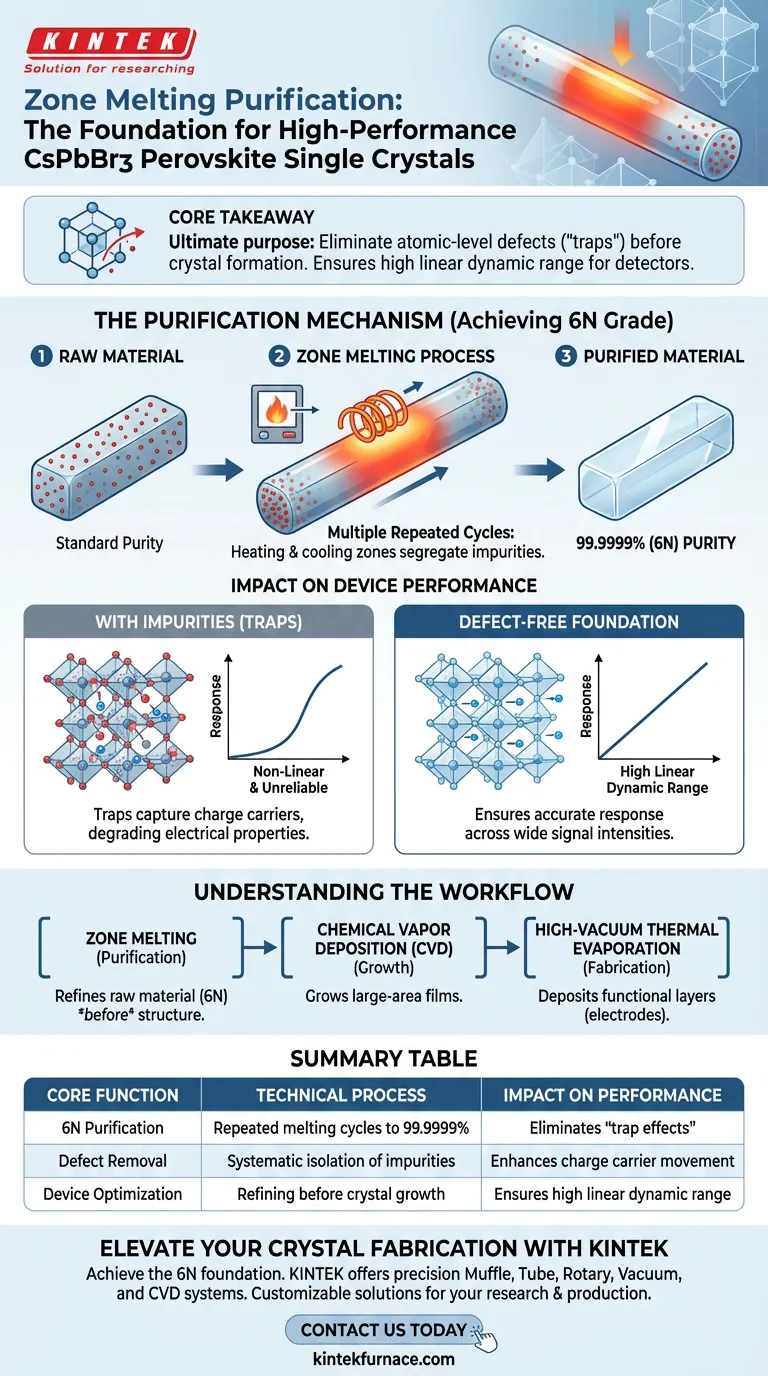
Zone melting purification equipment functions as the primary refinement tool to process raw materials into an ultra-high purity state of 99.9999% (6N grade). Through a process of multiple repeated melting cycles, this equipment systematically isolates and removes impurity elements to prepare the material for high-performance crystal growth.
Core Takeaway The ultimate purpose of zone melting is to eliminate material defects at the atomic level before crystal formation begins. This purification is the non-negotiable foundation required to prevent "trap effects," thereby ensuring the final detector achieves a high linear dynamic range.
