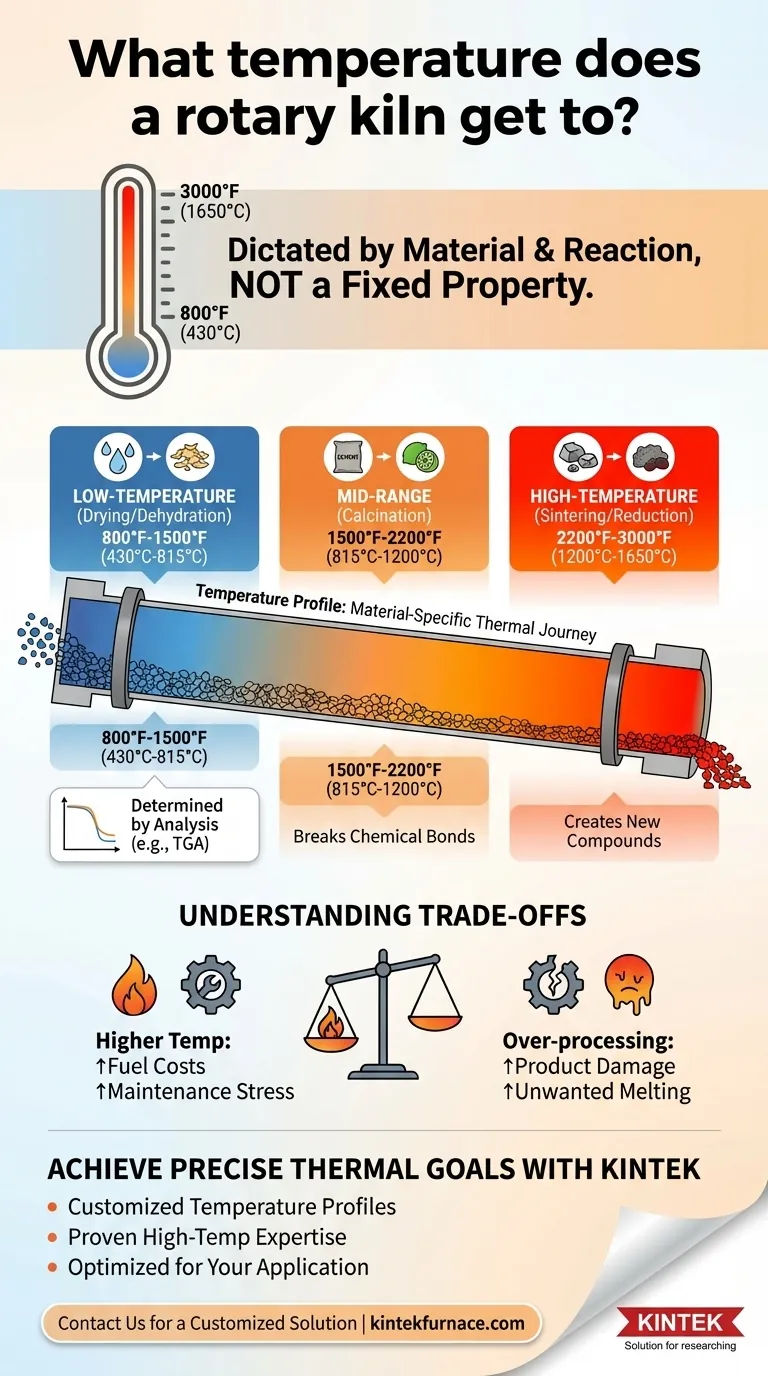
While there is no single answer, the operating temperature of a rotary kiln is dictated entirely by the material being processed and the desired reaction. In general, industrial rotary kilns can operate across a wide spectrum, from around 800°F (430°C) for simple drying up to 3000°F (1650°C) for high-temperature thermal processing.
The critical takeaway is that a kiln's temperature is not a fixed property of the equipment itself. It is a carefully engineered parameter designed to meet the specific chemical and physical requirements of the material inside it.

Why Temperature is a Variable, Not a Constant
The temperature inside a rotary kiln is the primary tool for driving a specific outcome. Different outcomes demand vastly different thermal conditions.
