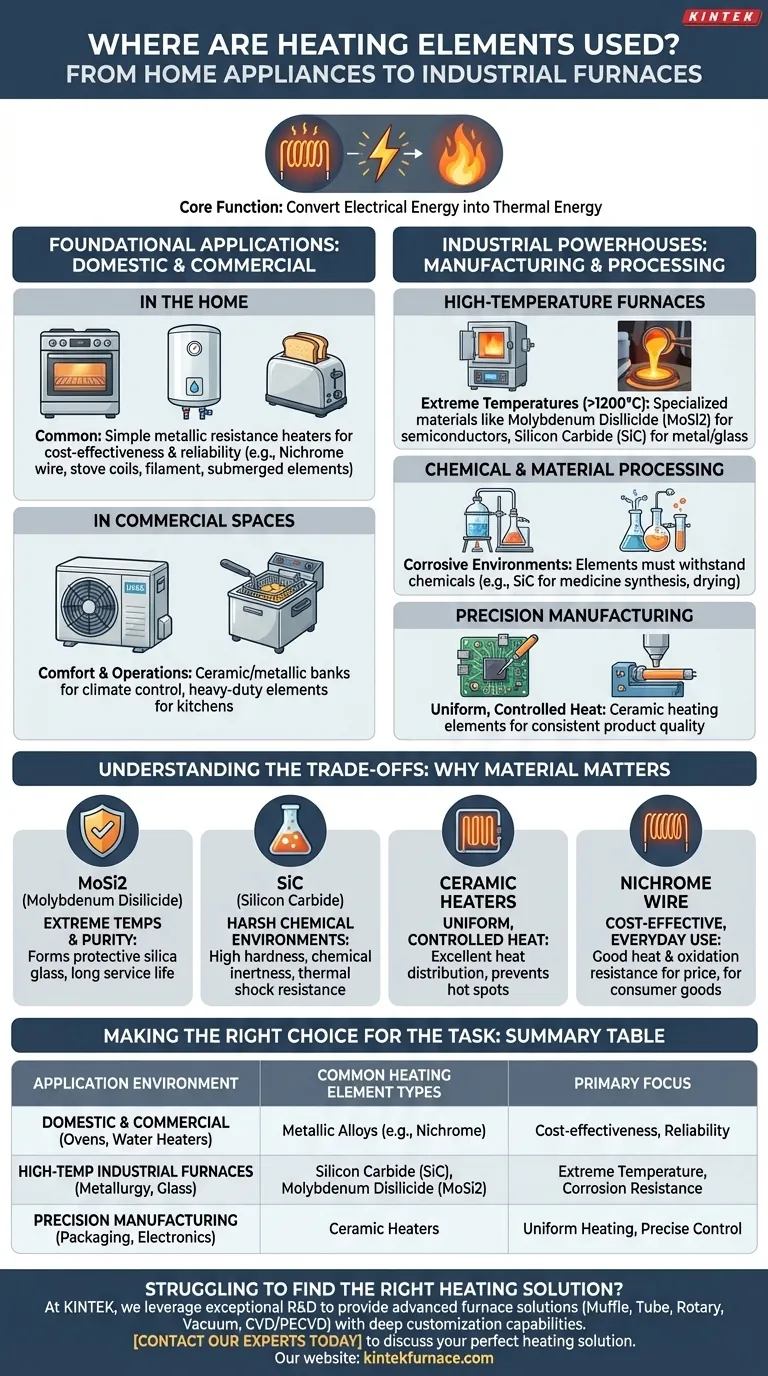
At their core, heating elements are used in any application that requires converting electrical energy into thermal energy. You will find them in an enormous range of settings, from common household appliances like ovens and water heaters to highly specialized industrial furnaces used for manufacturing semiconductors and processing metals at extreme temperatures.
While heating elements are ubiquitous, their application is not one-size-fits-all. The choice of a specific heating element is dictated by the precise demands of the task, balancing temperature requirements, environmental conditions, and the need for controlled, uniform heat.

