In short, batch furnaces are used for thermal processes that require high flexibility and precise control over the heating and cooling cycle, especially for low-to-medium volume production. Their primary applications include the heat treatment of metal components and raw materials (like slabs, billets, and plates), high-temperature forging, and specialized processes like annealing, coating, and advanced material synthesis in fields like semiconductors.
The core value of a batch furnace is its adaptability. Unlike a continuous furnace designed for one repetitive task, a batch furnace excels at handling diverse parts, sizes, and thermal profiles, making it the ideal choice for customized, high-precision work.

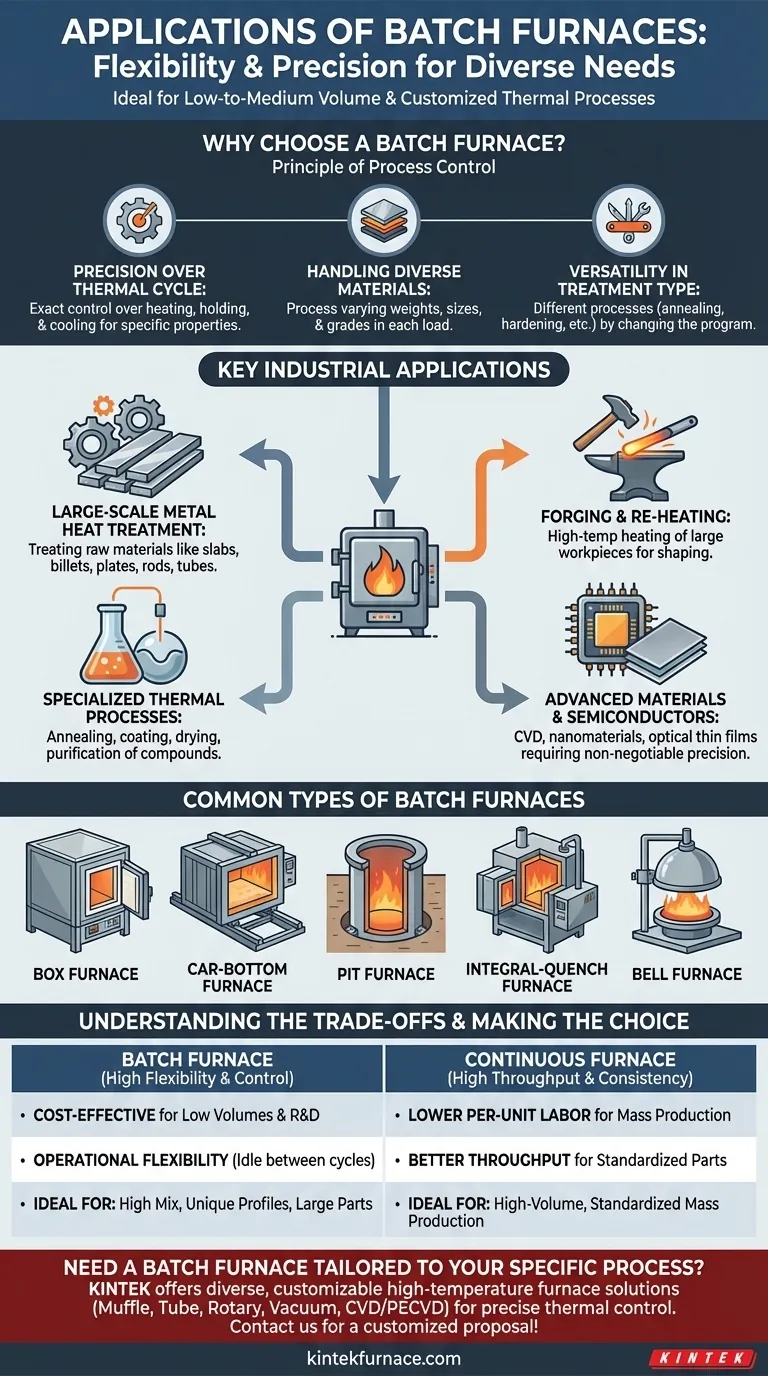
Why Choose a Batch Furnace? The Principle of Process Control
The decision to use a batch furnace is fundamentally about prioritizing control and flexibility over high-volume throughput. It operates by processing a single, discrete load—or "batch"—of material at a time.
Precision Over the Thermal Cycle
Each batch can be subjected to a unique, carefully programmed thermal cycle. This allows for exact control over heating rates, holding times, and cooling rates, which is critical for achieving specific material properties.
