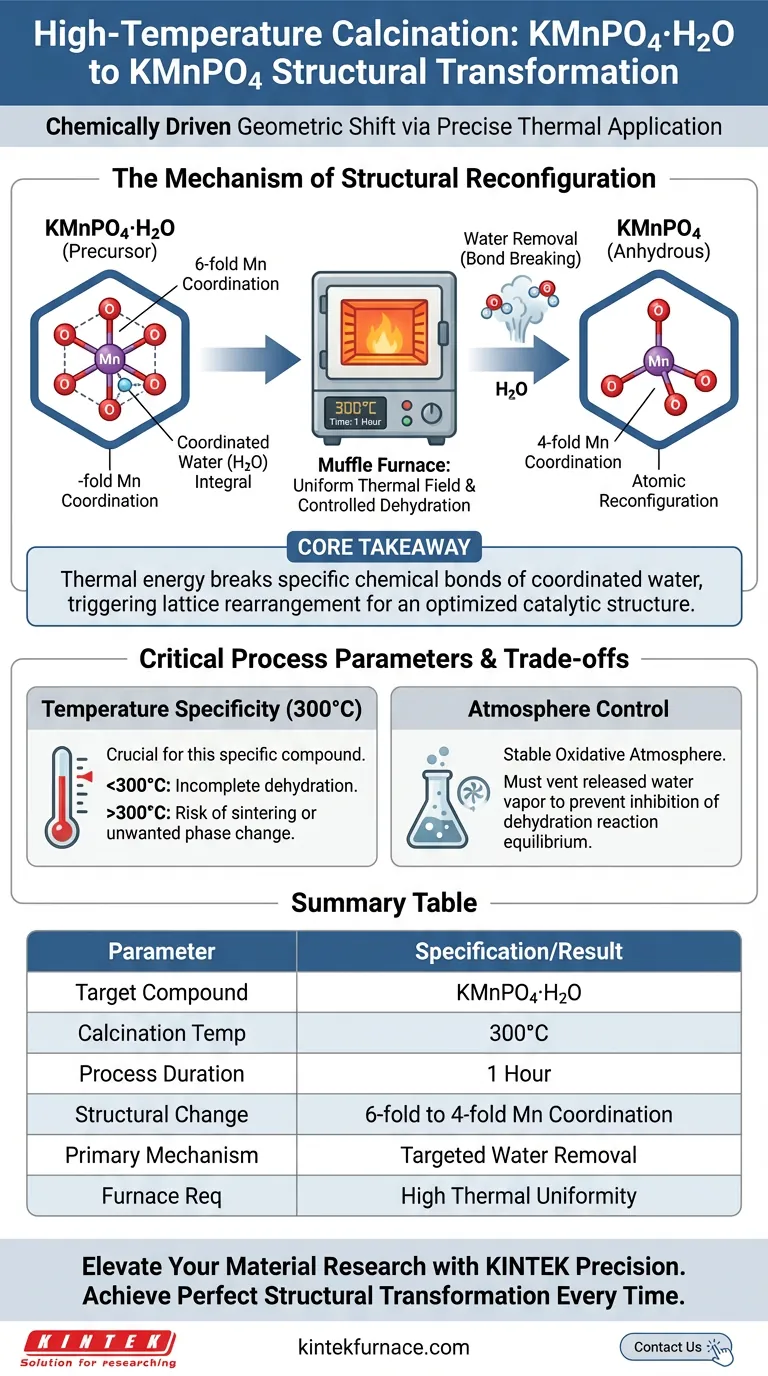
High-temperature calcination functions as a precise dehydration tool to alter atomic coordination. In the specific case of KMnPO4·H2O, subjecting the material to a uniform thermal field at 300°C for one hour drives the removal of coordinated water molecules. This loss of water forces a fundamental structural reconfiguration, transitioning the manganese centers from a six-fold coordination environment to a four-fold coordination in the resulting anhydrous KMnPO4.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace does not merely dry the material; it provides the stable thermal energy required to break specific chemical bonds holding coordinated water. This controlled vacancy triggers the rearrangement of the crystal lattice, converting the manganese geometry to create a structure optimized for catalytic performance analysis.
