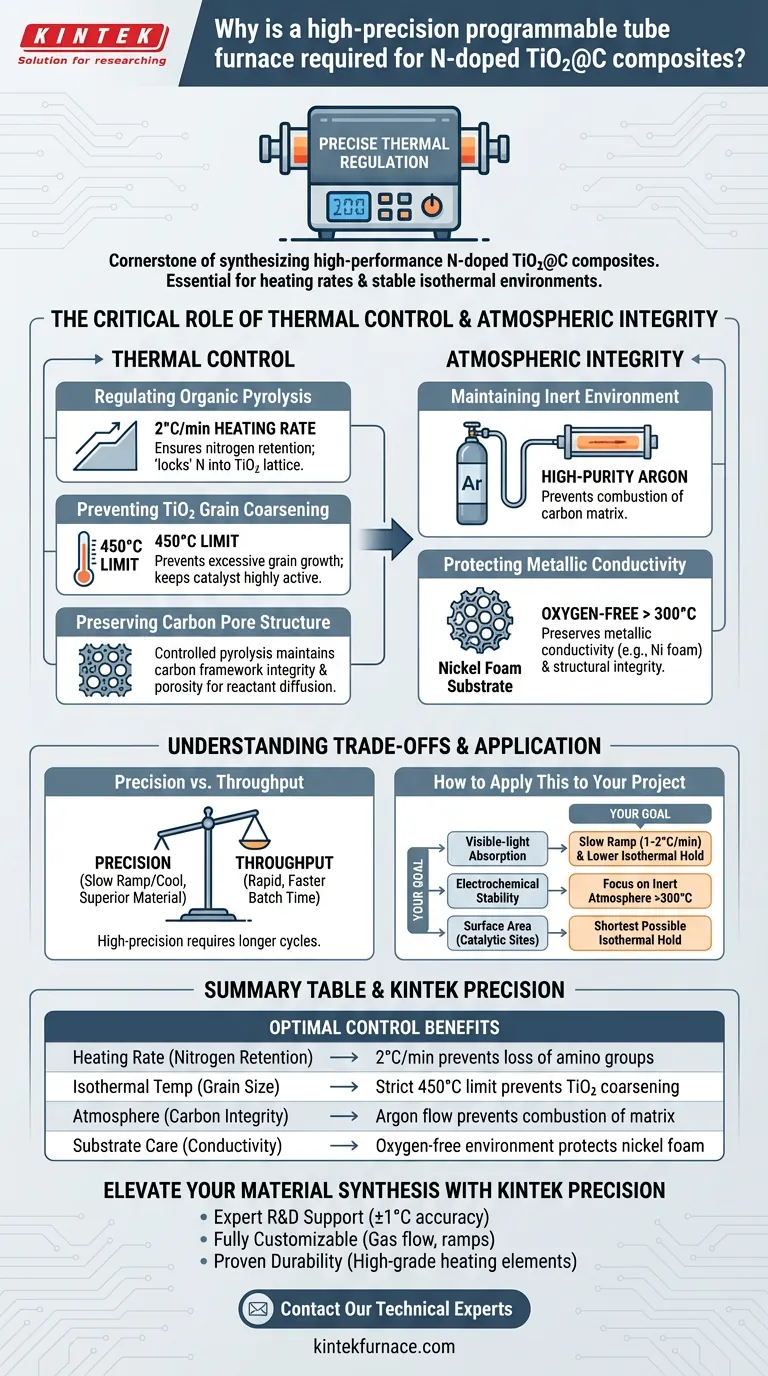
Precise thermal regulation is the cornerstone of synthesizing high-performance N-doped TiO2@C composites. A high-precision programmable tube furnace is required because it provides the exact heating rates and stable isothermal environments necessary to convert metal-organic frameworks (like NH2-MIL-125) into active catalysts. This specific hardware prevents the uncontrolled collapse of the carbon structure while ensuring nitrogen atoms are correctly integrated into the titanium dioxide lattice.
To achieve optimal photocatalytic activity, you must balance organic pyrolysis with inorganic grain growth. A programmable tube furnace facilitates this by maintaining a strict 2°C/min heating ramp and precise isothermal holding to preserve pore structure and electrical conductivity.

The Critical Role of Thermal Control in Phase Transformation
Regulating the Pyrolysis of Organic Frameworks
The transformation of NH2-MIL-125 into a composite requires a slow, controlled breakdown of the organic ligands. A high-precision furnace allows for a steady heating rate of 2°C/min, which ensures that the nitrogen from the amino groups is effectively "locked" into the TiO2 lattice rather than being lost as gas.
