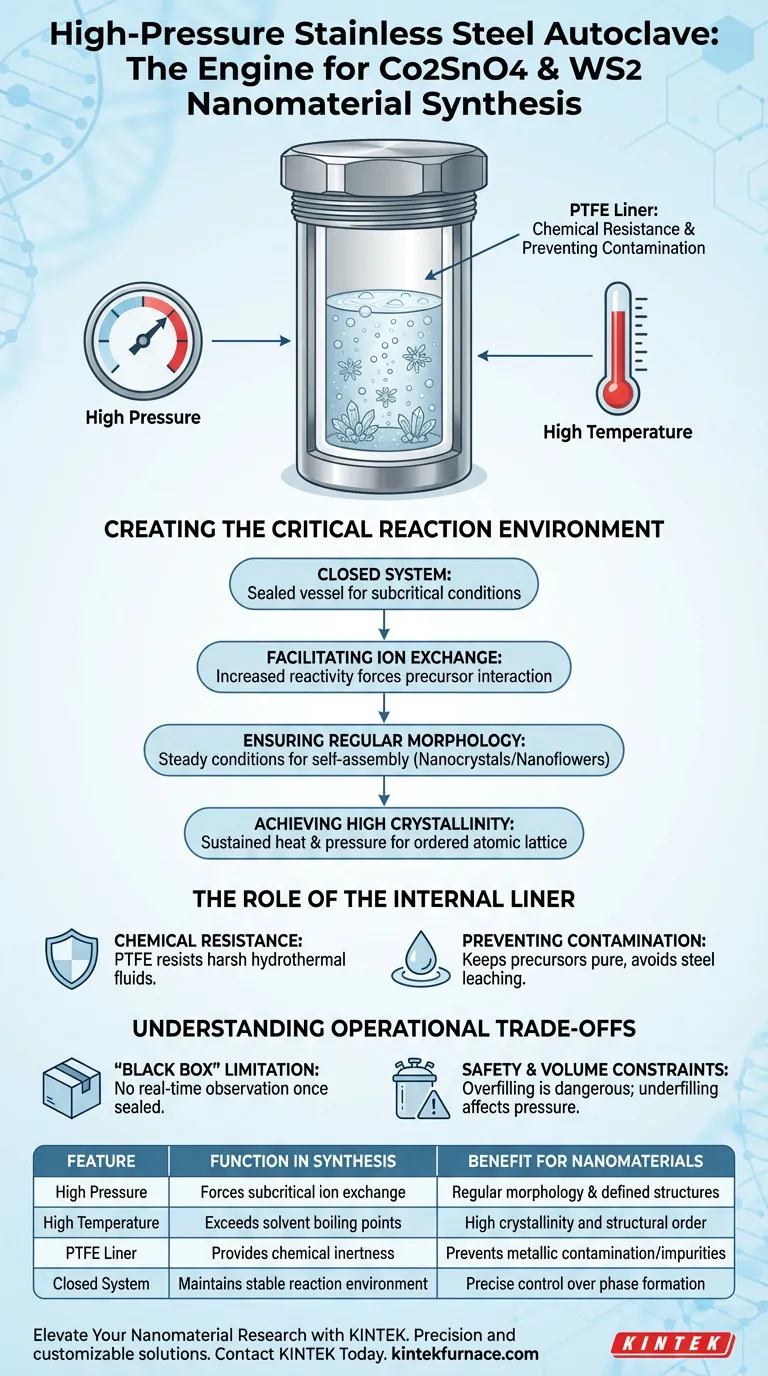
The primary function of a high-pressure stainless steel autoclave is to create a sealed, high-temperature, and high-pressure environment essential for the hydrothermal synthesis of Co2SnO4 nanocrystals and WS2 nanoflowers. It utilizes a corrosion-resistant polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) liner to facilitate sufficient ion exchange and crystal growth, ensuring the final nanostructures possess regular morphology and high crystallinity.
The autoclave acts as a containment vessel that forces chemical precursors to interact under subcritical conditions. By maintaining high pressure and protecting the reactants from contamination, it converts liquid solutions into highly crystalline solid nanostructures.
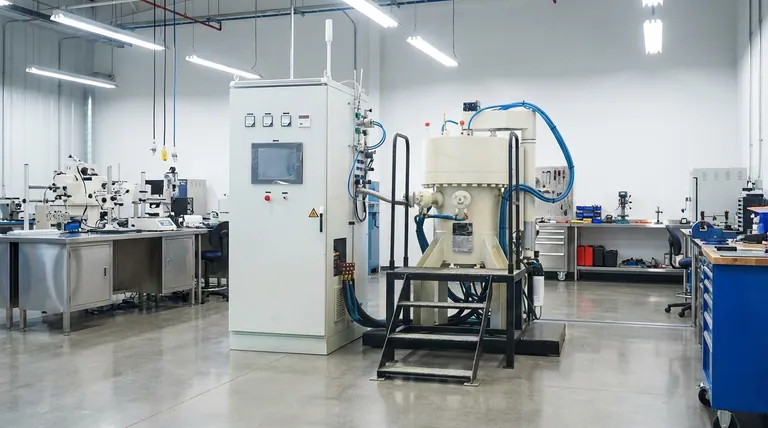

Creating the Critical Reaction Environment
The Necessity of a Closed System
In the synthesis of Co2SnO4 and WS2, standard ambient conditions are insufficient for the required chemical transformations.