Foundational Applications: Domestic and Commercial Use
The most familiar applications of heating elements are in the devices we use every day for comfort and cooking.
In the Home
Simple metallic resistance heaters are the workhorses of most home appliances. Their primary benefit is cost-effectiveness and reliability for moderate temperature ranges.
Common examples include the coils in electric stoves and ovens, the filaments in toasters, and the submerged elements in electric water heaters. They are also the core component in portable space heaters and clothes dryers.
In Commercial Spaces
Commercial environments use heating elements for both comfort and operational processes. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems often use banks of ceramic or metallic elements for climate control.
Commercial kitchens rely on heavy-duty versions of these elements for ovens, grills, and deep fryers that require consistent and rapid heating.
The Industrial Powerhouses: Manufacturing and Processing
In industry, heating elements are critical tools for fabricating materials, driving chemical reactions, and enabling precision manufacturing. The choice of element becomes highly specialized.
High-Temperature Furnaces
Processes like metallurgy, glass production, and ceramic firing require furnaces that can operate reliably at extreme temperatures, often well above 1200°C (2192°F).
For these tasks, specialized materials are required. Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements are common in laboratory and semiconductor furnaces, while Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are used in metal and glass processing.
Chemical and Material Processing
The chemical industry uses heating elements for distillation, drying, and synthesizing materials like medicines and fluorescent compounds.
Here, the element must not only provide heat but also withstand potentially corrosive chemical environments, making materials like SiC particularly valuable.
Precision Manufacturing
Tasks like soldering electronics, extruding plastics, or heat-sealing packages demand uniform and tightly controlled heat.
Ceramic heating elements are frequently used in these applications because they provide excellent heat distribution and stability, ensuring consistent product quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Material Matters
The specific material of a heating element is chosen to solve a specific problem. Understanding this is key to understanding their application.
For Extreme Temperatures and Purity
MoSi2 elements are chosen for laboratory furnaces and semiconductor manufacturing because they form a protective layer of silica glass at high temperatures. This gives them exceptional resistance to oxidation and a very long service life in stable, high-heat environments.
For Harsh Chemical Environments
SiC elements are ideal for demanding processes like metal casting and chemical production. Their inherent hardness and chemical inertness allow them to withstand corrosive agents and thermal shock far better than standard metallic elements.
For Uniform, Controlled Heat
Ceramic heaters excel where even heat is paramount, such as in HVAC systems or on packaging machinery. The material's ability to radiate heat uniformly across a surface prevents hot spots and ensures a consistent process.
For Cost-Effective, Everyday Use
The simple nickel-chromium (nichrome) wire found in a toaster is a perfect example of a cost-effective solution. It provides good heat and oxidation resistance for its price point, making it the default choice for mass-produced consumer appliances where extreme performance is not the primary goal.
Making the Right Choice for the Task
To select or understand a heating element's use, you must first define the primary goal of the application.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability (>1500°C): MoSi2 elements are the definitive choice for research furnaces and specialized manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and high heat: SiC elements are purpose-built for harsh industrial processes in metallurgy and chemical production.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating and precise control: Ceramic elements are the best solution for applications like packaging, plastic extrusion, and advanced HVAC.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective consumer goods: Simple metallic alloys like nichrome provide the necessary performance for appliances like ovens and toasters.
Understanding these distinct applications empowers you to see heating elements not just as sources of heat, but as precision tools engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Application Environment | Common Heating Element Types | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic & Commercial (Ovens, Water Heaters) | Metallic Alloys (e.g., Nichrome) | Cost-effectiveness, Reliability |
| High-Temp Industrial Furnaces (Metallurgy, Glass) | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Extreme Temperature, Corrosion Resistance |
| Precision Manufacturing (Packaging, Electronics) | Ceramic Heaters | Uniform Heating, Precise Control |
Struggling to find the right heating solution for your unique process? At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental and industrial requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can engineer the perfect heating solution for your lab or facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















