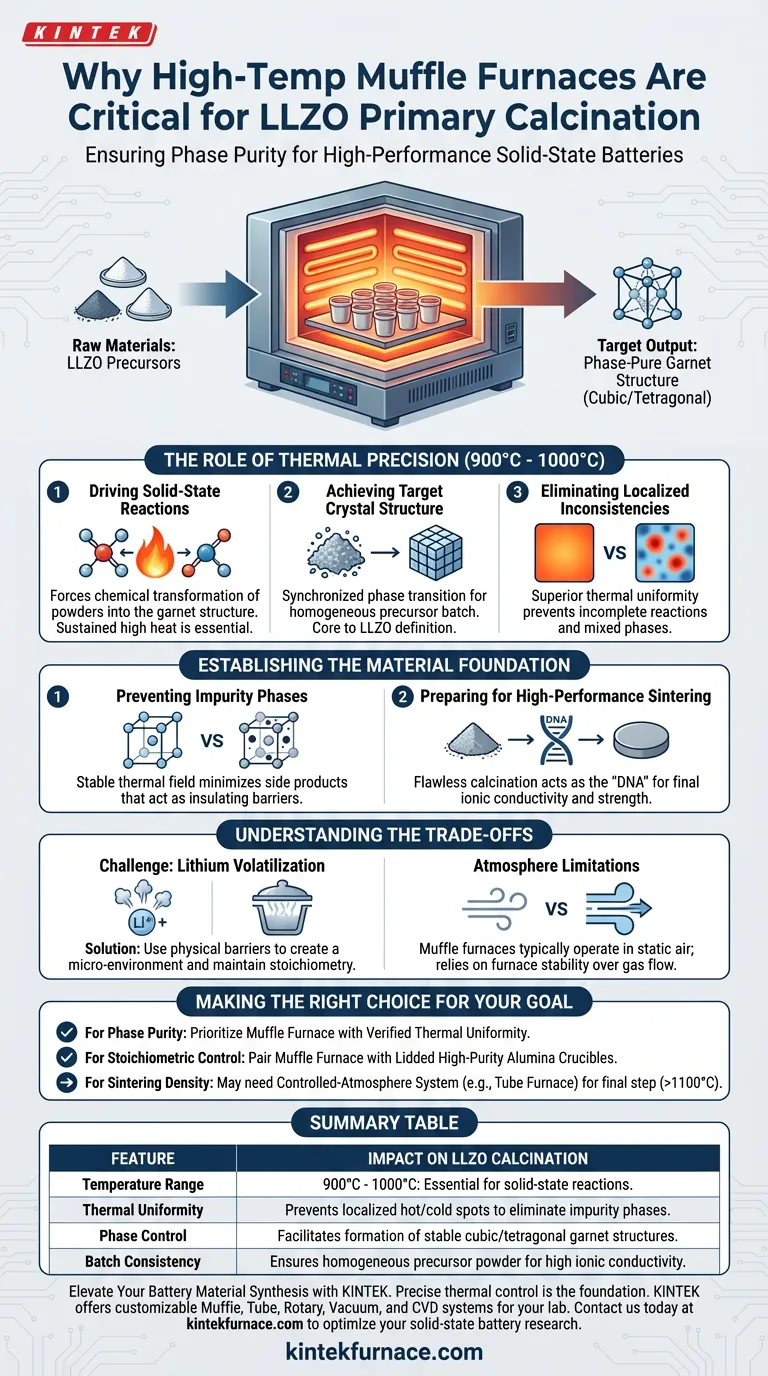
A high-temperature muffle furnace is the critical instrument for ensuring phase purity during the primary calcination of Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO). It provides the precisely controlled thermal environment necessary to drive solid-state reactions between 900°C and 1000°C, transforming raw materials into the correct initial crystal structure.
The Core Insight Success in LLZO synthesis is determined before the final sintering step; it begins with the quality of the precursor powder. A muffle furnace provides the exceptional thermal uniformity required to prevent incomplete reactions, ensuring the material forms a stable garnet structure without the impurities that degrade ionic conductivity.
The Role of Thermal Precision
Driving Solid-State Reactions
Primary calcination is not merely about drying; it is a chemical transformation. The muffle furnace maintains a stable temperature range, typically between 900°C and 1000°C.
This specific thermal energy is required to force the raw material powders to react chemically. Without this sustained high heat, the solid-state reaction mechanism cannot initiate or complete effectively.