Handling Diverse Materials
A single batch furnace can process varying weights, sizes, and grades of material from one load to the next. One batch might be small steel components, while the next could be a large, single aluminum billet.
Versatility in Treatment Type
This flexibility extends to the type of heat treatment performed. The same furnace can be used for different processes like annealing, hardening, tempering, or stress relieving simply by changing the program for each batch.
Key Industrial Applications
The adaptability of batch furnaces makes them essential across a wide range of industries, from heavy manufacturing to high-tech research.
Large-Scale Metal Heat Treatment
This is a primary application. Batch furnaces are used to treat raw materials such as steel or aluminum slabs, billets, plates, rods, and tubes before they undergo further manufacturing.
Forging and Re-heating
High-temperature re-heat furnaces used in forging operations are often batch-type. They heat a large workpiece to the precise temperature required for shaping, ensuring uniformity throughout the material.
Specialized Thermal Processes
Many advanced processes rely on the controlled environment of a batch furnace. These include annealing to soften metals, applying coatings, drying materials, and purifying organic or inorganic compounds.
Advanced Materials and Semiconductors
Specialized batch systems, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces, are critical for high-tech manufacturing. They are used to create semiconductor devices, optical thin films, functional coatings, and nanomaterials where precision is non-negotiable.
Common Types of Batch Furnaces
Different designs are optimized for specific material handling needs and processes.
Box Furnaces
These are the simplest type, featuring a single chamber with a front-opening door. They are highly versatile and used for a wide variety of general-purpose heat-treating applications.
Car-Bottom Furnaces
Ideal for extremely large and heavy workpieces, these furnaces feature a hearth built on a rail-guided car. The car is rolled out for loading and unloading, then rolled into the furnace for processing.
Pit Furnaces
Used for treating long parts like shafts or tubes that are best loaded vertically to minimize distortion. The furnace is a cylindrical chamber installed in a pit in the factory floor.
Integral-Quench Furnaces
These systems combine a heating chamber with an enclosed quenching tank. This allows the entire heat-treat and quench cycle to occur in a controlled atmosphere, which is critical for preventing surface reactions like oxidation.
Bell Furnaces
In this design, a movable, dome-shaped furnace ("the bell") is lowered over a stationary hearth where the material is loaded. This is often used for processes requiring a specific protective atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Batch vs. Continuous
Choosing between a batch and a continuous furnace involves clear trade-offs tied directly to your production goals.
Advantage: Cost-Effectiveness for Low Volumes
Batch furnaces generally have a lower initial investment cost. They are the most economical choice for job shops, R&D labs, and facilities with low-to-medium production volumes or a high mix of different parts.
Advantage: Operational Flexibility
Batch furnaces can achieve a wide range of temperatures and can be easily shut down or idled between cycles, which can be more energy-efficient than running a large continuous furnace for a small amount of product.
Limitation: Throughput and Labor
The primary drawback is lower throughput compared to a continuous furnace. Each batch must be manually or semi-automatically loaded and unloaded, making it less suitable for high-volume, standardized mass production.
Limitation: Consistency in Mass Production
While a single batch has excellent uniformity, achieving perfect consistency between thousands of batches can be more challenging than in a fully automated continuous system where every part sees the exact same conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is low-to-medium volume, high-mix production: A batch furnace is the superior choice due to its inherent flexibility and lower upfront cost.
- If your primary focus is a process requiring a unique or highly precise thermal profile: A batch furnace provides the granular control needed to execute complex heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is processing very large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped components: A specialized design like a car-bottom or pit furnace is often the only practical solution.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized mass production: A continuous furnace will deliver better throughput and lower per-unit labor costs.
Ultimately, a batch furnace is the definitive tool for operations where process control and adaptability are more valuable than sheer speed.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Application | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Thermal Cycle Control | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Hardening) | Metal Components, Slabs, Billets |
| High Flexibility & Adaptability | High-Temperature Forging & Re-heating | Large, Heavy Workpieces |
| Unique Programmable Profiles | Advanced Material Synthesis (CVD, Coatings) | Semiconductors, Nanomaterials |
| Diverse Batch Handling | Specialized Processes (Drying, Purification) | R&D Labs, Job Shops |
Need a Batch Furnace Tailored to Your Specific Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you require a standard box furnace or a specialized car-bottom design for heavy components, we can deliver a solution that ensures precise thermal control and operational flexibility for your low-to-medium volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your application and receive a customized solution proposal!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures



















