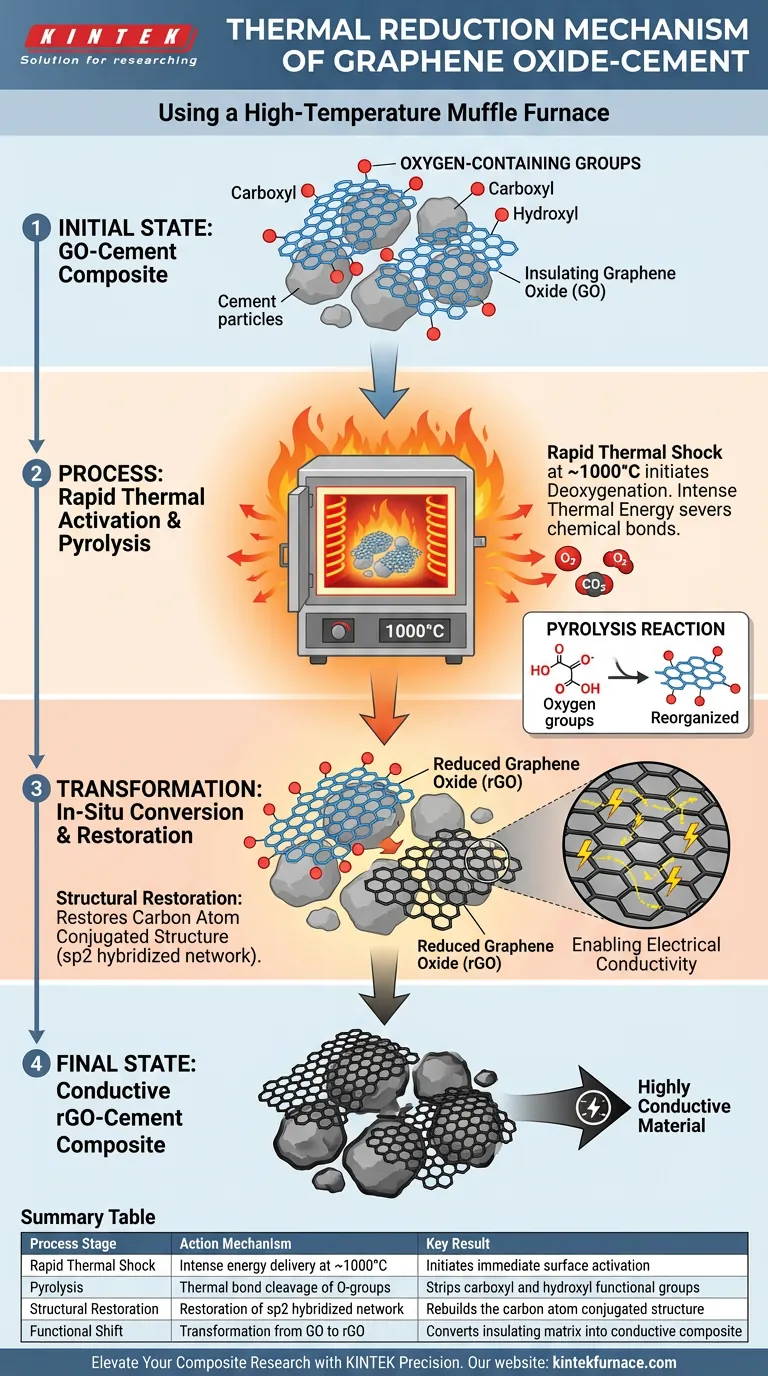
The thermal reduction of graphene oxide (GO) within a cement matrix is fundamentally a process of rapid thermal activation and chemical decomposition. By utilizing a high-temperature muffle furnace to reach temperatures around 1000°C, you induce a pyrolysis reaction that systematically strips away unstable oxygen-containing functional groups. This effectively facilitates the in-situ conversion of insulating graphene oxide into highly conductive reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
Core Takeaway: The muffle furnace does not simply dry the material; it acts as a reactor for "deoxygenation." By applying intense thermal energy, you sever the bonds of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, restoring the carbon atom conjugated structure and transforming the material's electrical properties.

The Mechanism of Thermal Activation
Rapid Thermal Shock
The primary function of the high-temperature muffle furnace in this context is to provide a stable, intense heat source.
