High-alumina (Alundum) crucibles are the critical standard for synthesis because they provide a chemically inert barrier against aggressive melts. During the creation of monazite glass-ceramic matrices, the phosphate glass components become highly corrosive at elevated temperatures. Alundum crucibles withstand this chemical attack while resisting thermal shock, ensuring the containment vessel does not degrade or introduce impurities into the sample.
The integrity of a monazite glass-ceramic matrix depends entirely on precise stoichiometry. High-alumina crucibles prevent the container walls from leaching into the melt, ensuring the final product reflects the intended chemical composition without contamination.
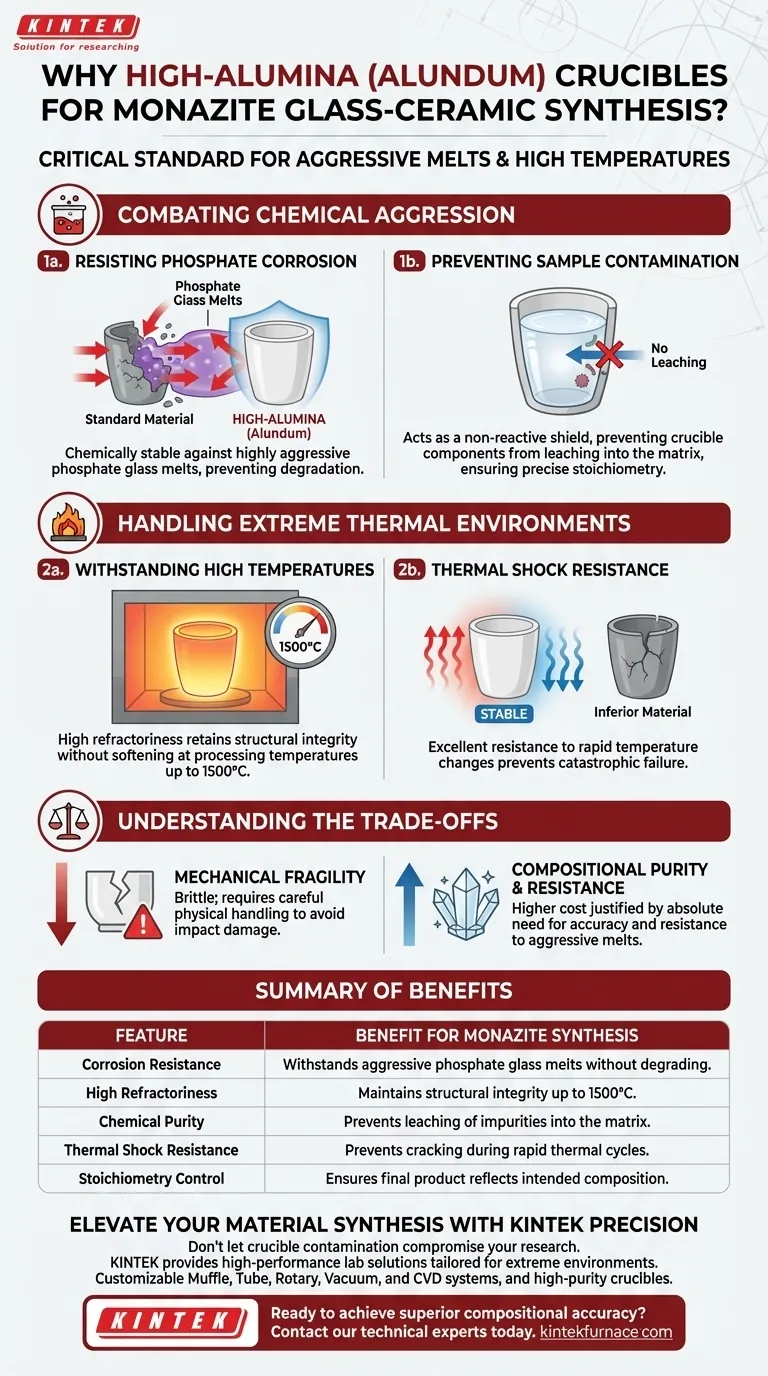
Combating Chemical Aggression
Resisting Phosphate Corrosion
Phosphate glass melts are known for being chemically aggressive, particularly when in a liquid state. Standard crucible materials often degrade rapidly under these conditions. High-alumina crucibles possess the necessary chemical stability to resist this specific type of corrosion.
