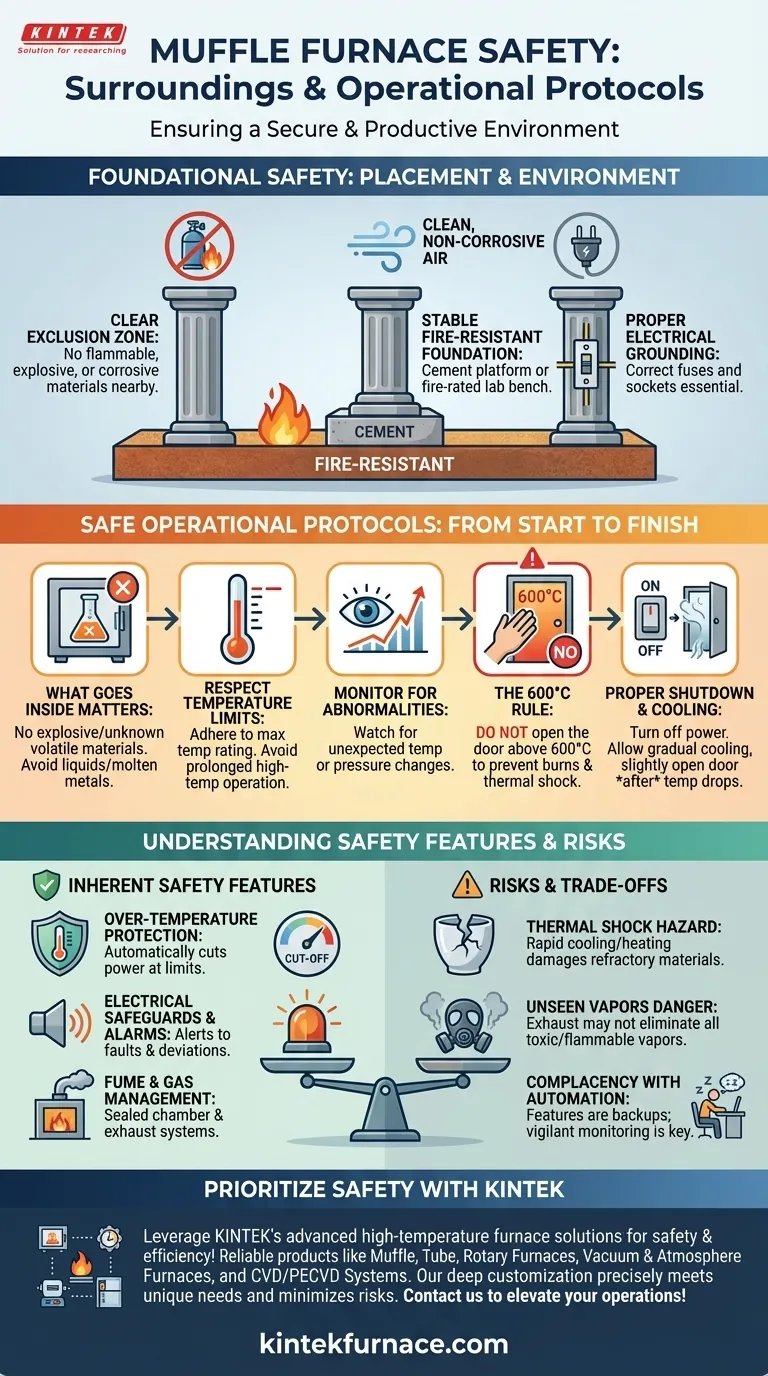
To ensure safety around a muffle furnace, the immediate area must be completely free of flammable, explosive, or corrosive materials. The furnace itself requires placement on a stable, fire-resistant platform, such as cement, and must be connected to a properly grounded electrical circuit with appropriate fuses and sockets. This foundational setup is the first line of defense against fire and electrical hazards.
True muffle furnace safety extends beyond the immediate surroundings. It requires a systemic approach that combines correct environmental setup, strict operational protocols, and a clear understanding of the furnace's inherent risks and protective features.

Foundational Safety: Placement and Environment
Properly situating the furnace is a non-negotiable prerequisite for safe operation. The environment dictates the baseline level of risk before you even turn the unit on.
Establish a Clear Exclusion Zone
The most critical rule is to maintain a clear space around the furnace. No flammable or explosive materials should be stored anywhere near the unit. This includes solvents, paper, cleaning chemicals, and compressed gas cylinders.
