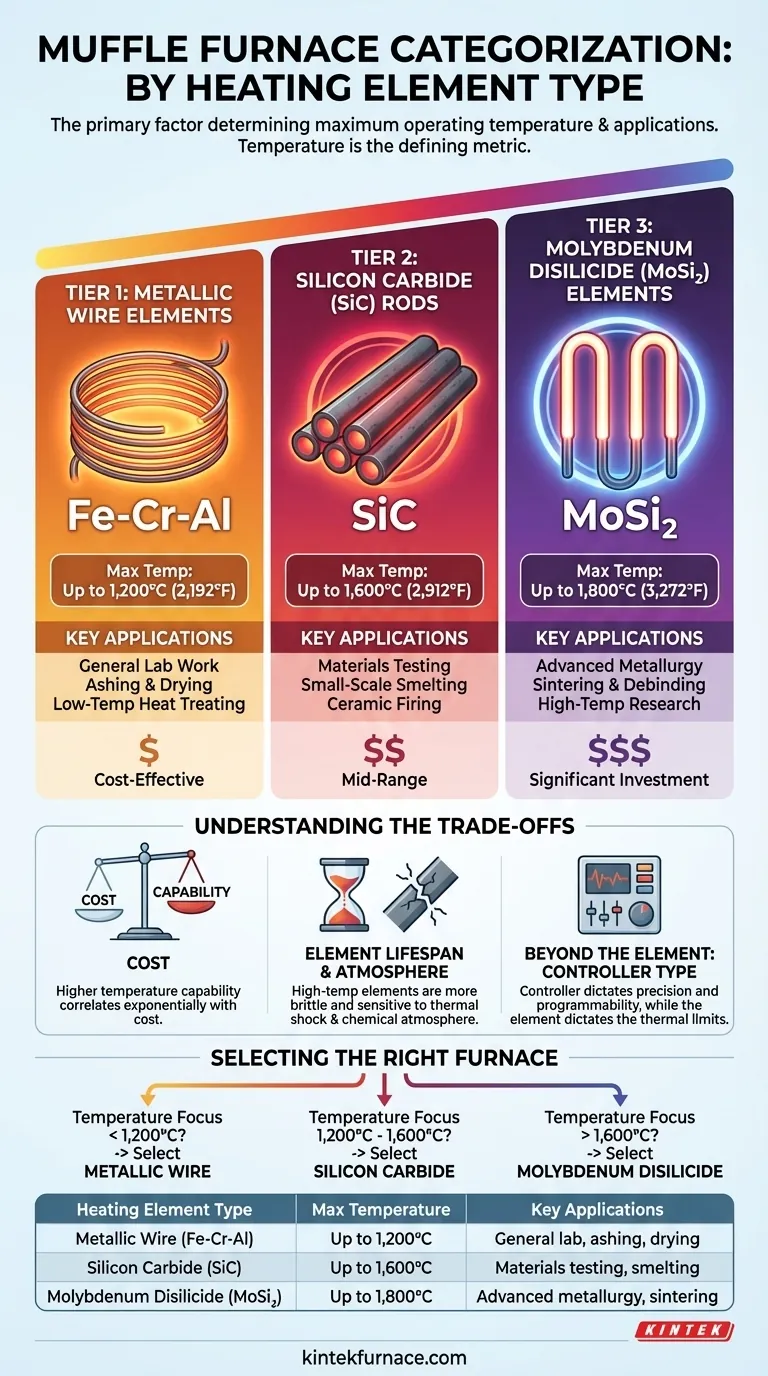
Muffle furnaces are primarily categorized by the material of their heating element, which directly dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature and its suitable applications. The three principal types are furnaces using metallic wire elements, those using silicon carbide elements, and high-temperature models using molybdenum disilicide elements. This classification is the most critical factor for matching a furnace to a specific scientific or industrial process.
The choice of a muffle furnace is fundamentally a choice about temperature. The material used for the heating element—metallic wire, silicon carbide, or molybdenum disilicide—is the single most important factor determining the furnace's maximum temperature range and, therefore, its suitability for your specific application.