The Purification Mechanism
Achieving 6N Grade Purity
The primary technical metric for this equipment is the achievement of 6N grade purity (99.9999%).
Standard raw materials often contain trace elements that disrupt crystal lattice structures. Zone melting equipment subjects these materials to repeated heating and cooling zones, effectively segregating impurities from the pure material.
Multiple Repeated Cycles
Purification is not a single-pass event; it requires multiple repeated zone melting cycles.
Each cycle further concentrates impurities at one end of the ingot, leaving the remaining material progressively purer. This iterative process is essential to reach the rigorous standards required for semiconductor-grade CsPbBr3.
Impact on Device Performance
Elimination of Defects and Traps
The presence of impurity elements in a crystal lattice creates defects, often referred to as "traps."
These traps capture charge carriers (electrons or holes), impeding their movement and degrading the electrical properties of the material. Zone melting removes the impurities that cause these traps, ensuring a pristine crystalline structure.
Enabling High Linear Dynamic Range
For radiation detectors, performance is defined by the linear dynamic range.
If a crystal has high trap density due to impurities, the detector's response to radiation becomes non-linear and unreliable. By providing a defect-free foundation, zone melting ensures the detector responds accurately across a wide range of signal intensities.
Understanding the Workflow Distinctions
Purification vs. Growth vs. Fabrication
It is vital to distinguish the role of zone melting from other equipment in the production line.
Zone Melting is strictly for refining the raw material before the final device structure is created.
In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) systems are used later to actually grow the large-area perovskite films on substrates. Similarly, High-vacuum thermal evaporation is used at the very end to deposit functional layers, such as C60 passivation and Bismuth (Bi) electrodes. Zone melting provides the clean canvas; CVD and thermal evaporation paint the picture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve optimal results in CsPbBr3 device fabrication, you must apply the correct process at the correct stage:
- If your primary focus is reducing electronic noise and trap effects: Prioritize zone melting purification to ensure your starting raw materials reach 6N (99.9999%) purity.
- If your primary focus is creating large-area, uniform films: Focus on optimizing the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) parameters to control precursor transport and crystallinity.
- If your primary focus is charge collection and polarity adjustment: Concentrate on high-vacuum thermal evaporation to precisely manage the thickness of electrode and passivation layers.
High-performance detectors are impossible without the foundational purity established by zone melting.
Summary Table:
| Core Function | Technical Process | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| 6N Purification | Repeated melting cycles to reach 99.9999% purity | Eliminates atomic-level "trap effects" |
| Defect Removal | Systematic isolation of impurity elements | Enhances charge carrier movement |
| Device Optimization | Refining raw materials before crystal growth | Ensures high linear dynamic range in detectors |
Elevate Your Crystal Fabrication with KINTEK
Achieving 6N purity is the non-negotiable foundation for high-performance CsPbBr3 detectors. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers precision-engineered Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique research or production needs.
Don't let impurity traps limit your device potential. Contact us today to discover how our advanced thermal processing solutions can ensure the defect-free results your project demands!
Visual Guide
References
- Jincong Pang, Guangda Niu. Reconfigurable perovskite X-ray detector for intelligent imaging. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46184-0
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of the thermal reduction process for graphene oxide-cement? Master Thermal Activation in Furnaces
- What are the advantages of Zr2Cu alloy over pure zirconium in RMI? Optimize Fiber Integrity at Lower Temperatures
- What are the primary advantages of using a downdraft fixed-bed reactor for co-gasification? Pure Syngas Made Simple
- How do atomizers and furnaces function in Spray Pyrolysis? Master Nanoparticle Synthesis
- What is the temperature of a sintering furnace? From 1100°C to 2200°C+ for Your Material
- What happens during the recovery stage of the annealing process? Unlock Stress Relief and Material Restoration
- How do industrial molds and 10 MPa pressure impact PEEK quality? Unlock Superior Density & Structural Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature heating environment play in the hydrothermal synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite crystals?



















