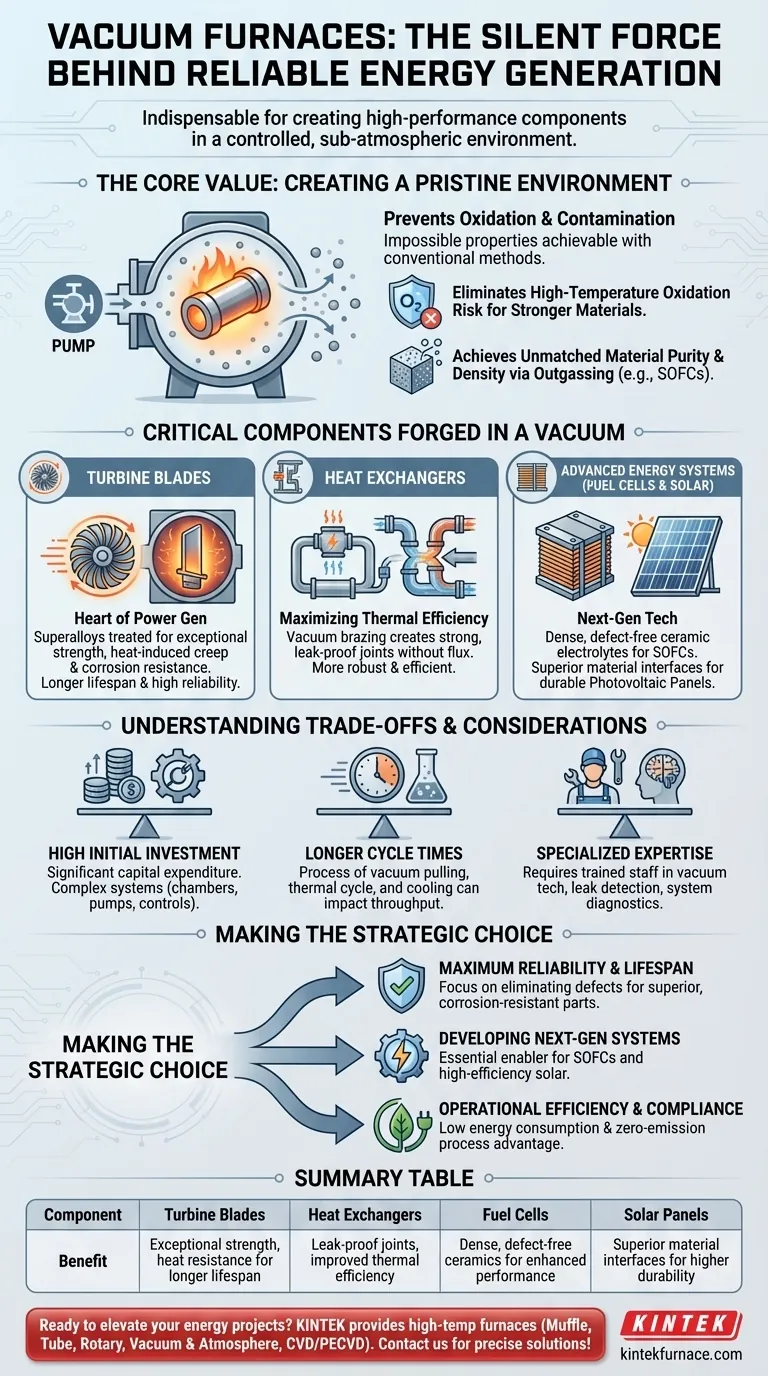
In the energy and power generation sector, vacuum furnaces are indispensable for creating the high-performance, ultra-reliable components that modern energy infrastructure demands. By heating materials in a controlled, sub-atmospheric environment, these furnaces produce parts like turbine blades and heat exchangers with superior strength, purity, and resistance to heat and corrosion, which are critical for safe and efficient power generation.