Why the Heating Element is the Core Differentiator
Understanding the heating element is not just a technical detail; it is the key to understanding the furnace's core capability. The evolution and design of these components define what a modern muffle furnace can achieve.
### From Combustion to Clean Heat
Historically, muffle furnaces used external combustion to heat a sealed chamber, or "muffle," protecting the sample from fuel byproducts. With the advent of modern electrical heating elements, the heat source could be placed inside the chamber itself without contamination.
This innovation has made the terms "muffle furnace" and "chamber furnace" largely interchangeable today. The focus has shifted from how the sample is isolated to the performance of the electrical elements that generate the heat.
### Temperature as the Defining Factor
The material composition of a heating element sets a physical limit on how hot it can get before degrading or failing. This establishes the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Therefore, classifying furnaces by their element type is a direct way of classifying them by their primary performance metric: achievable heat.
The Three Tiers of Muffle Furnace Elements
Each category of heating element corresponds to a distinct temperature range and a set of typical applications.
### Type 1: Metallic Wire Elements (Up to 1,200°C)
These are the most common and cost-effective types of muffle furnaces. The heating elements are made from metallic alloys, often a blend of iron, chromium, and aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al).
They are ideal for general-purpose laboratory work and low-temperature heat-treating processes that operate comfortably below 1,200°C (2,192°F).
### Type 2: Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods (Up to 1,600°C)
For processes requiring higher temperatures, furnaces equipped with silicon carbide rods are the next tier. These robust ceramic elements can operate at significantly higher temperatures than metallic wires.
With a maximum temperature of around 1,600°C (2,912°F), these furnaces are suited for more demanding applications in materials testing, small-scale smelting, and certain ceramic firing processes.
### Type 3: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements (Up to 1,800°C)
At the top of the performance spectrum are furnaces using molybdenum disilicide elements. These advanced cermet materials can withstand extreme temperatures while resisting oxidation.
Reaching up to 1,800°C (3,272°F), these furnaces are essential for sophisticated metallurgical applications, including sintering, debinding for metal injection molding, and high-temperature materials research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves more than just picking the highest temperature. Each element type comes with a distinct set of practical and financial implications.
### Cost vs. Capability
The relationship between temperature capability and cost is exponential. An electric wire furnace is a standard piece of lab equipment, while a high-temperature MoSi₂ furnace represents a significant capital investment.
Over-specifying your furnace by choosing one with a much higher temperature range than you need leads to unnecessary expense, both in initial purchase price and long-term energy consumption.
### Element Lifespan and Atmosphere
Heating elements are consumables with a finite lifespan. High-temperature elements like SiC and MoSi₂ are more brittle and can be sensitive to rapid temperature cycling ("thermal shock").
Furthermore, the chemical atmosphere inside the furnace can react with certain elements, accelerating their degradation. It is crucial to ensure the element material is compatible with your process environment.
### Beyond the Element: Controller Type
While the element dictates the potential temperature, the furnace's controller dictates the precision. Furnaces can also be classified by their controller, from simple Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers to fully programmable systems.
A programmable controller allows for complex, multi-stage heating and cooling cycles essential for advanced processes, but the furnace's heating element still defines the absolute thermal limits.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by a clear understanding of your temperature requirements.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing, drying, or heat treating below 1,200°C: An electric wire element furnace is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is process development or materials testing requiring temperatures between 1,200°C and 1,600°C: A furnace with silicon carbide elements provides the necessary mid-range capability.
- If your primary focus is advanced metallurgy, sintering, or research at temperatures up to 1,800°C: You must invest in a furnace with molybdenum disilicide elements to meet these demanding requirements.
By understanding the direct link between the heating element and performance, you can confidently select a furnace that precisely matches your technical requirements and budget.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Max Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (Fe-Cr-Al) | Up to 1,200°C | General lab work, ashing, drying, low-temperature heat treating |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1,600°C | Materials testing, small-scale smelting, ceramic firing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1,800°C | Advanced metallurgy, sintering, high-temperature research |
Ready to optimize your laboratory processes with the perfect muffle furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results with a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















