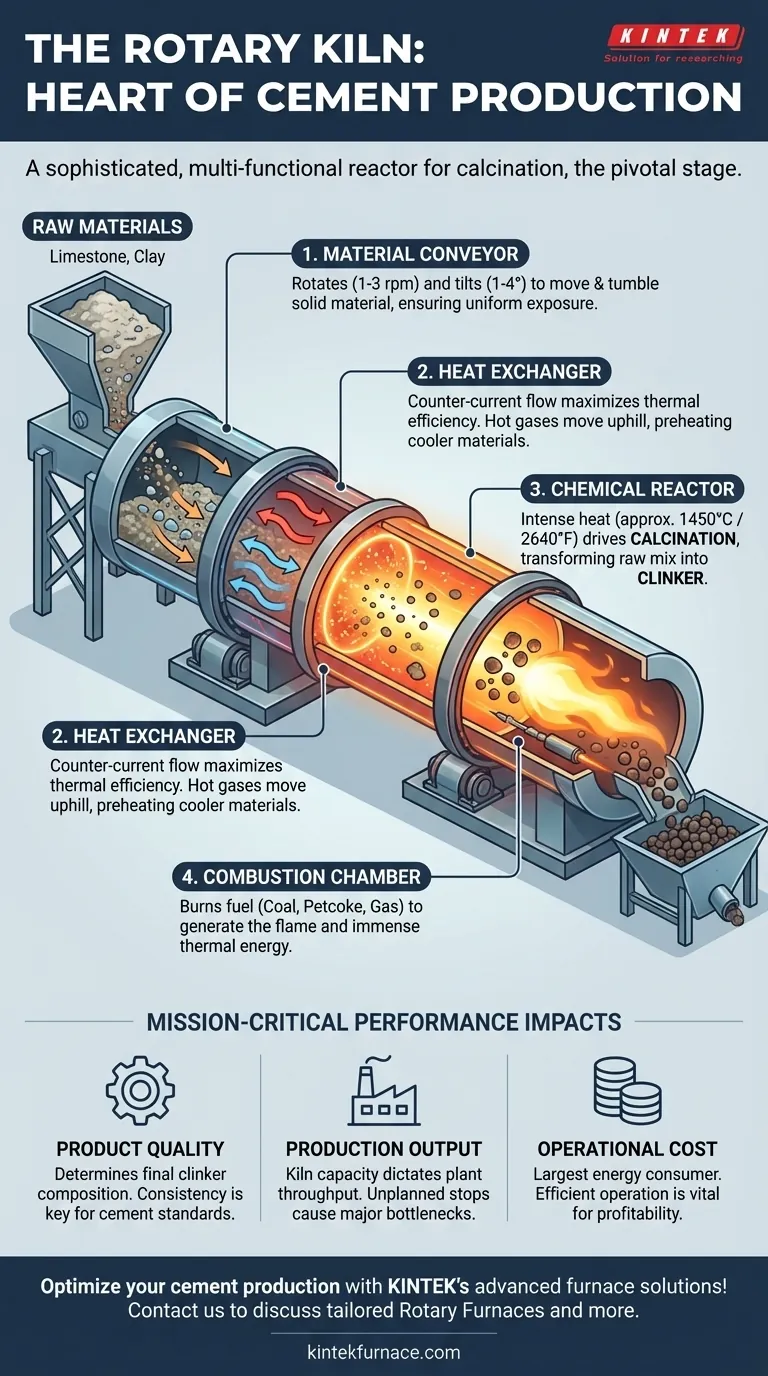
In essence, the rotary kiln is the heart of the modern cement plant. It is a massive, slowly rotating industrial furnace responsible for the chemical transformation of raw materials into a new substance called clinker—the primary component of finished cement. This thermal process, known as calcination, is the pivotal "one firing" stage in the industry's "two grinding, one firing" production sequence.
