A high-temperature laboratory box furnace acts as the precision thermal engine required to synthesize Ba7Nb4MoO20 through a rigorous two-stage solid-state reaction. It facilitates this by executing exact temperature profiles: maintaining 900°C to drive preliminary decomposition, followed by a sustained 1100°C sintering phase to crystallize the final structure.
The success of this synthesis depends heavily on the furnace's ability to deliver long-term thermal stability. Without precise temperature uniformity during the extended 24-hour sintering phase, it is impossible to achieve the high crystalline purity required for the 7H hexagonal perovskite phase.

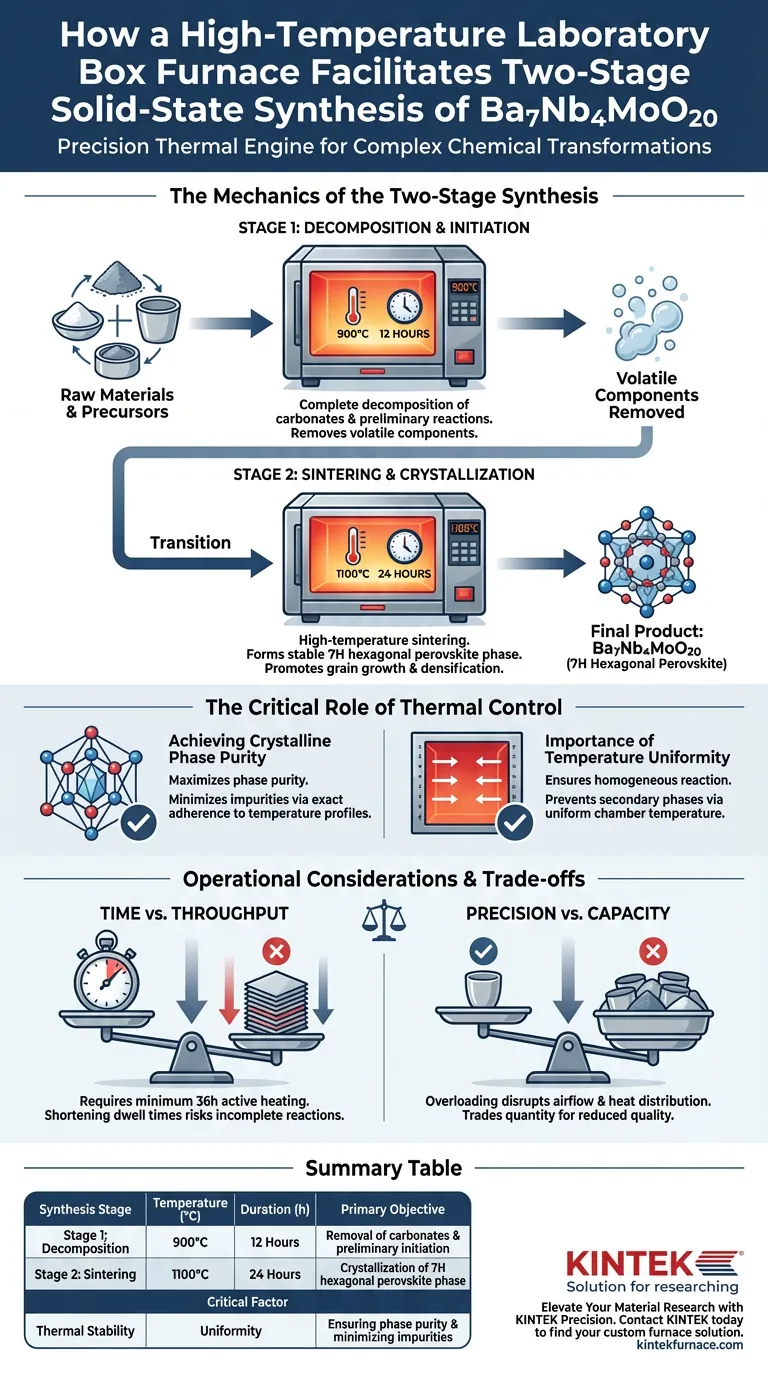
The Mechanics of the Two-Stage Synthesis
The laboratory box furnace is not merely a heating element; it is a programmable environment that manages chemical transformation through two distinct thermal distinct stages.
