In essence, a muffle furnace provides an exceptionally uniform and contaminant-free high-temperature environment. Its primary advantages are precise temperature control and the isolation of materials from heating elements, making it ideal for sensitive applications. The main disadvantages are its relatively low heating efficiency and higher energy consumption compared to direct-heating methods.
The decision to use a muffle furnace hinges on a critical trade-off: prioritizing an immaculate, uniform heating environment over raw energy efficiency. Its core value lies in protecting a sample from contamination, which is an absolute requirement for many analytical and materials science processes.
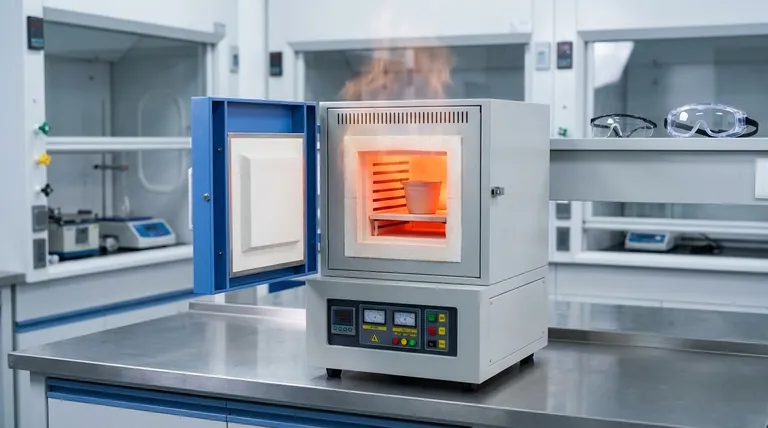

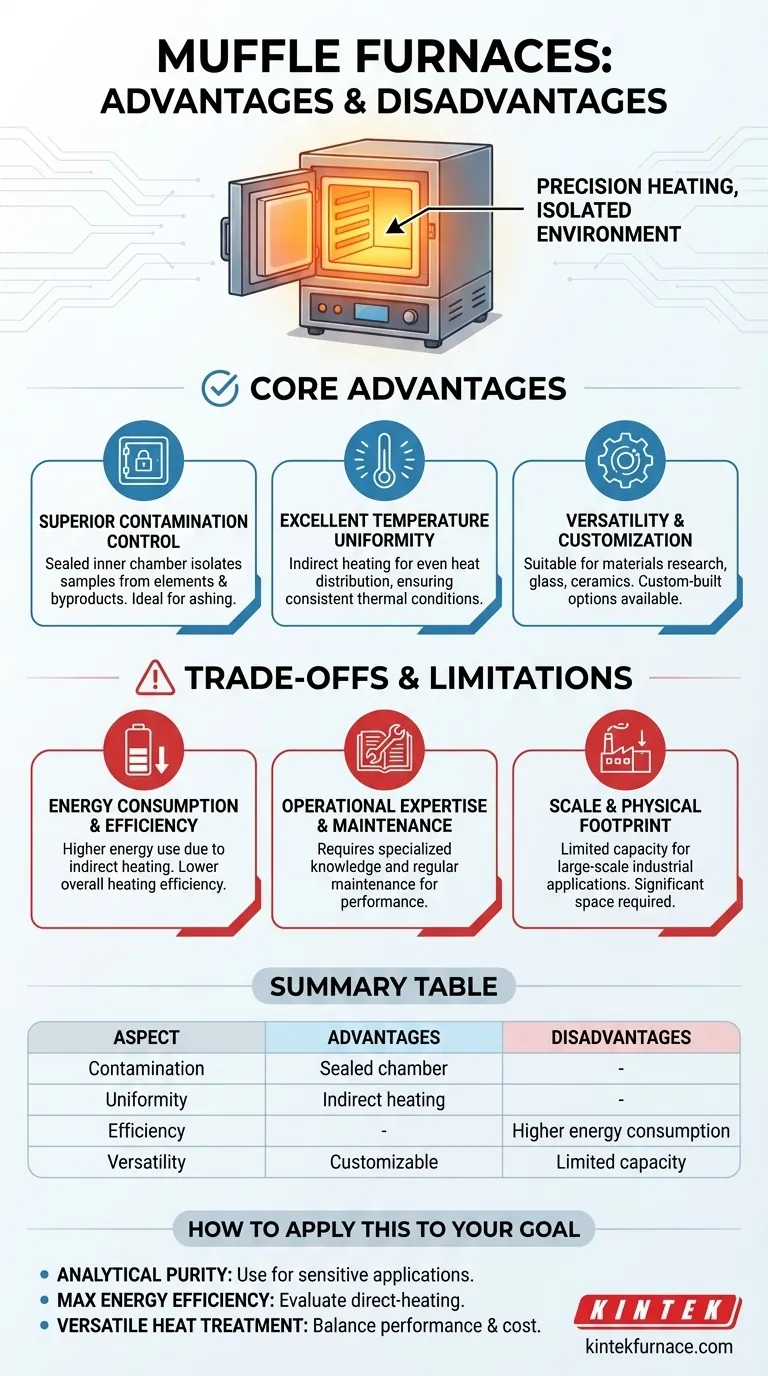
The Core Advantages of a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace's design directly creates its primary benefits. The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber that isolates the sample from the actual heating elements and any combustion byproducts.