Ensure a Stable, Fire-Resistant Foundation
The furnace must be placed on a stable and level platform that can support its weight without risk of tipping. A cement platform or a dedicated, fire-rated lab bench is ideal. This prevents physical accidents and contains potential heat damage.
Verify Proper Electrical Grounding
A muffle furnace is a high-power device that demands a robust electrical connection. Ensure it is plugged into a circuit with the correct plugs, sockets, and fuses rated for its power draw. Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical shock.
Maintain a Clean, Non-Corrosive Atmosphere
The air in the workspace should be free of corrosive substances. Over time, chemical vapors can degrade the furnace's external components and internal electronics, leading to premature failure.
Safe Operational Protocols: From Start to Finish
How you interact with the furnace during operation is just as important as its initial setup. Following a strict protocol minimizes the risk of accidents, burns, and equipment damage.
What Goes Inside Matters
Never place explosive or unknown volatile materials inside the furnace. Furthermore, avoid baking liquids or pouring molten metals directly into the chamber, as this can cause dangerous pressure buildup or damage the refractory lining.
Respect Temperature Limits
Adhere strictly to the maximum temperature rating specified by the manufacturer. Avoid operating the furnace at its highest rated temperature for extended periods, as this can shorten its lifespan.
Monitor for Abnormalities
Always monitor temperature changes during operation. If you notice any sudden, unexpected fluctuations or other abnormalities, cut the power immediately and investigate the cause once the unit has cooled.
The 600°C Rule: Handling the Door
To prevent severe burns and thermal shock to both yourself and the furnace components, do not open the furnace door when the internal temperature is above 600°C.
Proper Shutdown and Cooling
After a cycle is complete, turn off the main power. Once the temperature has dropped to a safe level, you can remove your samples. Slightly open the door to allow the chamber to cool down gradually.
Understanding the Inherent Safety Features
Modern muffle furnaces are equipped with features designed to protect the user, the sample, and the equipment itself. Understanding these allows for safer operation.
Over-Temperature Protection
Most furnaces include an over-temperature protection mechanism. This feature automatically cuts power to the heating elements if the temperature exceeds a set safety limit, preventing catastrophic overheating.
Electrical Safeguards and Alarms
Circuit breakers and safety alarms are standard features. They protect against electrical faults and alert the operator to deviations from the set parameters, allowing for timely intervention.
Fume and Gas Management
Many models feature a sealed muffle chamber to isolate the sample from heating elements and contain generated gases. Some also include an exhaust system or adjustable air inlets to safely vent fumes and aggressive gases out of the work area.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
Automated features do not eliminate risk. Awareness of potential failure points is the mark of a true professional.
The Hazard of Thermal Shock
Opening the door too quickly or at high temperatures creates a rapid temperature change known as thermal shock. This can crack the furnace's delicate refractory materials, leading to costly repairs and compromising future heating performance.
The Danger of Unseen Vapors
Even with an exhaust port, heating certain materials can generate flammable or toxic vapors. A sealed chamber reduces contamination risk but does not eliminate the need for a safe working environment and proper ventilation in the lab itself.
Complacency with Automated Features
Relying solely on safety features like over-temperature protection can lead to complacency. These systems are backups, not substitutes for vigilant monitoring and adherence to proper operational protocols.
Prioritizing Safety for Your Application
Use this guidance to tailor your safety focus to your specific task.
- If your primary focus is setting up a new lab: Prioritize the physical placement, establishing a clear exclusion zone, and verifying the electrical infrastructure before any other step.
- If your primary focus is training new users: Emphasize the operational protocols, especially the rules for what materials can be heated and the strict temperature limit for opening the door.
- If your primary focus is material processing: Pay close attention to the specific properties of the materials you are heating and actively monitor the furnace for any signs of abnormal pressure or temperature changes.
By treating the furnace as a complete system requiring both environmental and operational diligence, you ensure a secure and productive environment.
Summary Table:
| Safety Aspect | Key Measures |
|---|---|
| Placement & Environment | Clear exclusion zone, stable fire-resistant platform, proper electrical grounding, non-corrosive atmosphere |
| Operational Protocols | Avoid explosive materials, respect temperature limits, monitor for abnormalities, handle door above 600°C with caution |
| Safety Features | Over-temperature protection, electrical safeguards, fume and gas management systems |
| Risk Awareness | Thermal shock dangers, unseen vapors, complacency with automated features |
Ensure your laboratory's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and minimizing risks. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and elevate your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