The Material Dictates the Process
The central goal of using a kiln is to induce a change, such as drying, calcination, or chemical reduction. Each of these processes has a unique temperature threshold that must be met.
For example, simply driving off free water requires a relatively low temperature, while breaking down a stable chemical compound requires significantly more thermal energy.
Understanding the Temperature Profile
Professionals rarely speak of a single kiln temperature. Instead, they design a temperature profile, which maps the temperature of the material as it travels from the feed end to the discharge end of the kiln.
This profile ensures the material is heated, held at a peak temperature for a specific residence time, and sometimes cooled in a controlled manner, all within the same machine.
How the Ideal Temperature is Determined
The precise temperature profile is determined through material analysis. A technique called Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) is often used to see where a material loses mass as it is heated.
For instance, TGA can show that free water evaporates around 212°F (100°C), but chemically bound water might only be released at temperatures up to 500°F (260°C). This data is fundamental to designing an effective and efficient process.
Common Temperature Ranges by Application
While every process is unique, we can group common applications into general temperature bands.
Low-Temperature Processes (Drying & Dehydration)
For applications focused on removing surface moisture or loosely bound water, kilns operate at the lower end of their range. This is typically between 800°F and 1500°F (430°C - 815°C).
Mid-Range Processes (Calcination)
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process used to create materials like cement clinker and lime. This requires breaking stronger chemical bonds and typically occurs at temperatures between 1500°F and 2200°F (815°C - 1200°C).
High-Temperature Processes (Sintering & Reduction)
Processes that involve creating new compounds, reducing ores, or sintering materials into a hardened mass require the highest temperatures. These applications can push a kiln to its operational limit, from 2200°F up to 3000°F (1200°C - 1650°C).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operating a kiln is a balance of achieving the desired reaction without introducing negative consequences.
The Cost of Higher Temperatures
Higher temperatures require more fuel, which directly increases operational costs. They also place greater thermal stress on the kiln's refractory lining and steel shell, leading to more frequent and expensive maintenance.
The Risk of Over-processing
Applying too much heat can be as bad as not applying enough. It can damage the final product, create unwanted chemical phases, or cause materials to melt or sinter when that is not the intended outcome.
Equipment Limitations
Not all kilns are built for all temperatures. The type of refractory brick used, the design of the burner system, and even the type of kiln (e.g., an electromagnetic kiln may max out around 2000°F or 1100°C) will impose a hard limit on the maximum achievable temperature.
Determining the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your process requirements are the only factor that can define the correct operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is drying or removing moisture: You will operate at the lower end of the kiln's range, typically below 1500°F (815°C), to efficiently remove water without altering the material's chemistry.
- If your primary focus is calcination for cement or lime: You require a mid-to-high temperature profile, often exceeding 1650°F (900°C), to drive the necessary chemical decomposition.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis or reduction: You will need a kiln designed for the upper thermal limits, potentially approaching 3000°F (1650°C), which requires specialized refractory and robust engineering.
Ultimately, defining your target material transformation is the essential first step to determining the correct kiln operating temperature.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Typical Temperature Range (°F) | Typical Temperature Range (°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature (Drying) | 800°F - 1500°F | 430°C - 815°C | Removing surface moisture, dehydration |
| Mid-Range (Calcination) | 1500°F - 2200°F | 815°C - 1200°C | Cement clinker production, lime calcination |
| High-Temperature (Sintering/Reduction) | 2200°F - 3000°F | 1200°C - 1650°C | Ore reduction, high-temperature synthesis, sintering |
Achieve Your Precise Thermal Processing Goals
Your material's unique requirements dictate the ideal temperature profile. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom rotary kilns, perfectly engineered for your application—whether it's drying, calcination, or high-temperature reduction.
Let our experts design a solution for you:
- Deep Customization: We tailor the temperature profile, refractory lining, and burner system to your specific material transformation goals.
- Proven Expertise: Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, is built for reliability and precision across the entire temperature spectrum.
- Optimized Performance: We ensure efficient operation that balances reaction requirements with operational costs and equipment longevity.
Contact us today to discuss your process requirements and receive a customized solution proposal.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















