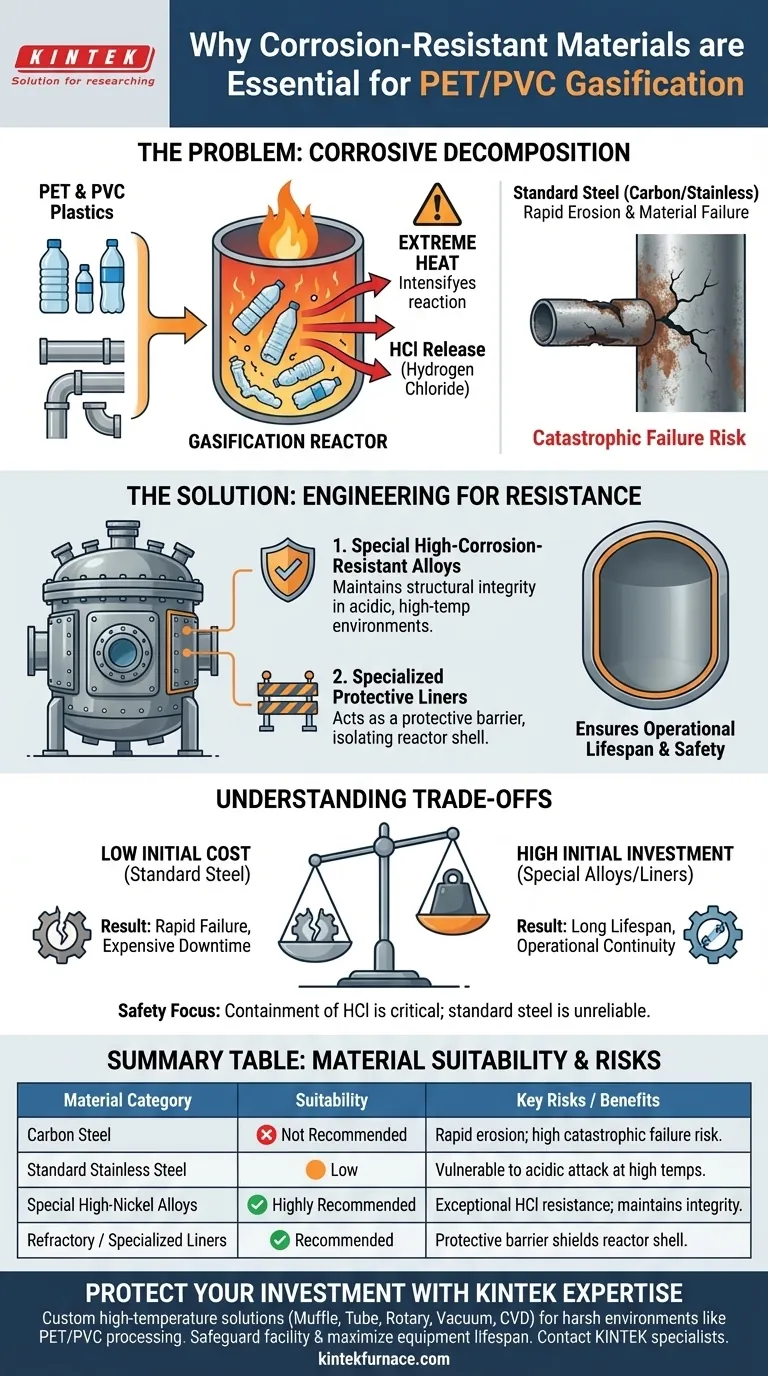
Processing PET and PVC plastics triggers the release of corrosive gases, specifically hydrogen chloride (HCl), during high-temperature decomposition. These gases aggressively attack standard reactor materials like carbon and stainless steel, necessitating the use of specialized corrosion-resistant alloys or liners to prevent catastrophic equipment failure.
When exposed to the intense heat of gasification, plastics like PET and PVC break down and release acidic byproducts that rapidly degrade standard metals. Utilizing high-corrosion-resistant materials is not optional; it is a critical requirement to ensure the structural integrity, safety, and operational lifespan of the gasification system.

