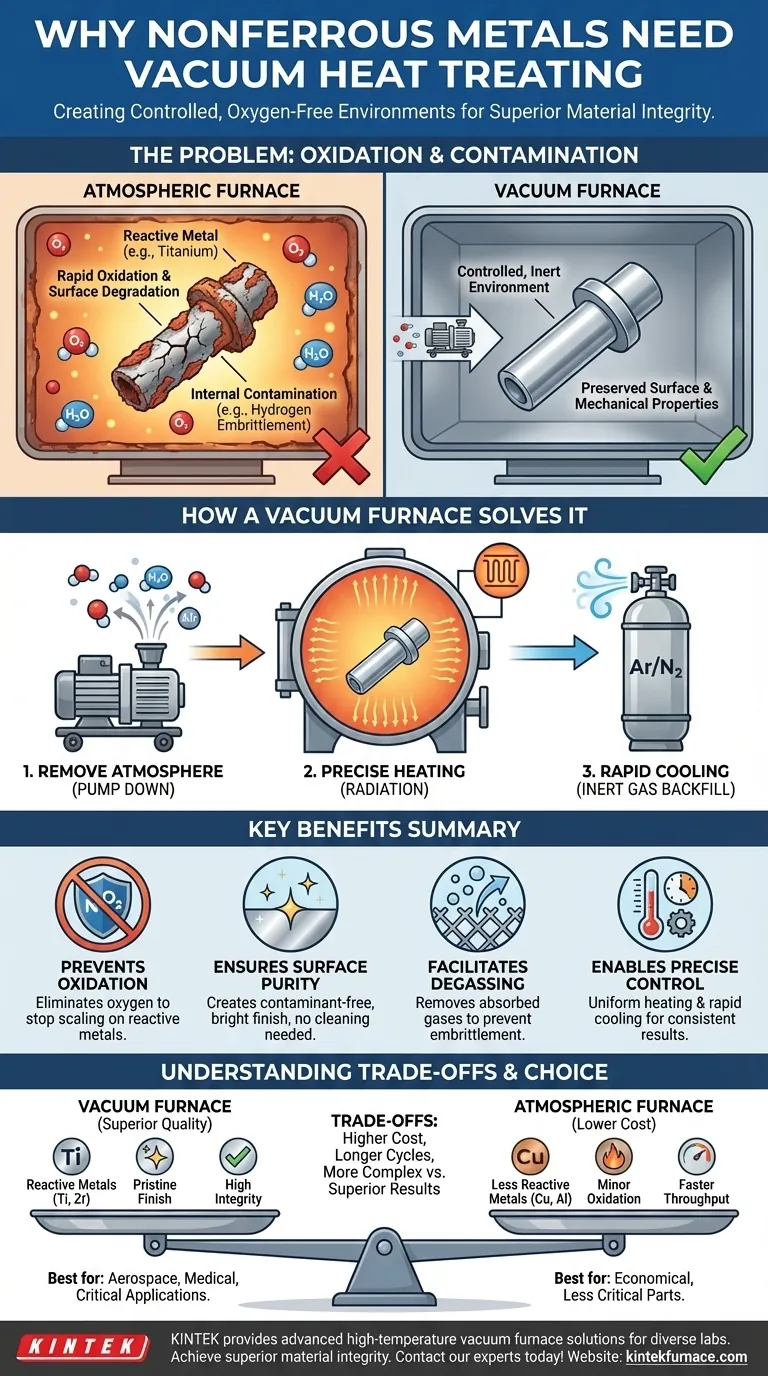
The primary reason some nonferrous metals require a vacuum furnace for heat treatment is to create a controlled, oxygen-free environment. At the high temperatures needed for processes like annealing or brazing, many metals—especially reactive ones like titanium—will rapidly oxidize, which degrades their surface quality and mechanical properties. A vacuum furnace removes the atmospheric gases, preventing these destructive chemical reactions from occurring.
A vacuum furnace is not simply a better oven; it's a tool for absolute atmospheric control. Its necessity is dictated by a metal's chemical reactivity and the required purity of the final product, transforming heat treatment from a thermal process into a precise materials science operation.