Achieving the Target Crystal Structure
The goal of this process is to create the initial cubic or tetragonal garnet structures. This structural arrangement is the fundamental definition of LLZO material.
The muffle furnace ensures that the entire batch of powder reaches the transition temperature simultaneously. This synchronization is vital for creating a homogeneous batch of precursor powder.
Eliminating Localized Inconsistencies
High-quality muffle furnaces offer superior thermal uniformity across the chamber.
If temperature gradients exist (hot spots or cold spots), parts of the powder may fail to undergo the phase transition. This leads to a mixture of reacted and unreacted material, which severely hampers the performance of the final electrolyte.
Establishing the Material Foundation
Preventing Impurity Phases
Inconsistent heating is the primary cause of side products. If the temperature fluctuates or differs across the sample, unwanted compounds (impurities) will form alongside the desired LLZO.
The stable thermal field of the muffle furnace minimizes these deviations. By keeping the temperature constant, it suppresses the formation of secondary phases that would otherwise act as insulating barriers in the final ceramic.
Preparing for High-Performance Sintering
The powder produced in this stage acts as the "DNA" for the final sintered pellet.
If the calcination in the muffle furnace is flawed, the subsequent sintering step cannot correct it. A high-temperature muffle furnace ensures the precursor powder has the correct phase purity to eventually achieve high ionic conductivity and mechanical strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Challenge of Lithium Volatilization
While the muffle furnace provides excellent heat, it creates an environment where lithium can easily vaporize at high temperatures. This can lead to lithium deficiency in the final product.
To counteract this, the muffle furnace must often be used in conjunction with lidded alumina crucibles or "mother powder" bedding. These physical barriers create a micro-environment inside the furnace to trap lithium vapor and maintain the correct stoichiometry.
Atmosphere Limitations
Standard muffle furnaces typically operate in static air. They do not inherently offer the advanced atmosphere control (such as vacuum or pure argon flow) found in tube furnaces.
While static air is generally sufficient for primary calcination, it requires careful management of humidity and contaminants. The operator must rely on the furnace's stability rather than gas flow to control the reaction environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your LLZO synthesis yields high-conductivity electrolytes, consider the following regarding your equipment and process:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Prioritize a muffle furnace with verified thermal uniformity to prevent the formation of insulating side products during calcination.
- If your primary focus is Stoichiometric Control: Always pair your muffle furnace with lidded high-purity alumina crucibles to minimize lithium loss during the heating cycle.
- If your primary focus is Sintering Density: Recognize that while the muffle furnace handles calcination, you may need a controlled-atmosphere system (like a tube furnace) for the final high-temperature sintering step (above 1100°C).
The muffle furnace is not just a heat source; it is the tool that standardizes the chemical structure of your material, determining the ultimate potential of your solid-state battery.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on LLZO Calcination |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 900°C - 1000°C: Essential for solid-state reactions. |
| Thermal Uniformity | Prevents localized hot/cold spots to eliminate impurity phases. |
| Phase Control | Facilitates the formation of stable cubic/tetragonal garnet structures. |
| Batch Consistency | Ensures homogeneous precursor powder for high ionic conductivity. |
Elevate Your Battery Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the foundation of high-performance LLZO electrolytes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique lab requirements. Whether you are focused on primary calcination or high-density sintering, our high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability needed to prevent lithium loss and ensure phase purity.
Ready to optimize your solid-state battery research? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your material needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Degradation mechanisms in low-voltage Wadsley–Roth TiNb<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub> electrodes upon cycling with Li. DOI: 10.1039/d4ta06441k
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces in the battery manufacturing and research industry? Unlock Precision for Battery Innovation
- What is the function of a laboratory muffle furnace in preparing BiVO4 nanosheets? Optimize Your Material Performance
- What precautions should be taken when using a muffle furnace? Essential Safety Guidelines for Lab Success
- How does chamber size affect muffle furnace selection? Ensure Precision with the Right Fit
- Why is atmosphere control important in a Muffle furnace, and what types of atmospheres can be used?
- How does the insulation system in a muffle furnace function? Unlock Efficient and Safe High-Temperature Control
- What is the significance of using a box-type furnace for molybdenum aluminide coating oxidation? Master Thermal Testing
- How does advanced technology in muffle furnaces improve their performance in pharmaceutical applications? Boost Precision and Purity in Pharma Labs



