The core value of a vacuum furnace is not simply heating material; it is the creation of a pristine, controlled environment. This unique capability prevents oxidation and contamination, allowing for the production of materials with properties that are impossible to achieve with conventional methods, directly translating to more durable and efficient energy systems.

The Foundation: Why a Vacuum Environment Is Critical
A vacuum furnace works by removing the atmosphere from its chamber before heating. This fundamental difference from a conventional furnace is the source of all its advantages.
Preventing High-Temperature Oxidation
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment and brazing, most high-performance metals will react with oxygen. This oxidation weakens the material, introduces impurities, and can lead to premature component failure.
A vacuum environment eliminates this risk entirely. By removing the oxygen, the furnace ensures the material's surface and internal structure remain pure and uncompromised, which is non-negotiable for parts operating under extreme stress.
Achieving Unmatched Material Purity and Density
Beyond oxidation, the vacuum removes other gases and volatile contaminants from the material itself, a process known as outgassing.
This purification results in finished components with higher density and fewer internal defects. For technologies like solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which rely on dense ceramic components, this is a critical enabling factor.
Critical Components Forged in a Vacuum
The theoretical benefits of vacuum processing directly translate into tangible improvements for the most vital components in power generation.
Turbine Blades: The Heart of Power Generation
Turbine blades in gas and steam power plants spin at incredible speeds in extremely hot, corrosive environments. Any material flaw can lead to catastrophic failure.
Vacuum furnaces are used to heat-treat the superalloys these blades are made from, creating a final product with exceptional strength and resistance to heat-induced creep and corrosion. This ensures a longer operational lifespan and higher reliability.
Heat Exchangers: Maximizing Thermal Efficiency
Heat exchangers are crucial for capturing and transferring thermal energy within a power plant. Their efficiency depends on the integrity of the materials used.
Vacuum brazing, a process performed in a vacuum furnace, creates strong, leak-proof joints between dissimilar metals without the use of flux, which can be a source of corrosion. The result is a more robust and efficient heat exchanger.
Advanced Energy Systems: Fuel Cells and Solar
The role of vacuum furnaces extends to next-generation energy technologies.
Vacuum hot presses are used to create the dense, defect-free ceramic electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. In solar energy, vacuum bonding processes improve the efficiency and durability of photovoltaic panels by creating superior material interfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the benefits are significant, vacuum furnace technology is a specialized industrial process with specific operational realities.
High Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital expenditure compared to their conventional atmospheric counterparts. The systems are complex, involving robust vacuum chambers, high-performance pumps, and sophisticated control systems.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pulling a vacuum, running the thermal cycle, and then cooling the chamber under controlled conditions can take longer than atmospheric furnace processes. This can impact overall production throughput.
Specialized Maintenance and Operation
Operating and maintaining a vacuum furnace requires a higher level of technical expertise. Staff must be trained in vacuum technology, leak detection, and system diagnostics to ensure optimal performance and prevent costly downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic decision driven by the end-goal for the component or system.
- If your primary focus is maximum component reliability and lifespan: The furnace's ability to eliminate oxidation and internal defects to produce superior, corrosion-resistant parts is the key justification.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation power systems: The technology is an essential enabler for producing critical components for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and high-efficiency solar panels.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and environmental compliance: The furnace's own low energy consumption and zero-emission process provide a clear advantage over conventional, fossil-fuel-fired furnaces.
Ultimately, vacuum furnaces are a cornerstone technology that directly enables the safety, reliability, and efficiency of modern and future energy generation systems.
Summary Table:
| Component | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Turbine Blades | Exceptional strength and heat resistance for longer lifespan |
| Heat Exchangers | Leak-proof joints and improved thermal efficiency |
| Fuel Cells | Dense, defect-free ceramics for enhanced performance |
| Solar Panels | Superior material interfaces for higher durability |
Ready to elevate your energy and power generation projects with advanced vacuum furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















