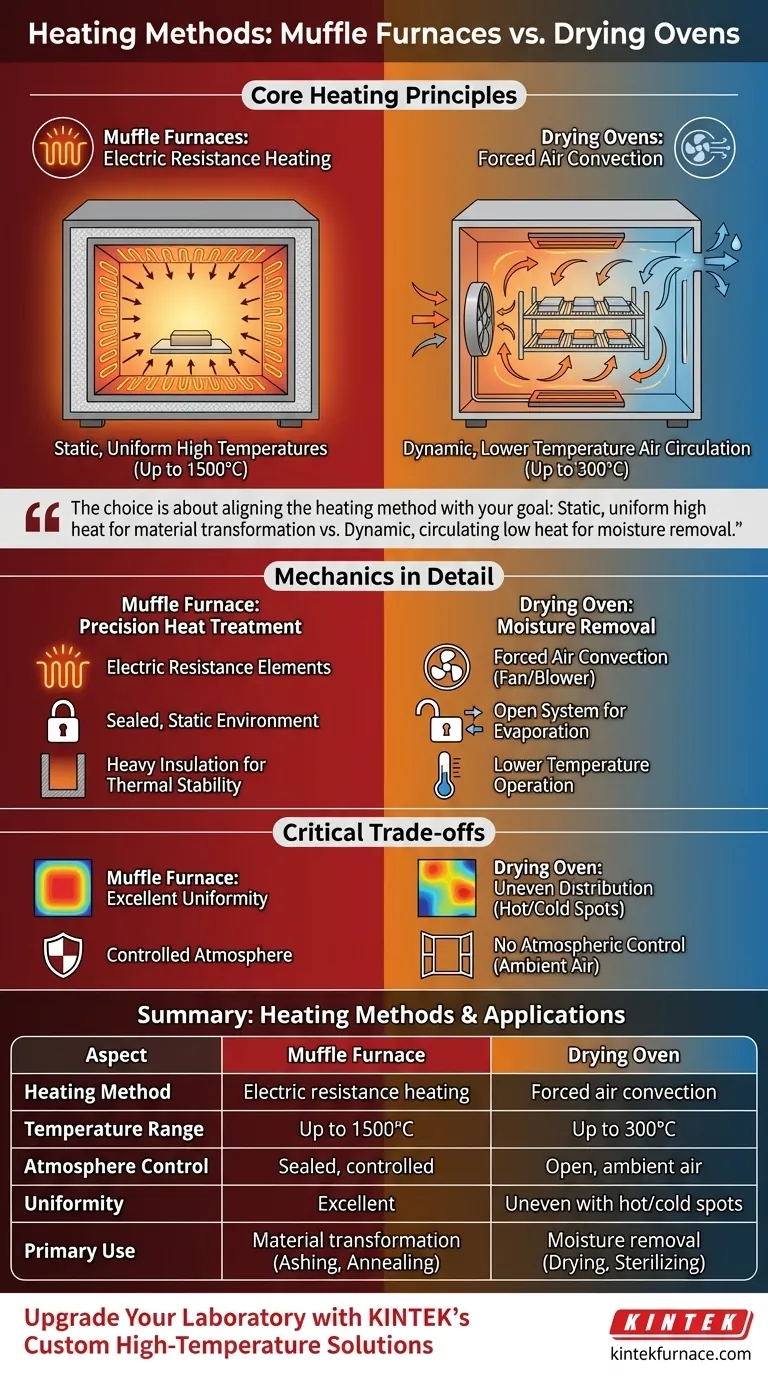
At their core, muffle furnaces and drying ovens use fundamentally different heating principles designed for distinct purposes. Muffle furnaces utilize electric resistance heating within a sealed, heavily insulated chamber to create static, uniform high temperatures. In contrast, drying ovens employ forced air convection, circulating heated air through a less-insulated chamber specifically to remove moisture.
The choice between these tools is not about which is "better," but which heating method aligns with your goal. A muffle furnace delivers static, high-temperature, uniform heat for material transformation, while a drying oven uses dynamic, lower-temperature air circulation for moisture removal.

The Mechanics of Muffle Furnace Heating
A muffle furnace is engineered for precision heat treatment in a controlled environment. Its heating method is a direct reflection of this purpose.
Electric Resistance Heating
The heat source consists of high-resistance wire elements, typically lining the chamber walls. When a high electric current is passed through them, they glow hot, radiating heat into the chamber.
A Sealed, Static Environment
The term "muffle" refers to the sealed inner chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements and the outside atmosphere. During operation, no air is circulated, creating a static environment where heat transfers evenly through radiation.
The Role of Heavy Insulation
To achieve and maintain extreme temperatures, often up to 1500°C, muffle furnaces are built with thick, multi-layered insulation. This design minimizes heat loss and ensures thermal stability.
How Drying Ovens Heat and Remove Moisture
A drying oven's primary function is not just to heat a sample, but to carry moisture away from it. Its heating system is built around this principle of active removal.
Forced Air Convection
Drying ovens use a fan or blower to force ambient air across heating elements (which can be electric or gas-fired). This hot air is then actively circulated throughout the larger chamber.
An Open System for Evaporation
The system is designed to be "open." Air enters, is heated, passes over the samples absorbing moisture, and is then exhausted from the chamber. This constant airflow is highly effective at drying, hardening, or sterilizing materials.
Lower Temperature Operation
Due to the constant airflow and less robust insulation, drying ovens operate at much lower temperatures, typically around 300°C. They are designed for drying efficiency, not extreme heat retention.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The difference in heating methods creates critical trade-offs in performance, uniformity, and application.
Temperature Uniformity
A muffle furnace's static, sealed environment allows heat to equalize naturally, resulting in excellent temperature uniformity across the entire chamber. This is critical for processes like annealing or calcination where every part of the sample must experience the same temperature.
Inevitable Hot and Cold Spots
The forced air in a drying oven inherently creates uneven temperature distribution. Areas closer to the blower or heating elements will be hotter, while other areas may be cooler. While acceptable for general drying, this makes it unsuitable for precision heat treatment.
Atmosphere Control
The sealed chamber of a muffle furnace provides a controlled atmosphere, protecting the sample from oxidation and contamination. A drying oven constantly introduces and exhausts ambient air, offering no atmospheric control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be based on the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material transformation (ashing, sintering, annealing): A muffle furnace is the correct tool due to its uniform, static heat and controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture (drying parts, curing coatings, sterilizing equipment): A drying oven is superior due to its effective use of forced air convection to carry moisture away.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature uniformity for a sensitive process: The muffle furnace's static heating environment is fundamentally more uniform than any forced-air system.
Understanding the heating method is the key to selecting the right tool and achieving reliable, repeatable results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Muffle Furnace | Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electric resistance heating | Forced air convection |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1500°C | Up to 300°C |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed, controlled | Open, ambient air |
| Uniformity | Excellent | Uneven with hot/cold spots |
| Primary Use | Material transformation (e.g., ashing, annealing) | Moisture removal (e.g., drying, sterilizing) |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Custom High-Temperature Solutions
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your specific needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, tailored solutions. Our product line includes Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all designed with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need uniform high-temperature processing or efficient drying, we have the expertise to enhance your lab's performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnaces can solve your challenges and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















