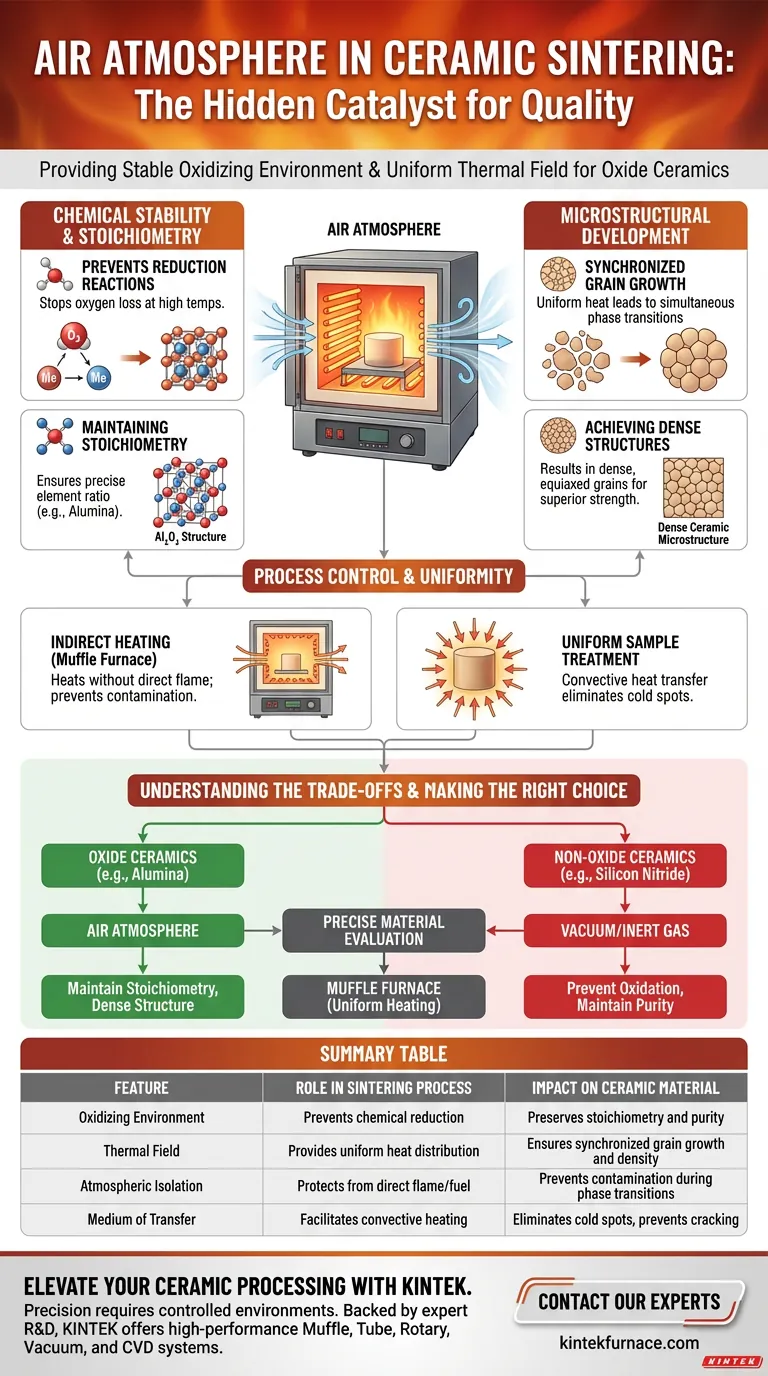
The primary role of the air atmosphere in a high-temperature box or muffle furnace is to provide a stable oxidizing environment necessary for processing oxide ceramics. By maintaining an oxygen-rich setting, the atmosphere preserves the material's chemical balance (stoichiometry) and prevents unwanted reduction reactions. Furthermore, the air medium facilitates a uniform thermal field, which is critical for consistent microstructural development.
The air atmosphere acts as a chemical stabilizer for oxide ceramics, ensuring stoichiometry is maintained while promoting synchronized grain growth through a uniform thermal field.

Chemical Stability and Stoichiometry
Preventing Reduction Reactions
For many ceramic materials, particularly oxides, exposure to high temperatures in an inert or reducing atmosphere can cause the material to lose oxygen. The air atmosphere in a box furnace prevents this reduction, ensuring the chemical composition remains stable throughout the sintering process.