The Mechanism of Structural Reconfiguration
The transformation of KMnPO4·H2O is not a simple phase change; it is a chemically driven geometric shift enabled by precise thermal application.
Controlled Removal of Coordinated Water
The primary function of the calcination process at 300°C is the targeted elimination of water molecules that are chemically bound (coordinated) to the crystal lattice.
Unlike surface moisture, these molecules are integral to the initial structure. The muffle furnace provides the sustained thermal energy necessary to overcome the binding energy of these coordinated water molecules, effectively stripping them from the compound.
Shift in Manganese Coordination
The removal of water creates a vacancy in the coordination sphere of the manganese atoms.
To stabilize the structure following this loss, the manganese centers undergo a reconfiguration. They transition from a six-fold coordination (bonded to six surrounding atoms/molecules) to a four-fold coordination. This geometric shift is the defining characteristic of the transition from KMnPO4·H2O to KMnPO4.
The Role of the Uniform Thermal Field
The efficacy of this transformation relies heavily on the muffle furnace's ability to maintain a uniform thermal field.
Inconsistencies in temperature would lead to partial dehydration, resulting in a mixed phase where some manganese centers remain six-fold coordinated while others shift to four-fold. A uniform field ensures the entire sample transforms homogeneously, which is critical for accurate correlation between atomic structure and material performance.
Critical Process Parameters and Trade-offs
While the primary reference highlights the success of this process at 300°C, understanding the limitations and requirements of the equipment is essential for reproducibility.
Temperature Specificity
The 300°C setpoint is distinct and critical for this specific phosphate compound.
Operating significantly below this threshold may fail to provide enough energy to break the coordinated water bonds, leaving the six-fold structure intact. Conversely, while muffle furnaces can reach much higher temperatures (up to 900°C for other applications), excessive heat applied to this specific compound could risk sintering or unwanted phase decomposition rather than the desired lattice rearrangement.
Atmosphere Control
A muffle furnace typically provides a stable oxidative atmosphere.
For KMnPO4, this environment allows the precursors to react fully and stabilizes the oxide phases. However, the operator must ensure the furnace allows for the venting of the released water vapor; otherwise, the local humidity pressure could theoretically inhibit the dehydration reaction equilibrium.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The structural transformation of KMnPO4·H2O is a clear example of using thermal energy to engineer atomic geometry.
- If your primary focus is basic material synthesis: Ensure your furnace is calibrated to maintain a strict 300°C with high thermal uniformity to guarantee complete dehydration across the entire sample batch.
- If your primary focus is catalytic research: Verify the transition to four-fold coordination using structural analysis (like XRD) post-calcination, as this specific atomic geometry is the variable that correlates with catalytic activity.
Precision in thermal treatment is the only pathway to achieving the specific atomic coordination required for high-performance catalytic materials.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification/Result |
|---|---|
| Target Compound | KMnPO4·H2O |
| Calcination Temperature | 300°C |
| Process Duration | 1 Hour |
| Structural Change | 6-fold to 4-fold Manganese Coordination |
| Primary Mechanism | Targeted removal of coordinated water molecules |
| Furnace Requirement | High thermal uniformity for homogeneous phase change |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise atomic reconfiguration requires more than just heat; it demands absolute thermal stability. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, and vacuum systems designed to give you total control over your calcination parameters.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are customizable to your unique catalytic research or material synthesis needs. Ensure perfect structural transformation every time with KINTEK’s uniform thermal fields.
Ready to optimize your lab’s high-temperature processes? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Shujiao Yang, Wei Zhang. Electrocatalytic water oxidation with manganese phosphates. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45705-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnaces? Achieve Contaminant-Free Heating for Sensitive Applications
- What is the defining characteristic of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- How do chamber dimensions impact the selection of a muffle furnace? Optimize Heating and Save Costs
- What are the applications of batch furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Your Unique Materials
- What paint industry processes utilize muffle furnaces? Essential for Lab Analysis and Quality Control
- What are the key applications of muffle furnaces in research and industry? Unlock Precision in Material Transformation
- Why is a box resistance furnace utilized for the homogenization annealing of alloy micro-wires? Key Benefits Explained
- How is temperature controlled in a box type electric furnace? Master Precise Heat Regulation for Your Lab



