Preventing TiO2 Grain Coarsening
High temperatures naturally encourage titanium dioxide particles to grow and aggregate, which reduces surface area. By using a programmable controller to maintain a strict temperature (such as 450°C), the furnace prevents excessive grain growth, keeping the catalyst highly active.
Preserving the Carbon Pore Structure
The "C" in N-doped TiO2@C refers to a carbon matrix that must remain porous to allow for reactant diffusion. Precise temperature management ensures the carbon framework undergoes controlled pyrolysis, maintaining its integrity rather than burning away or collapsing into a dense, inactive mass.
Atmospheric Integrity and Substrate Protection
Maintaining an Inert Environment
Beyond temperature, these furnaces allow for the introduction of high-purity argon to create an inert protective atmosphere. This is vital when working with sensitive substrates or the carbon matrix itself, as any presence of oxygen at high temperatures would lead to unwanted combustion.
Protecting Metallic Conductivity
When composites are grown on substrates like nickel foam, oxidation must be strictly avoided. The tube furnace ensures that once temperatures exceed 300°C, the environment remains oxygen-free, preserving the metallic conductivity and structural integrity of the base material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precision vs. Throughput
High-precision programmable furnaces often require slow ramp-up and cool-down cycles to protect the heating elements and ensure uniformity. While this produces a superior material, it significantly increases the processing time per batch compared to rapid thermal processing.
Cost of Failure in Calibration
If the furnace's thermocouple is poorly calibrated, even a 10-degree variance can lead to "over-roasting." This results in the loss of nitrogen dopants and a shift from the active anatase phase to the less desirable rutile phase of TiO2.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the Right Parameters for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your N-doped TiO2@C composites, tailor your furnace programming to your specific performance metric.
- If your primary focus is visible-light absorption: Prioritize a slow heating ramp (1-2°C/min) and a lower isothermal hold to ensure maximum nitrogen doping density.
- If your primary focus is electrochemical stability: Focus on the inert atmosphere integrity at temperatures above 300°C to prevent substrate oxidation.
- If your primary focus is surface area (catalytic sites): Use the shortest possible isothermal holding time at the target temperature to stop TiO2 grain growth early.
By mastering the programmable nuances of the tube furnace, you transform a simple heat treatment into a precise tool for molecular engineering.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Influence on Composite | Optimal Control Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Nitrogen Retention | 2°C/min prevents loss of amino groups |
| Isothermal Temp | Grain Size | Strict 450°C limit prevents TiO2 coarsening |
| Atmosphere | Carbon Integrity | Argon flow prevents combustion of the matrix |
| Substrate Care | Conductivity | Oxygen-free environment protects nickel foam |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't let temperature fluctuations compromise your catalysts. KINTEK’s advanced Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems provide the ultra-stable thermal environments and inert atmosphere integrity required for complex in-situ transformations like N-doped TiO2@C synthesis.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D Support: Our systems are designed for researchers requiring strict ±1°C accuracy.
- Fully Customizable: Tailored gas flow and programmable ramps to match your specific pyrolysis needs.
- Proven Durability: High-grade heating elements for consistent batch-to-batch performance.
Ready to achieve superior photocatalytic activity? Contact our technical experts today to customize your high-temp furnace!
Visual Guide
References
- Wenbin Wang, Dongping Sun. NH2-MIL-125-Derived N-Doped TiO2@C Visible Light Catalyst for Wastewater Treatment. DOI: 10.3390/polym16020186
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in the carbonization process of porous carbon particles? Expert Insights
- Why is a sealed vacuum quartz tube required for synthesis of 1T-SnS2 via CVT? Ensure Pure Crystal Growth
- What are the specific roles of a high-temperature tube furnace during the two-stage heat treatment of BN@PyC aerogels?
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- Why is a high-vacuum tube furnace necessary for TMD annealing? Protect Your Monolayers from Oxidative Ablation
- What is the role of a Cyclone Collector in sample recovery in a DTF? Enhance Solid Residue Analysis Accuracy
- Why do we use a tubular furnace? For Unmatched Temperature Uniformity and Atmospheric Control
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the accuracy of microplastic thermal decomposition? Ensure Pyrolysis Precision



