Maintaining Material Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the precise ratio of elements within the ceramic compound. By providing a consistent supply of oxygen, the furnace atmosphere ensures that materials like alumina maintain their correct chemical structure, which is vital for achieving the desired mechanical and electrical properties.
Microstructural Development
Synchronized Grain Growth
The atmosphere contributes to a uniform thermal field within the furnace chamber. This uniformity ensures that the entire ceramic green body reaches phase transition temperatures simultaneously, leading to synchronized grain growth rather than uneven crystallization.
Achieving Dense Structures
Proper atmospheric control results in a specific microstructure characterized by dense, equiaxed grains. This structure is the hallmark of a successfully sintered ceramic, offering superior strength and durability compared to structures formed under uneven thermal or atmospheric conditions.
Process Control and Uniformity
Indirect Heating Benefits
In muffle furnaces specifically, the design ensures that the air atmosphere heats the sample without direct exposure to flames. This isolation prevents contamination from fuel sources and allows for precise temperature regulation, which is essential for accurate material evaluation.
Uniform Sample Treatment
The air atmosphere serves as the medium for convective heat transfer. This ensures that the sample is heated uniformly from all sides, eliminating cold spots that could lead to cracking or incomplete sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Limitations for Non-Oxide Ceramics
While an air atmosphere is ideal for oxides, it is detrimental to non-oxide ceramics like aluminum nitride or silicon nitride. In an air furnace, these materials would oxidize and degrade; therefore, they require vacuum or inert gas atmospheres to maintain purity.
Integrated Degreasing Capabilities
Standard air sintering in a box furnace may not be suitable for complex processing steps like integrated degreasing and sintering. Vacuum sintering furnaces are often preferred for these advanced applications as they allow for precise atmospheric manipulation to remove binders before densification occurs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace atmosphere, you must align the environment with the chemical needs of your specific material.
- If your primary focus is oxide ceramics (e.g., Alumina): Rely on an air atmosphere to maintain stoichiometry and achieve a dense, equiaxed grain structure.
- If your primary focus is non-oxide ceramics (e.g., Silicon Nitride): Avoid air atmospheres and opt for vacuum or inert gas sintering to prevent oxidation and ensure high-quality production.
- If your primary focus is precise material evaluation: Utilize a muffle furnace to ensure uniform heating and protect samples from direct flame exposure.
Choosing the right atmosphere is not just about temperature; it is about controlling the chemical destiny of your material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Sintering Process | Impact on Ceramic Material |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing Environment | Prevents chemical reduction | Preserves stoichiometry and material purity |
| Thermal Field | Provides uniform heat distribution | Ensures synchronized grain growth and density |
| Atmospheric Isolation | Protects from direct flame/fuel | Prevents contamination during phase transitions |
| Medium of Transfer | Facilitates convective heating | Eliminates cold spots and prevents structural cracking |
Elevate Your Ceramic Processing with KINTEK
Precision in sintering requires more than just heat—it requires a perfectly controlled environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you are processing oxide ceramics in air or require advanced vacuum systems for non-oxide materials, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces ensure uniform thermal fields and superior microstructural development. Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace solution tailored to your unique research and production needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaoxiao Li, Yanjie Ren. The Influence of an Alternating Current Field on Pack Boriding for Medium Carbon Steel at Moderate Temperature. DOI: 10.3390/coatings15010039
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are Box Furnaces typically loaded? Manual Methods for Flexible Batch Processing
- How does the high-temperature calcination process in a muffle furnace facilitate the structural transformation of KMnPO4·H2O?
- How are muffle furnaces categorized based on heating elements? Choose the Right Type for Your Temperature Needs
- What are the different heating methods used in muffle furnaces and drying ovens? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab
- What role does a muffle furnace play in pharmaceutical applications? Ensuring Drug Purity and Compliance
- How does a high-temperature laboratory box furnace facilitate the synthesis of Ba7Nb4MoO20? Achieve Phase Purity
- What are the key applications of muffle furnaces in research and industry? Unlock Precision in Material Transformation
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the post-treatment of cobalt-based catalysts? Optimize Phase Purity via Annealing



