The rotary kiln is far more than a simple heater. It is a sophisticated, multi-functional reactor where heat transfer, chemical reaction, and material transport are precisely controlled to determine the final quality, output, and cost of the entire cement manufacturing operation.

The Kiln as a Multi-Functional System
To understand the kiln's central role, you must see it not as a single piece of equipment but as an integrated system performing four distinct functions simultaneously.
The Chemical Reactor
The kiln's primary purpose is to act as a chemical reactor. Raw mix, composed mainly of limestone, clay, and other materials, is fed into the kiln and heated to extreme temperatures, typically around 1450°C (2640°F).
This intense heat drives a chemical reaction called calcination, breaking down the raw materials and causing them to form new, complex mineral compounds. The result of this transformation is clinker, a nodular material that forms the basis of cement.
The Heat Exchanger
A rotary kiln is an incredibly effective heat exchange device. It operates on a counter-current flow principle: the raw material slowly tumbles downhill while hot combustion gases flow uphill, moving in the opposite direction.
This design maximizes thermal efficiency. As the hot gases travel the length of the kiln, they progressively transfer their heat to the cooler material, ensuring energy is used effectively throughout the entire process.
The Material Conveyor
The kiln is a physical conveyor. It is installed at a slight angle to the horizontal, typically inclined by 1 to 4 degrees.
As the kiln rotates slowly (about 1-3 revolutions per minute), this inclination causes the solid material to tumble and gradually move from the upper inlet end to the lower discharge end. This tumbling action is critical, as it ensures every particle is evenly exposed to the hot gases, leading to uniform and consistent clinker production.
The Combustion Chamber
The kiln itself serves as the combustion chamber where fuel—such as coal, petcoke, or natural gas—is burned to generate the immense thermal energy required for the process. The flame and hot gases produced here are the engine of the entire system.
Why Kiln Performance is Mission-Critical
The technical performance and operational stability of the rotary kiln directly dictate the success of the entire plant. As the industry saying goes, "As long as the kiln turns, there will be tens of millions," highlighting its financial importance.
Impact on Product Quality
The final chemical composition of the clinker is determined by the temperature profile and the amount of time the material spends in the kiln (retention time). Minor deviations in kiln operation can lead to improperly formed clinker, resulting in substandard cement that fails to meet quality specifications.
Impact on Production Output
The throughput of the entire cement plant is limited by the capacity of its kiln. Any unplanned stop or reduction in kiln speed immediately creates a bottleneck, halting production and causing significant financial losses from lost output.
Impact on Operational Cost
The rotary kiln is the single largest consumer of energy in a cement plant, accounting for a massive portion of the production cost. An inefficiently operated kiln wastes fuel and increases energy consumption per ton of clinker, directly eroding the plant's profitability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the kiln's function allows you to focus on the variables that matter most for your specific role.
- If your primary focus is process engineering: Your goal is to optimize the delicate balance between the material feed rate, kiln rotational speed, and fuel combustion to maximize thermal efficiency and produce consistent clinker.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and reliability: The kiln's continuous operation is paramount; you must ensure the mechanical integrity of the drive system and the refractory lining to prevent catastrophic failures and costly downtime.
- If your primary focus is product quality control: You must treat the kiln as the primary variable influencing the chemical makeup of the clinker, constantly monitoring its parameters to guarantee the final product meets specifications.
Ultimately, mastering the principles of the rotary kiln is fundamental to understanding the entire cement manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Reactor | Heats raw materials to 1450°C for calcination | Forms clinker, the basis of cement |
| Heat Exchanger | Uses counter-current flow for efficient heating | Maximizes thermal energy use |
| Material Conveyor | Rotates and tilts to move materials | Ensures uniform exposure and consistent output |
| Combustion Chamber | Burns fuel to generate high temperatures | Powers the entire production process |
Optimize your cement production with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and industrial facilities with high-temperature furnace systems like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental and production needs, enhancing efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















