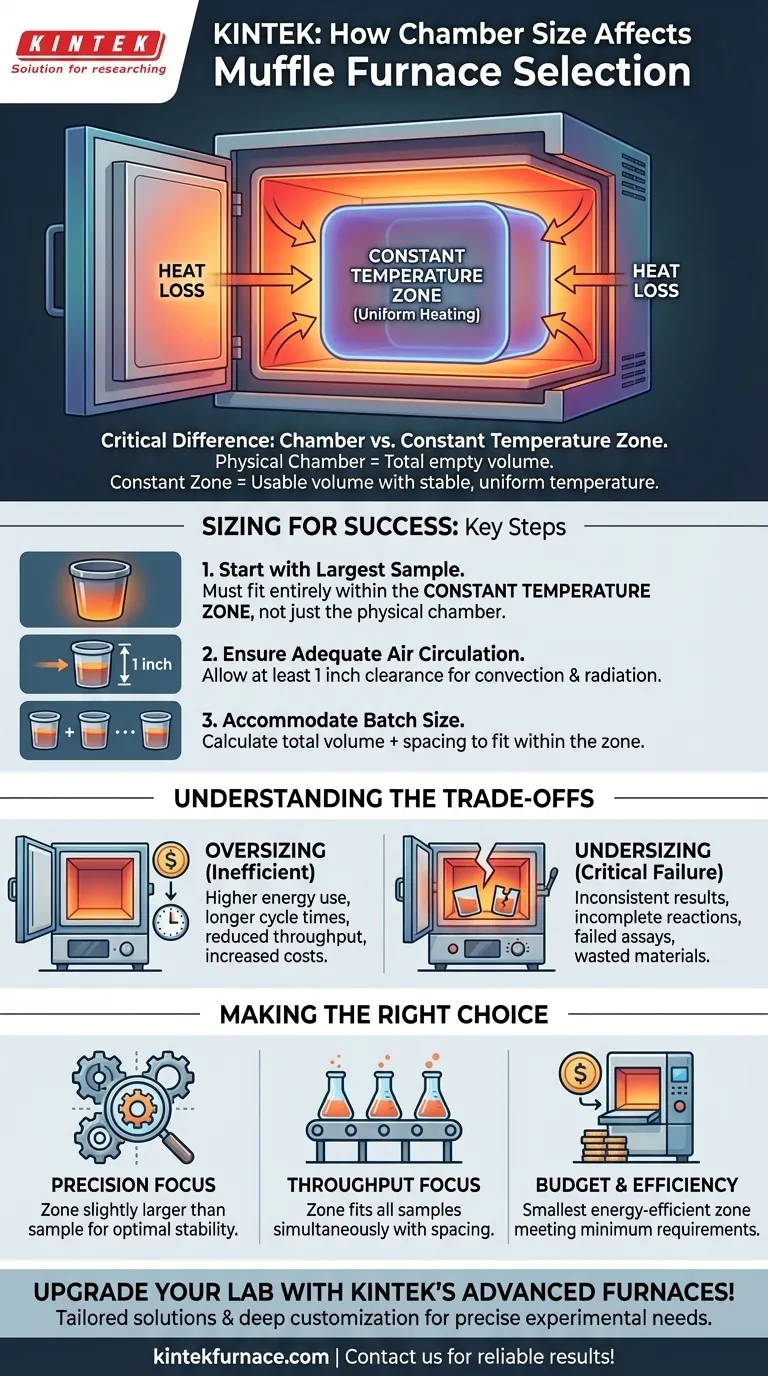
At its core, selecting a muffle furnace based on chamber size is about matching the furnace's usable heating area to your sample's dimensions. While it seems straightforward to pick a chamber that your sample fits into, the most critical factor is not the physical interior volume, but the size of the constant temperature zone within that chamber. This zone is always smaller than the physical dimensions and is the only area that guarantees uniform heating.
The most common mistake is selecting a furnace based on its internal physical dimensions alone. The true determining factor for successful thermal processing is ensuring your sample fits entirely within the furnace's constant temperature zone, with adequate clearance for heat circulation.
