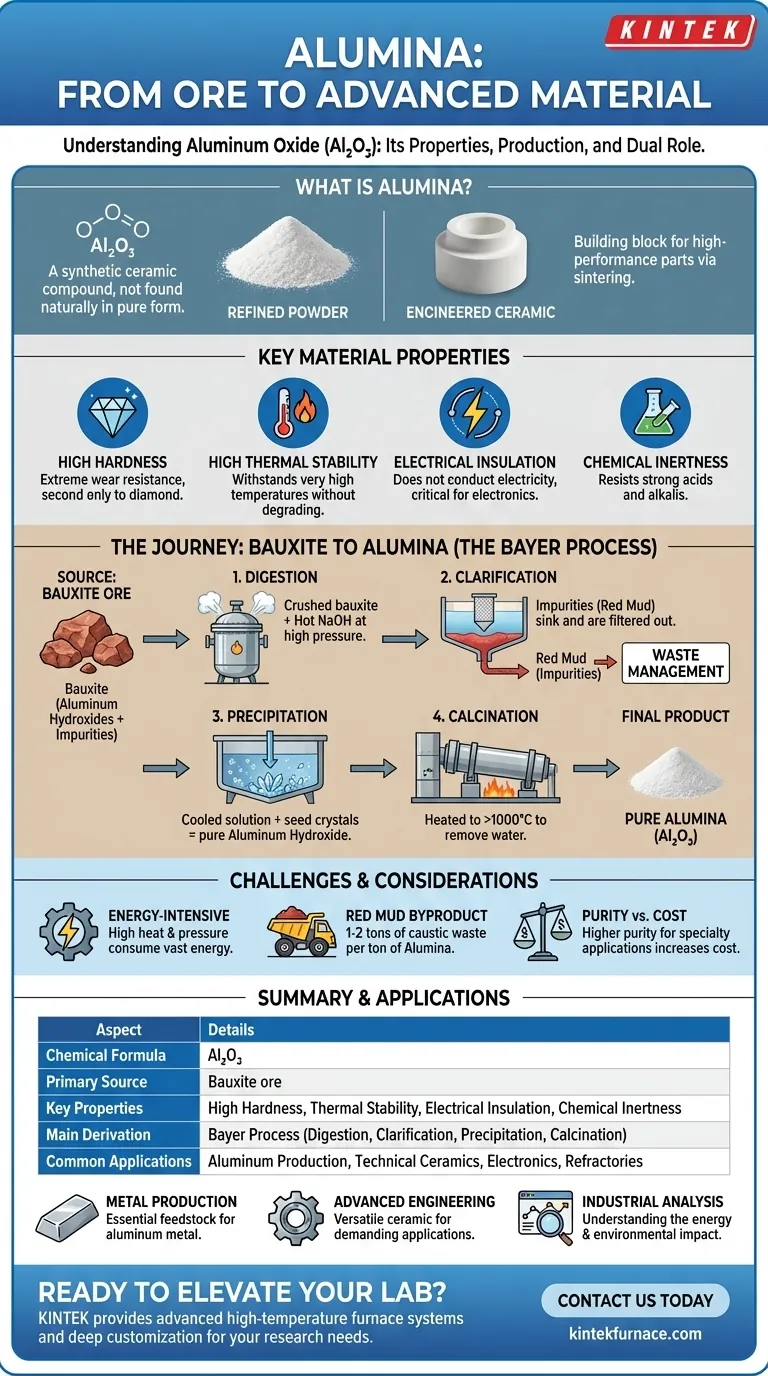
In technical terms, Alumina is aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), a synthetic compound prized for its hardness and stability. It is not found naturally in this pure form but is most commonly derived from a raw ore called bauxite. In its refined state, Alumina is a fine, white, granular powder that looks much like common table salt, serving as the primary feedstock for producing aluminum metal.
While often seen simply as a step in making aluminum, Alumina's true significance lies in its dual identity. It is both the critical intermediate raw material for the entire aluminum industry and, on its own, a high-performance technical ceramic used in countless advanced applications.

What is Alumina? A Deeper Look
Understanding Alumina begins with its fundamental properties. It is far more than just a powder; it is an engineered material with a specific chemical identity and a unique set of performance characteristics that make it valuable.
