Specific temperature gradients are utilized in vacuum drying ovens to precisely control the rate of solvent removal during the preparation of mixed matrix membranes. By employing a multi-stage heating program—such as a gradual increase from 60°C to 160°C—manufacturers effectively manage the evaporation of solvents like N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) without compromising the material's physical structure.
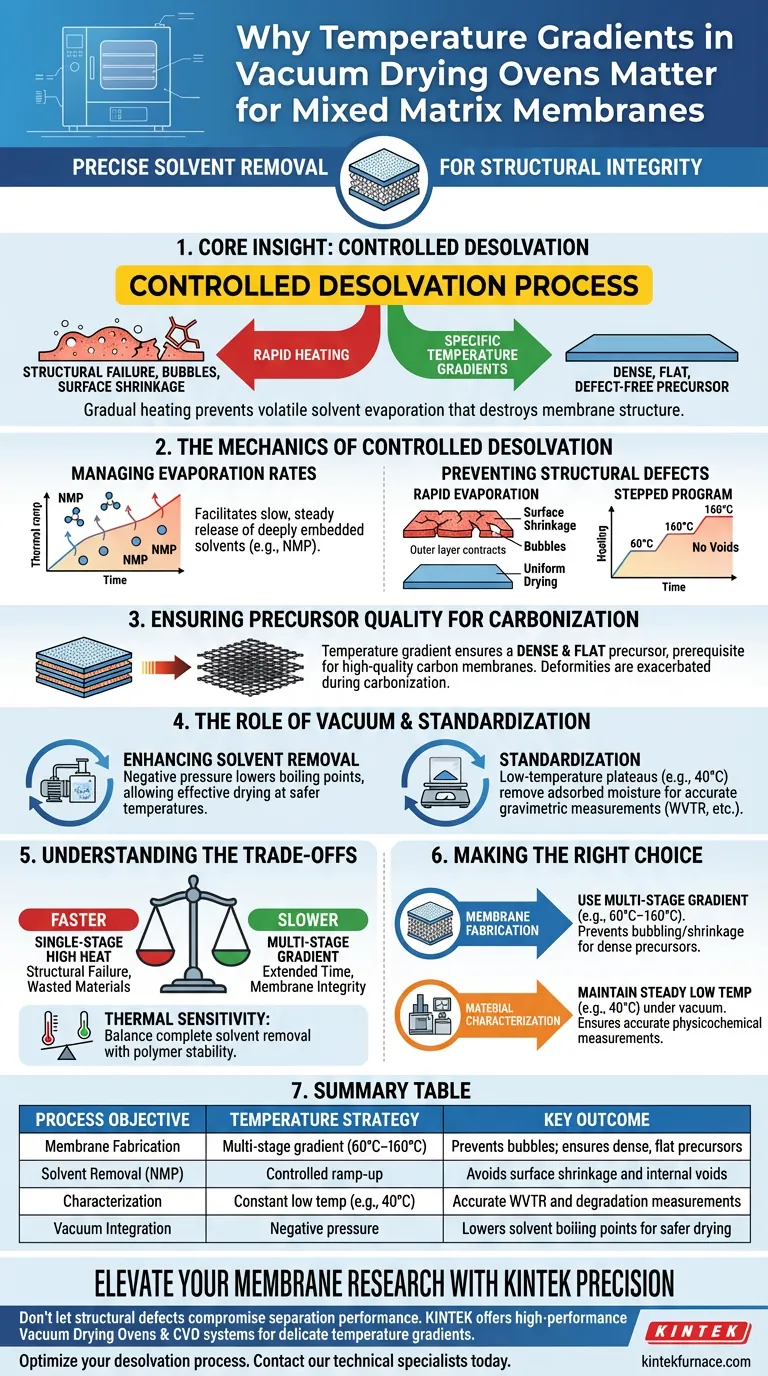
Core Insight: The integrity of a mixed matrix membrane relies on a controlled desolvation process. Rapid heating induces volatile evaporation that destroys membrane structure; specific temperature gradients ensure the precursor remains dense, flat, and defect-free for subsequent processing.

The Mechanics of Controlled Desolvation
Managing Solvent Evaporation Rates
The primary purpose of a temperature gradient is to facilitate a slow, steady release of solvent molecules.
In membrane preparation, solvents such as NMP are deeply embedded within the matrix.