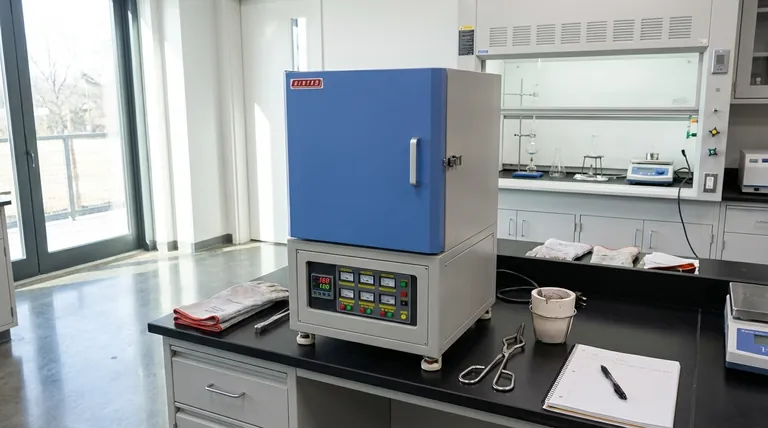

The Critical Difference: Chamber vs. Constant Temperature Zone
Understanding the distinction between the physical chamber and its functional heating zone is the key to choosing the right furnace and achieving repeatable, accurate results.
Defining Chamber Size
Chamber size, typically listed in cubic feet, liters, or dimensional measurements (W x H x D), refers to the total empty space inside the furnace. This is the simple, physical volume from wall to wall.
Defining the Constant Temperature Zone
The constant temperature zone is the usable volume within the chamber where the temperature is stable and uniform to a specific tolerance (e.g., ±5°C). This zone is always smaller than the physical chamber because the areas near the walls, floor, ceiling, and especially the door are susceptible to heat loss.
High-quality insulation, intelligent heating element placement, and precise PID controllers are all designed to maximize the size and stability of this zone.
Why This Distinction Matters
Placing a sample, or even part of a sample, outside the constant temperature zone will result in uneven heating. This can lead to inaccurate test results, incomplete chemical reactions, thermal stress in the material, or failed assays. Your process relies on the entire sample experiencing the same target temperature.
Sizing Your Furnace for Success
Proper sizing moves beyond simple measurements and considers the physics of heat transfer and your specific workflow requirements.
Start with Your Largest Sample
The primary rule is that your largest sample or crucible must fit completely inside the furnace's specified constant temperature zone, not just the physical chamber. Always check the manufacturer's technical data sheet for this specification.
Ensure Adequate Air Circulation
For uniform heating via convection and radiation, heat must be able to circulate freely around the entire sample. A good rule of thumb is to choose a constant temperature zone that allows for at least one inch of clearance on all sides of your sample.
Accommodate Batch Size and Throughput
If you plan to process multiple samples at once, calculate the total volume required for all samples plus the necessary spacing between them. This total volume must then fit within the constant temperature zone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong size—either too large or too small—comes with significant consequences for both your results and your operational efficiency.
The Problem with Oversizing
A furnace that is excessively large for your sample is inefficient. You will expend more energy and time heating a large, empty volume. This increases operational costs and can significantly lengthen heat-up and cool-down cycles, reducing laboratory throughput.
The Risk of Undersizing
This is the more critical failure mode. If the constant temperature zone is smaller than your sample, you will get inconsistent and unreliable results. Parts of the sample will not reach the setpoint temperature, invalidating the entire process and wasting valuable materials and time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your final selection.
- If your primary focus is maximum precision for a single part: Choose a furnace where the constant temperature zone is only slightly larger than your sample, ensuring optimal energy efficiency and temperature stability.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput batch processing: Select a furnace whose constant temperature zone can accommodate all your samples simultaneously while maintaining adequate spacing for uniform heat circulation.
- If your primary focus is budget and operational efficiency: Avoid significant oversizing. Select the smallest, most energy-efficient furnace whose constant temperature zone meets the absolute minimum size requirements for your samples.
Ultimately, proper furnace selection is an investment in the quality and reliability of your work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Constant Temperature Zone | Ensures uniform heating and accuracy for samples |
| Chamber Size | Total physical volume; must accommodate zone and clearance |
| Sample Clearance | At least 1 inch around sample for heat circulation |
| Oversizing | Increases energy use and cycle times |
| Undersizing | Leads to inconsistent results and wasted materials |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your workflow and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















