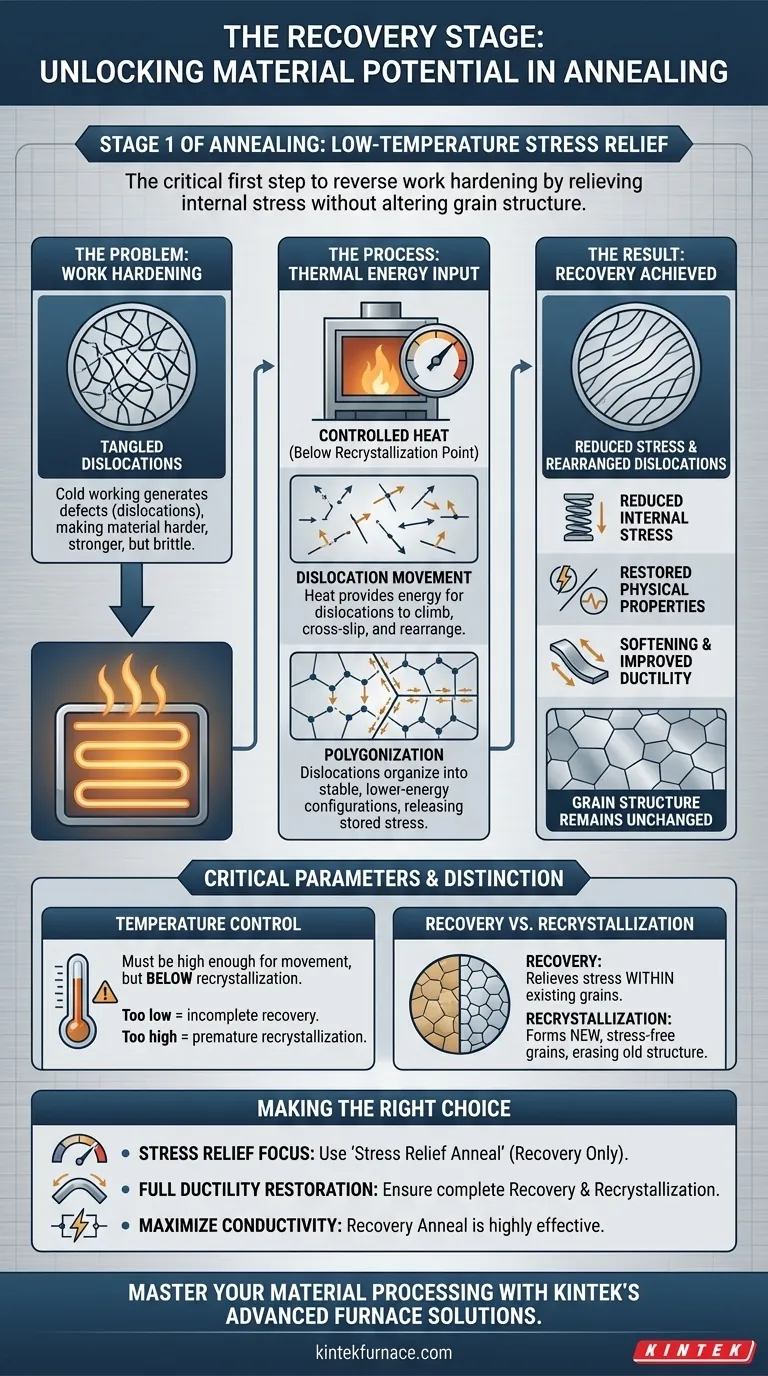
At its core, the recovery stage is the initial, low-temperature phase of the annealing process. During recovery, the primary goal is to relieve the internal stresses stored within a material from processes like cold working. This is achieved by heating the material to a carefully controlled temperature below its recrystallization point, which allows internal defects to rearrange without fundamentally altering the material's grain structure.
Annealing is used to reverse the effects of work hardening. Recovery is the critical first step in this reversal—it acts as a "stress relief" phase, repairing the internal crystal lattice damage before the more transformative stage of recrystallization begins.

The Purpose of Recovery: Reversing Work Hardening
To understand recovery, you must first understand the problem it solves: work hardening (or strain hardening).
The Effect of Work Hardening
When a metal is plastically deformed at a low temperature (e.g., bent, rolled, or drawn), defects called dislocations are generated and become tangled within its crystalline structure.
These tangled dislocations impede further deformation, making the material harder and stronger but also less ductile and more brittle. This stored internal energy is what recovery aims to release.
The Role of Thermal Energy
Heating the material provides the thermal energy necessary for atoms and dislocations to move.
During the recovery stage, the temperature is just high enough to allow dislocations to become mobile. They can then climb, cross-slip, and rearrange into lower-energy configurations.
What Changes (and What Doesn't)
The most critical distinction of the recovery phase is what changes. Dislocations rearrange and are partially annihilated, which significantly reduces stored internal stress.
However, the fundamental grain boundaries of the material do not move or change. The overall grain structure remains the same as it was in the cold-worked state.
Key Material Changes During Recovery
The rearrangement of dislocations has several measurable effects on the material's properties.
Reduction of Internal Stress
This is the primary outcome of recovery. As dislocations organize into more stable patterns (a process known as polygonization), the stored energy from cold working is substantially relieved.
Restoration of Physical Properties
Physical properties that are sensitive to crystal lattice defects, such as electrical and thermal conductivity, are largely restored during recovery. The more orderly lattice offers less resistance to the flow of electrons and heat.
Softening and Improved Ductility
By relieving internal stress, the material becomes softer and regains some of its ductility. While the most significant softening occurs later in recrystallization, recovery provides a noticeable improvement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Parameters
Effective annealing requires precise control, and the recovery stage is no exception.
The Importance of Temperature Control
The temperature must be high enough to enable dislocation movement but remain below the recrystallization temperature.
If the temperature is too low, recovery will be incomplete. If it is too high, the process will quickly proceed into recrystallization, which may not be the desired outcome if the goal is only stress relief. As noted, poor control can also induce new thermal stresses.
Recovery vs. Recrystallization
It is crucial to distinguish between these two stages.
- Recovery: Relieves stress within existing grains. The grain structure is unchanged.
- Recrystallization: Forms entirely new, stress-free grains, erasing the old grain structure.
Recovery is the essential preparatory step that must occur before recrystallization can begin.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding recovery allows you to apply heat treatment with greater precision to achieve specific engineering outcomes.
- If your primary focus is stress relief without major softening: A "stress relief anneal" is what you need, where you heat the material into the recovery range but intentionally stay below the recrystallization temperature.
- If your primary focus is to fully restore ductility for further forming: You must ensure the material passes completely through recovery and is held at the recrystallization temperature long enough to form a new grain structure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing electrical conductivity: A recovery anneal is highly effective, as it resolves the lattice defects that impede electron flow without changing the grain size.
Ultimately, mastering the recovery stage gives you precise control over a material's internal energy and resulting properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Stage | Initial phase of annealing, below recrystallization temperature |
| Primary Goal | Relieve internal stresses from cold working |
| Key Changes | Dislocations rearrange and annihilate; grain structure unchanged |
| Property Effects | Reduced stress, restored electrical/thermal conductivity, improved ductility |
| Temperature Control | Critical to avoid incomplete recovery or premature recrystallization |
Master Your Material Processing with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Are you looking to enhance your annealing processes with precise temperature control for stress relief and material restoration? KINTEK specializes in providing high-temperature furnaces tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our solutions meet your specific experimental requirements, helping you achieve superior results in material science and engineering.
Don't let inefficient equipment hold you back—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can optimize your laboratory's performance and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