Chemical Composition and Form
Alumina is the common name for aluminum oxide, a chemical compound with the formula Al₂O₃. It is a ceramic material, meaning it is an inorganic, non-metallic solid. While its refined form is a powder, this powder is the building block for creating dense, hard ceramic parts through processes like sintering.
Key Material Properties
The reason Alumina is so widely used is due to its exceptional combination of properties. It exhibits:
- High Hardness: It is extremely hard and wear-resistant, second only to diamond among common materials.
- High Thermal Stability: It can withstand very high temperatures without degrading or melting, making it an excellent refractory material.
- Electrical Insulation: It does not conduct electricity, even at high temperatures, which is critical for electronic components.
- Chemical Inertness: It resists attack from most strong acids and alkalis, making it ideal for handling corrosive substances.
The Journey from Bauxite to Alumina
Pure Alumina is not mined directly from the ground. It must be chemically extracted and refined from its primary source, bauxite ore, through a large-scale industrial process.
The Source: Bauxite Ore
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock that is the world's main source of aluminum. It is typically found near the surface in topsoil across tropical and subtropical regions. Bauxite is not a uniform material; it is a mixture of aluminum hydroxide minerals, iron oxides (which give it a reddish color), and other impurities like silica.
The Bayer Process: A Necessary Refinement
To isolate pure Alumina, the bauxite ore must undergo the Bayer process. This is a four-step chemical procedure:
- Digestion: The crushed bauxite is mixed with a hot solution of sodium hydroxide (caustic soda). At high pressure and temperature, the aluminum hydroxides dissolve, forming a sodium aluminate solution.
- Clarification: The mixture is passed into settling tanks where the insoluble impurities—primarily iron oxides and silica, collectively known as "red mud"—sink to the bottom and are filtered out.
- Precipitation: The clear sodium aluminate solution is cooled and seeded with crystals of aluminum hydroxide. This causes pure aluminum hydroxide to precipitate out of the solution.
- Calcination: The solid aluminum hydroxide crystals are washed and then heated to over 1,000°C (1,800°F) in a large kiln. This process, called calcination, drives off the water molecules, leaving behind a fine, pure white powder: aluminum oxide, or Alumina.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The production of Alumina is a feat of industrial chemistry, but it is not without significant operational and environmental considerations.
The Energy-Intensive Nature of Production
The Bayer process is highly energy-intensive. Maintaining the high temperatures and pressures required for the digestion and calcination steps consumes vast amounts of energy, making it a major operational cost and a significant factor in the material's carbon footprint.
Managing the "Red Mud" Byproduct
For every ton of Alumina produced, roughly one to two tons of red mud waste are generated. This caustic and saline slurry presents a major environmental challenge for the industry, requiring careful and costly management in large impoundment areas.
Purity Determines Application and Cost
Not all Alumina is created equal. The standard "smelter-grade" Alumina used for aluminum production is over 99% pure. However, specialty applications like electronics or medical implants require even higher purities (99.9% or more), which involve additional refining steps and significantly increase the final cost.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your perspective on Alumina will depend entirely on your objective. It can be viewed as a simple raw material, a complex ceramic, or a product of a challenging industrial process.
- If your primary focus is large-scale metal production: View Alumina as the essential feedstock for creating aluminum metal, where consistency and cost are the most critical factors.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials engineering: Recognize Alumina as a versatile technical ceramic valued for its hardness, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation in demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is industrial or environmental analysis: Understand that Alumina derivation is an energy-intensive process defined by the efficiency of the Bayer process and the challenge of managing its red mud byproduct.
Ultimately, Alumina is a foundational material, serving as both the heart of the global aluminum industry and a cornerstone of modern high-performance ceramics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Al₂O₃ |
| Primary Source | Bauxite ore |
| Key Properties | High hardness, thermal stability, electrical insulation, chemical inertness |
| Main Derivation Process | Bayer process (digestion, clarification, precipitation, calcination) |
| Common Applications | Aluminum production, technical ceramics, electronics, refractories |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with advanced high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