When the GO-adsorbed cement is exposed to temperatures such as 1000°C, the thermal energy acts immediately on the surface-adsorbed layers. This rapid delivery of energy is critical to initiate reactions that would not occur at standard curing temperatures.
Pyrolysis and Deoxygenation
At the molecular level, the mechanism is defined by pyrolysis.
Graphene oxide is laden with oxygen-containing functional groups, specifically carboxyl and hydroxyl groups. These groups are thermally unstable. The furnace's heat causes these chemical bonds to break, effectively "evaporating" the oxygen components from the carbon lattice.
In-Situ Conversion
This process is unique because it occurs in-situ—meaning the transformation happens directly on the cement surface.
The GO is not reduced separately and then added; it is reduced while adsorbed on the cement particles. This creates a deeply integrated composite where the transition from GO to rGO happens within the material's final physical framework.
Structural and Functional Restoration
Restoring the Carbon Lattice
The removal of oxygen groups has a profound structural impact.
As the oxygen atoms are expelled, the material undergoes a reorganization. This restores the carbon atom conjugated structure (the sp2 hybridized network). This restoration is the physical reversal of the damage caused during the initial oxidation of graphite to create GO.
Enabling Electrical Conductivity
The direct result of restoring the conjugated structure is a dramatic shift in properties.
GO is typically an electrical insulator due to the disruption of its electron flow. By converting it to rGO through thermal reduction, you restore the electron pathways. This significantly increases the electrical conductivity of the resulting cement composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision is Critical
While high heat is necessary for reduction, the precision of temperature control is equally vital.
As noted in industrial contexts, furnaces can reach temperatures ranging from 1350°C to 1450°C to simulate cement kilns. However, for GO reduction, adherence to the specific activation temperature (e.g., 1000°C) is key.
The Risk of Over-firing or Under-firing
There is a delicate balance to maintain during this process.
If the temperature is too low, the deoxygenation will be incomplete, leaving the material insulating. If the temperature is uncontrolled or excessively high (pushing toward sintering phases of 1400°C+), you risk altering the mineral phases of the cement or degrading the carbon structure entirely through oxidation (if the atmosphere isn't controlled).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of thermal reduction in graphene oxide-cement composites, consider your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize reaching the full activation temperature (approx. 1000°C) to ensure the complete removal of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups for maximum lattice restoration.
- If your primary focus is Material Integrity: Ensure your muffle furnace has precise programmable controls to prevent temperature overshoots that could induce unwanted liquid-phase sintering or degrade the cement mineral phases.
Success in this process relies not just on applying heat, but on precisely controlling the pyrolysis window to engineer the material's microstructure.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Action Mechanism | Key Result |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Thermal Shock | Intense energy delivery at ~1000°C | Initiates immediate surface activation |
| Pyrolysis | Thermal bond cleavage of O-groups | Strips carboxyl and hydroxyl functional groups |
| Structural Restoration | Restoration of sp2 hybridized network | Rebuilds the carbon atom conjugated structure |
| Functional Shift | Transformation from GO to rGO | Converts insulating matrix into conductive composite |
Elevate Your Composite Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect sp2 lattice restoration in graphene-cement composites requires more than just heat—it requires absolute thermal control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems designed to handle critical pyrolysis windows with precision.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are customizable to your unique research needs, ensuring you avoid the risks of under-firing or mineral phase degradation. Contact us today to discover how our high-temperature solutions can optimize your material's electrical conductivity and structural integrity.
Visual Guide
References
- Jie Yao, Ying Ma. In Situ Preparation of rGO-Cement Using Thermal Reduction Method and Performance Study. DOI: 10.3390/ma17051209
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is a forced-air drying oven necessary for impregnated kaolin catalysts? Achieve Uniform Component Immobilization
- Why is vacuum freeze-drying necessary for FeNC/MXene catalysts? Preserving 2D Architecture for Peak Performance
- What factors should be considered when selecting a furnace based on processing requirements? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Equipment
- Why is a high-pressure autoclave essential for nanomaterials? Unlock Superior Crystallinity and Quantum Yield
- What are the two methods of temperature control of resistance furnace? Optimize for Precision or Cost
- What is a batch furnace and how does it operate? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Diverse Applications
- What conditions are required for grafting norbornene functional groups onto S-glass fiber surfaces? Expert Protocol
- Why is a forced air circulation oven required for Al-Cu-Mn alloy aging? Achieve Peak Hardness with Uniform Heat



