The autoclave provides a closed system where the temperature can be raised above the boiling point of the solvent.
This generates significant internal pressure, which is the driving force behind the synthesis.
Facilitating Ion Exchange
The high-pressure environment increases the reactivity of the precursors.
It forces the materials to undergo sufficient ion exchange, a process that might be slow or impossible at atmospheric pressure.
This accelerated interaction is critical for assembling the complex atomic structures of Co2SnO4 and WS2.
Ensuring Regular Morphology
The physical shape of the nanomaterials is dictated by the stability of the environment.
The autoclave maintains steady conditions that allow the precursors to self-assemble into regular morphologies, such as defined nanocrystals or nanoflowers.
Without this controlled pressure, the materials would likely form irregular aggregates rather than specific nanostructures.
Achieving High Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the structural order of the atoms within the material.
The sustained heat and pressure promote high crystallinity, ensuring the atomic lattice is well-ordered.
High crystallinity is essential for the electronic and optical performance of the final nanomaterial.
The Role of the Internal Liner
Chemical Resistance
The stainless steel shell provides structural strength, but it cannot come into direct contact with the reactive chemicals.
An internal polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) liner is used to hold the solution.
This liner is chemically inert, meaning it is designed to resist chemical corrosion from the harsh hydrothermal fluids.
Preventing Contamination
Purity is paramount when synthesizing nanomaterials like Co2SnO4 and WS2.
If the reaction solution were to touch the steel walls, iron or other metals could leach into the mixture.
The PTFE barrier ensures the reaction precursors remain pure, preventing the steel vessel from contaminating the final product.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The "Black Box" Limitation
Because the autoclave creates a sealed, high-pressure environment, it functions as a "black box."
You cannot observe the reaction in real-time.
Once the vessel is sealed and heated, you cannot adjust parameters or visually monitor crystal growth until the process is complete and the vessel has cooled.
Safety and Volume Constraints
The pressure generation relies on the expansion of the liquid inside the liner.
Overfilling the liner can be dangerous, potentially exceeding the vessel's pressure rating.
Conversely, underfilling may result in insufficient pressure to drive the specific ion exchange required for Co2SnO4 and WS2 formation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To ensure successful synthesis of these specific nanostructures, consider your primary objective:
- If your primary focus is Structural Purity: Ensure the PTFE liner is free of scratches or defects to prevent even trace amounts of metallic contamination from the outer shell.
- If your primary focus is Morphology Control: Precisely control the temperature and fill volume, as these directly dictate the internal pressure that shapes the nanocrystals and nanoflowers.
The autoclave is not just a heating vessel; it is a pressure chamber that forces order out of chaotic chemical solutions.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Synthesis | Benefit for Nanomaterials |
|---|---|---|
| High Pressure | Forces subcritical ion exchange | Regular morphology & defined structures |
| High Temperature | Exceeds solvent boiling points | High crystallinity and structural order |
| PTFE Liner | Provides chemical inertness | Prevents metallic contamination/impurities |
| Closed System | Maintains stable reaction environment | Precise control over phase formation |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between irregular aggregates and perfect nanoflowers. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside customizable high-pressure hydrothermal autoclaves.
Whether you are synthesizing Co2SnO4 or complex WS2 nanostructures, our lab equipment is engineered to provide the stable, contamination-free environment your research demands.
Contact KINTEK Today to Customize Your Synthesis Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Nitrogen-Doped Hollow Carbon Spheres-Decorated Co2SnO4/WS2 Heterostructures with Improved Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dye. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30092081
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does the vacuum pumping principle of a circulating water vacuum pump differ from jet pumping? Compare Mechanisms & Uses
- What is the temperature range for Laboratory Type Furnaces? Find Your Ideal Heat Solution
- Why is toluene used as a grinding aid in wet ball milling? Master Fine Metal Powder Synthesis with PCAs
- What chemical resistance properties should be verified for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure High-Temperature Durability
- Why is a high-precision DC power supply necessary for PFS? Control Electric Fields for Perfect Plasma Sintering
- What is Alumina and how is it derived? Discover Its Role in Advanced Materials and Production
- What is the primary function of the alumina crucible set in the synthesis of Eu5.08-xSrxAl3Sb6? Expert Analysis
- What functions does the hot pressing mold perform? Key Roles in Al3Ti/Al Composite Powder Metallurgy



