Superior Contamination Control
The sealed inner chamber is the defining feature. It ensures that the material being heated is never exposed to fuel, combustion gases, or the electric heating elements themselves.
This isolation is non-negotiable for applications like ashing, where the goal is to determine the non-combustible content of a sample without introducing external contaminants.
Excellent Temperature Uniformity
Because the entire muffle chamber is heated from the outside, it radiates heat evenly onto the sample from all directions. This indirect heating method results in superior temperature uniformity.
For heat-treating metals or developing new materials, this uniformity guarantees that the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, leading to consistent and predictable results.
Versatility and Customization
Muffle furnaces are workhorses in many fields, including materials research, glass and ceramic manufacturing, foundry work, and analytical chemistry.
They can often accommodate larger samples and offer more internal capacity for their price compared to alternatives like tube furnaces. Furthermore, they can be custom-built to meet very specific production or testing requirements.
Simple and Safe Operation
Modern muffle furnaces are designed with a straightforward structure and clear controls. They incorporate critical safety features like insulated chambers, heat-resistant construction, and circuit breakers for emergency shutdowns.
While they require trained operation, their fundamental design is robust and relatively easy to manage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The strengths of a muffle furnace are directly linked to its weaknesses. Objectively evaluating these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Heating a sample indirectly is inherently inefficient. A significant amount of energy is consumed to bring the thick, insulated muffle chamber up to temperature before that heat can be radiated to the sample.
This results in higher energy consumption and lower overall heating efficiency compared to direct-fire kilns or furnaces. This is the primary and most significant disadvantage.
Operational Expertise and Maintenance
Achieving and maintaining precise temperature profiles requires specialized knowledge. These are not simple "plug-and-play" devices for untrained users.
They also require regular maintenance to ensure the integrity of the muffle, heating elements, and control systems, which is critical for ensuring continued performance and safety.
Scale and Physical Footprint
While excellent for laboratory and small-batch production, standard muffle furnaces have a limited capacity for large-scale industrial applications.
They can also require significant floor space and dedicated ventilation, which must be factored into any lab or facility planning.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your specific objective determines whether a muffle furnace is the right tool. The choice is less about which furnace is "best" and more about which is best for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity and repeatability: The muffle furnace is the definitive choice for applications like ashing, materials analysis, and sensitive research where sample contamination cannot be tolerated.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency or high-volume production: You should evaluate direct-heating kilns or continuous furnaces, as a muffle furnace's energy use and batch size may become a significant operational cost.
- If your primary focus is versatile heat treatment on a budget: A muffle furnace provides an excellent balance of performance and capacity for its cost, making it ideal for general-purpose materials processing, provided you can accommodate its energy needs.
Ultimately, understanding this balance between environmental purity and energy efficiency is the key to leveraging a muffle furnace effectively.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Contamination Control | Sealed chamber isolates samples from heating elements and gases | - |
| Temperature Uniformity | Indirect heating ensures even heat distribution | - |
| Efficiency | - | Higher energy consumption and lower heating efficiency |
| Versatility | Customizable for various applications like ashing and materials research | Limited capacity for large-scale industrial use |
| Operation | Simple, safe with modern controls | Requires trained expertise and regular maintenance |
Ready to enhance your lab's precision and efficiency? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need contaminant-free heating or tailored solutions for materials science, KINTEK is here to help. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