The Fundamental Problem: Oxidation and Contamination
When selecting a heat treatment method, the primary consideration is how the furnace's atmosphere will interact with the metal at elevated temperatures. For many nonferrous alloys, this interaction is the single greatest threat to quality.
How Heat Triggers Oxidation
Heat acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions. When a metal is heated in the presence of oxygen, a process of oxidation begins, forming a layer of metal oxide on the surface.
This is the same fundamental process that causes rust on iron, but it happens much faster and more aggressively at heat treatment temperatures.
The Impact on Material Integrity
This oxide layer is not just a cosmetic issue of discoloration or scaling. It can compromise the part's integrity, inhibit subsequent processes like brazing or welding, and alter its final mechanical properties.
Furthermore, gases in the atmosphere can diffuse into the metal itself, causing internal contamination and creating points of weakness. This can lead to issues like hydrogen embrittlement, where absorbed hydrogen makes the metal brittle and prone to failure.
The Sensitivity of Reactive Metals
Some nonferrous metals are far more susceptible to oxidation than others. Reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, and certain nickel or aluminum superalloys have a very high affinity for oxygen.
For these materials, even a tiny amount of oxygen at high temperatures can cause significant surface and subsurface damage. Therefore, processing in a standard atmospheric furnace is not an option if you need to preserve the material's intended properties.
How a Vacuum Furnace Solves the Problem
A vacuum furnace directly counters the threat of atmospheric contamination by removing the atmosphere itself. This provides a level of control that is impossible to achieve in a conventional furnace.
Creating a Controlled Environment
The core function of a vacuum furnace is to pump out the air and other gases from a sealed chamber before heating begins. This removes the oxygen, moisture, and other elements that would react with the hot metal.
This process ensures that the heat treatment happens in a chemically inert environment, preventing both oxidation and contamination.
Ensuring Surface Purity and Degassing
A significant benefit of the vacuum is its ability to purify the material's surface. The low-pressure environment can actually pull contaminants, such as oils or residual gases from prior manufacturing steps, off the part.
This process, known as degassing, results in an exceptionally clean, bright, and pure surface finish that requires no post-process cleaning.
Achieving Uniform and Rapid Heating
Vacuum furnaces offer high thermal efficiency. With no air to transfer heat via convection, heating occurs primarily through radiation. This allows for extremely uniform and precisely controlled heating cycles.
The lack of atmosphere also enables rapid cooling, often by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like argon or nitrogen, which can be circulated to cool the parts quickly and uniformly without causing oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum heat treatment offers superior results, it is not always the necessary or most practical choice. Its advantages come with clear trade-offs.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than conventional atmospheric furnaces. The need for robust vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems adds to the cost.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time. The pump-down phase adds to the overall cycle time for each batch, which can impact throughput compared to a continuous atmospheric furnace.
Increased Process Complexity
Operating a vacuum furnace requires a higher level of technical skill. Monitoring vacuum levels, leak rates, and gas backfilling systems adds complexity to the heat treatment process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a vacuum furnace must be based on the material being processed and the desired outcome for the final part.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium, zirconium, nickel superalloys): A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic oxidation and preserve material properties.
- If your primary focus is achieving a pristine, bright surface finish with zero contamination: A vacuum furnace is the definitive choice for applications in aerospace, medical, or electronics.
- If your primary focus is brazing or joining dissimilar metals: The ultra-clean environment created by a vacuum ensures superior joint strength and integrity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heat treatment of less reactive metals (e.g., some copper or aluminum alloys): An atmospheric furnace may be sufficient and more economical if minor surface oxidation is acceptable or can be removed.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is an investment in achieving the highest possible material integrity and surface quality.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Why It Matters for Nonferrous Metals |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Eliminates oxygen to stop surface scaling and property degradation in reactive metals like titanium and zirconium. |
| Ensures Surface Purity | Creates a contaminant-free environment for a bright, clean finish without post-process cleaning. |
| Facilitates Degassing | Removes absorbed gases (e.g., hydrogen) from the metal, preventing embrittlement. |
| Enables Precise Control | Allows uniform heating and rapid cooling in an inert atmosphere for consistent results. |
Need to heat treat reactive metals like titanium or achieve a pristine, oxide-free finish?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let us help you achieve superior material integrity and surface quality. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific heat treatment challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