The Chemistry of Decomposition
The Release of Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
Polymers such as Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) contain specific chemical components that react under heat. When these plastics undergo the high-temperature decomposition required for gasification, they release hydrogen chloride (HCl). This gas is highly reactive and forms a corrosive environment within the reactor.
The Thermal Environment
The gasification process inherently requires extreme temperatures to break down feedstock. This high thermal energy acts as a catalyst, intensifying the chemical aggressiveness of the released gases. The environment becomes far more destructive than it would be at ambient temperatures.
The Impact on Standard Equipment
Vulnerability of Standard Steels
Common construction materials, including carbon steel and standard stainless steel, are fundamentally unsuited for this specific chemical environment. While effective for many applications, they lack the chemical resilience to withstand concentrated acidic attack.
Rapid Material Erosion
The presence of HCl leads to severe erosion of the reactor walls. This is not a slow cosmetic process; it is a rapid degradation of the material's physical structure. Over time, this erosion compromises the pressure boundary of the vessel.
Engineering for Longevity and Safety
Utilizing Special Alloys
To counteract the effects of HCl, gasification systems must be constructed using special high-corrosion-resistant alloys. These materials are specifically formulated to maintain their structural integrity even when exposed to acidic gases at high temperatures.
Implementing Protective Liners
In addition to solid alloy construction, systems may utilize specialized liners. These act as a protective barrier, isolating the structural shell of the reactor from the corrosive environment inside. This is essential for ensuring the operational lifespan of the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Initial Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
High-corrosion-resistant alloys and specialized liners represent a significant upfront investment compared to standard steel. However, attempting to reduce costs by using inferior materials is a false economy. The result will inevitably be rapid equipment failure and expensive downtime.
Maintenance Implications
Even with resistant materials, processing corrosive feedstocks like PET and PVC adds complexity to maintenance. Operators must remain vigilant, as the consequences of a liner breach or alloy failure are severe due to the toxicity and heat of the gases involved.
Ensuring System Integrity in Plastic Gasification
Selecting the right materials is the single most important factor in designing a viable PET/PVC gasification plant. Failing to account for HCl production is a primary cause of system failure.
- If your primary focus is Operational Continuity: Specify high-grade alloys or liners immediately to prevent rapid erosion that leads to unscheduled shutdowns.
- If your primary focus is Safety: Treat the containment of HCl gas as a critical safety parameter; standard steel cannot be relied upon to prevent leaks in this environment.
By accounting for the chemical reality of PET and PVC decomposition, you safeguard both your capital investment and your operational personnel.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Suitability for PET/PVC Gasification | Key Risks / Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Not Recommended | Rapid erosion; high risk of catastrophic failure from HCl. |
| Standard Stainless Steel | Low | Vulnerable to acidic attack at high temperatures. |
| Special High-Nickel Alloys | Highly Recommended | Exceptional resistance to HCl; maintains structural integrity. |
| Refractory / Specialized Liners | Recommended | Acts as a protective barrier to shield the reactor shell. |
Protect Your Investment with KINTEK Expertise
Don't let acidic corrosion compromise your gasification operations. KINTEK provides advanced, high-temperature lab solutions backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing. Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our equipment is fully customizable to withstand the harshest chemical environments, including PET and PVC processing.
Safeguard your facility and maximize equipment lifespan today. Contact our technical specialists to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Mariana Busto, Carlos R. Vera. Catalytic and Non-Catalytic Co-Gasification of Biomass and Plastic Wastes for Energy Production. DOI: 10.3390/catal15090844
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the production of hydrochar? Optimize Biomass Carbonization
- Why are temperature control and pressure critical for V-NbOPO4@rGO electrode sheets? Optimize Your Battery Performance
- What is the function of zone melting purification equipment in the preparation of CsPbBr3 perovskite single crystals? Key for 6N.
- What is the physicochemical mechanism of phosphoric acid in ceramic sintering? Master Berlinite Densification
- What are the uses of furnace in laboratory? The Essential Tool for Material Transformation
- How does a precision carbon dioxide gas flow control system influence the precipitation of high-purity lithium carbonate?
- What role does a closed pressure vessel play during the carbonation of gamma-C2S? Unlock Rapid Mineralization
- What are the advantages of using batch furnaces? Boost Your Process Flexibility and Precision



