If the temperature is raised too quickly, the solvent evaporates violently, leading to internal pressure that the delicate membrane structure cannot withstand.
Preventing Structural Defects
A vacuum drying oven that utilizes a stepped temperature program prevents common physical defects.
Rapid evaporation causes surface shrinkage, where the outer layer dries and contracts faster than the interior.
Furthermore, uncontrolled heating leads to the formation of bubbles, which create voids in the membrane and permanently compromise its separation performance.
Ensuring Precursor Quality for Carbonization
Achieving Density and Flatness
For mixed matrix membranes intended for high-temperature carbonization, the physical state of the precursor is critical.
The temperature gradient ensures the resulting membrane is both dense and flat.
This structural uniformity is a prerequisite for producing high-quality carbon membranes, as any initial deformities will be exacerbated during the carbonization phase.
The Role of Vacuum and Standardization
Enhancing Solvent Removal
While the temperature gradient manages the rate of removal, the negative pressure (vacuum) lowers the boiling point of the solvents.
This allows for effective drying at temperatures that might otherwise be too low to remove solvents like NMP under atmospheric pressure.
Standardization for Characterization
Beyond fabrication, vacuum drying at specific low-temperature plateaus (e.g., 40°C) is essential for standardizing membrane samples.
This process removes physically adsorbed water and residual solvents to establish a baseline state.
This ensures that subsequent measurements of properties like swelling rate, degradation rate, and water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) are based on accurate gravimetric data.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Time vs. Membrane Integrity
The primary trade-off in using temperature gradients is the extended processing time required.
A multi-stage heating program (e.g., ramping from 60°C to 160°C) takes significantly longer than a single-stage, high-heat flash dry.
However, attempting to accelerate this process almost invariably results in structural failure, rendering the time savings irrelevant due to wasted materials.
Thermal Sensitivity
Operators must balance the need for complete solvent removal against the thermal stability of the polymer matrix.
Setting the final temperature of the gradient too high can lead to polymer degradation before carbonization begins.
Conversely, a gradient that terminates at too low a temperature may leave residual NMP, leading to defects during the high-temperature carbonization step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your vacuum drying oven protocols, align your temperature strategy with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is Membrane Fabrication: Utilize a multi-stage gradient (e.g., 60°C–160°C) to prevent bubbling and shrinkage, ensuring a flat, dense precursor for carbonization.
- If your primary focus is Material Characterization: maintain a steady, lower temperature (e.g., 40°C) under vacuum to remove adsorbed moisture and ensure accurate physicochemical measurements.
Success in mixed matrix membrane preparation is defined not by how fast you dry the material, but by how precisely you control its densification.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Temperature Strategy | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane Fabrication | Multi-stage gradient (60°C–160°C) | Prevents bubbles; ensures dense, flat precursors |
| Solvent Removal (NMP) | Controlled ramp-up | Avoids surface shrinkage and internal voids |
| Characterization | Constant low temp (e.g., 40°C) | Accurate WVTR and degradation measurements |
| Vacuum Integration | Negative pressure | Lowers solvent boiling points for safer drying |
Elevate Your Membrane Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let structural defects compromise your separation performance. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum Drying Ovens and CVD systems designed to handle the delicate temperature gradients required for mixed matrix membrane preparation. Whether you need a standard laboratory furnace or a customizable high-temperature system for carbonization, our equipment ensures the density and flatness your precursors demand.
Ready to optimize your desolvation process? Contact our technical specialists today to find the perfect thermal solution for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Cascade Promotion of Gas Separation Performances in CMS Membranes: MOFs With Functional Groups and Loaded Noble Metals. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202503471
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of vacuum furnaces in energy and power generation? Boost Efficiency and Reliability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between a box furnace and a vacuum furnace? Key Insights for Your Lab
- Why do some nonferrous metals require a vacuum furnace for heat treating? To Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity
- Why must a vacuum system maintain 3.6 mbar for plasma nitriding? Master Precision Surface Hardening
- How is temperature controlled in a vacuum furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment for Your Materials
- How does a vacuum furnace work to prevent metal oxidation? Achieve Purity in High-Temperature Metal Processing
- Why is a high vacuum chamber system essential for the PLD of SrNbO3 thin films? Achieve High-Purity Epitaxial Growth
- What is the function of a vacuum quenching furnace in DMD? Optimize Durability and Finish for 3D Metal Parts



















