired correctly without weak spots.
Isolation from Contaminants
The "muffle" itself is a chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements and any potential combustion byproducts. This is crucial for high-purity applications in materials research and testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument introduces significant risk and inefficiency into your workflow. A muffle furnace is a powerful tool, but it has clear limitations.
The Risk of Damaged Samples
The temperature instability inherent in low-temperature muffle furnace operation can irreversibly damage or alter samples that require precise thermal control.
Significant Energy Inefficiency
Running a high-power device at its lowest, least-efficient threshold wastes a considerable amount of energy compared to using an instrument designed for that specific temperature range.
When to Use a Muffle Furnace (and When Not To)
Use a muffle furnace only for its intended purpose: high-temperature material processing above 300°C. For any application requiring drying, incubating, or gentle warming, it is the wrong tool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument is the first step toward reliable and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>300°C): A muffle furnace is the correct tool, offering rapid heating and isolation for processes like ashing, sintering, or heat-treating.
- If your primary focus is precise low-temperature work (<300°C): A convection laboratory oven is the appropriate choice, providing the necessary stability and fan-forced uniformity that a muffle furnace cannot.
- If your primary focus is near-ambient biological work: An incubator is the specialized tool designed for the tight temperature control required to sustain cultures.
By matching the instrument's design to your application's needs, you ensure the accuracy and success of your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Operating Range | 300°C to 1100°C (standard), 1200°C+ (high-temp models) |
| Low-Temperature Issues | Inefficient heating, poor control, temperature instability (overshoot/undershoot) |
| Ideal Applications | Ashing, incineration, metallurgy (e.g., hardening, annealing), ceramics firing |
| Better Alternatives | Convection ovens for <300°C, incubators for biological work |
Struggling with temperature control in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring precise, efficient, and reliable performance. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What necessary process conditions does a muffle furnace provide for fruit powder ash analysis? Mastering 550°C Oxidation
- What function does a muffle furnace serve in LaMO3 calcination? Master Perovskite Nanoparticle Synthesis
- How are box type resistance furnaces applied in electronic ceramics manufacturing? Essential for Precision Sintering and Polarization
- What is the use of muffle furnace in laboratory? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Heat for Accurate Analysis
- How is a muffle furnace utilized in the glass industry? Essential for Precision Heat Treatment
- What makes box furnaces suitable for demanding applications? Engineered for Precision and Durability in High-Stakes Processes
- How are industrial-grade high-temperature muffle furnaces utilized in experimental archaeology? Unlock Ancient Tech
- Why is thermal treatment of kaolin in a muffle furnace required for preparing AAMs? Unlock High-Performance Binders



