Preventing Sample Contamination
The primary risk during synthesis is the leaching of crucible wall components into the mixture. If the vessel corrodes, foreign elements contaminate the solidification matrix. Alundum acts as a pure, non-reactive shield, guaranteeing that the chemical makeup of the synthesized matrix remains accurate.
Handling Extreme Thermal Environments
Withstanding High Temperatures
Synthesis processes often reach extreme temperatures, sometimes approaching 1500°C. High-alumina materials possess high refractoriness, meaning they retain their structural integrity and do not soften or melt at these processing temperatures.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Rapid heating or cooling cycles are common in glass-ceramic synthesis. Inferior materials often crack under this stress. Alundum provides excellent thermal shock resistance, preventing catastrophic failure of the vessel during temperature transitions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Fragility
Despite their thermal and chemical strength, high-alumina ceramics can be mechanically brittle. They require careful physical handling to avoid chipping or cracking from impact, which differs from their resistance to thermal stress.
Cost vs. Necessity
High-purity Alundum is generally more expensive than lower-grade refractory materials. Its use is a calculated trade-off where the cost is justified by the absolute need for compositional purity and resistance to specific aggressive melts like phosphates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible is about balancing the aggressiveness of your melt with your tolerance for impurities.
- If your primary focus is compositional accuracy: Prioritize high-alumina crucibles to strictly prevent element leaching and maintain the exact stoichiometry of your glass-ceramic matrix.
- If your primary focus is thermal safety: Leverage Alundum's superior thermal shock resistance to protect your sample and equipment during rapid temperature cycling.
By mitigating both chemical corrosion and thermal stress, high-alumina crucibles provide the controlled environment necessary for high-precision materials science.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Monazite Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Withstands aggressive phosphate glass melts without degrading. |
| High Refractoriness | Maintains structural integrity at temperatures reaching 1500°C. |
| Chemical Purity | Prevents leaching of impurities into the glass-ceramic matrix. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Prevents cracking during rapid heating and cooling cycles. |
| Stoichiometry Control | Ensures the final product reflects the intended chemical composition. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't let crucible contamination compromise your research integrity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance lab solutions tailored for extreme environments. Whether you are synthesizing monazite glass-ceramics or developing new materials, our range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—along with high-purity crucibles—are fully customizable to meet your unique needs.
Ready to achieve superior compositional accuracy? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace and containment solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- S. V. Yudintsev, V. I. Malkovsky. Thermal Effects and Glass Crystallization in Composite Matrices for Immobilization of the Rare-Earth Element–Minor Actinide Fraction of High-Level Radioactive Waste. DOI: 10.3390/jcs8020070
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-pressure stainless steel autoclave? Master Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanomaterials
- Why is a gas mixing system essential for syngas annealing in copper powder production? Ensure Precise Embrittlement
- What are the typical applications of a circulating water vacuum pump? Essential for Lab Efficiency and Cost Savings
- What are the primary functions of a self-preheating heat exchanger? Maximize Thermal Efficiency in Double-P Tubes
- What is the specific purpose of using a graphite crucible equipped with a plug during the melting process of Mg3Sb2?
- What roles does a high-purity graphite mold serve during the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) of TiC-SiC composites?
- Why is high-purity graphite paper typically lined on the inner walls of the mold before loading Ti-6Al-4V alloy powder?
- Why is dimensional accuracy important for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure Reliable High-Temp Performance


