Stage 1: Decomposition and Initiation
The first requirement of the synthesis is the removal of volatile components from the raw materials. The furnace is set to maintain a temperature of 900°C for 12 hours.
This specific duration and temperature allow for the complete decomposition of carbonates. Simultaneously, it initiates the preliminary chemical reactions between the precursors, setting the stage for the final structure.
Stage 2: Sintering and Crystallization
Once the preliminary reactions are complete, the furnace must facilitate high-temperature sintering. The temperature is raised to 1100°C and held for 24 hours.
This extended dwell time is critical for forming the stable 7H hexagonal perovskite phase. The high heat promotes grain growth and densification, ensuring the material achieves the correct crystallographic structure.
The Critical Role of Thermal Control
Beyond simply reaching high temperatures, the box furnace ensures the quality of the final material through strict environmental control.
Achieving Crystalline Phase Purity
The primary goal of using a high-end box furnace is to maximize crystalline phase purity. Any deviation in the temperature profile can lead to incomplete reactions.
By maintaining exact adherence to the programmed setpoints, the furnace minimizes impurities that would otherwise degrade the material's properties.
Importance of Temperature Uniformity
Solid-state synthesis requires that every part of the sample experiences the exact same thermal history.
The box furnace provides temperature uniformity throughout the chamber. This ensures that the entire batch reacts homogeneously, preventing the formation of secondary phases in cooler spots of the crucible.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
While the box furnace enables high-quality synthesis, the process involves specific constraints that must be managed.
Time vs. Throughput
The synthesis of Ba7Nb4MoO20 is inherently time-intensive, requiring a minimum of 36 hours of active heating (excluding ramp times).
Attempting to accelerate this process to increase throughput is a common pitfall. Shortening the dwell times in the furnace will likely result in incomplete carbonate decomposition or a failure to fully stabilize the hexagonal phase.
Precision vs. Capacity
To maintain the required control accuracy, the furnace chamber should not be overcrowded.
Loading too many samples at once can disrupt the airflow and radiant heat distribution. This compromises the temperature uniformity essential for minimizing impurities, trading quantity for a drop in quality.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Strategy
To ensure consistent results when synthesizing Ba7Nb4MoO20, consider the following approach based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is maximum phase purity: Prioritize a furnace with verified spatial uniformity and calibrate it to hold 1100°C without drift for the full 24-hour cycle.
- If your primary focus is reproducibility: strictly enforce the 12-hour dwell at 900°C to ensure all carbonates are fully decomposed before the sintering phase begins.
By strictly adhering to these thermal parameters, you ensure the reliable formation of stable, high-purity hexagonal perovskite materials.
Summary Table:
| Synthesis Stage | Temperature (°C) | Duration (h) | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Decomposition | 900°C | 12 Hours | Removal of carbonates & preliminary initiation |
| Stage 2: Sintering | 1100°C | 24 Hours | Crystallization of 7H hexagonal perovskite phase |
| Critical Factor | Thermal Stability | Uniformity | Ensuring phase purity & minimizing impurities |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Consistency in Ba7Nb4MoO20 synthesis depends on the precision of your thermal equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the exact temperature profiles required for complex solid-state reactions.
Whether you need superior temperature uniformity for hexagonal perovskite phases or customizable lab high-temp furnaces for unique sintering requirements, KINTEK provides the reliability your lab demands.
Contact KINTEK today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Bettina Schwaighofer, Ivana Radosavljević Evans. Oxide ion dynamics in hexagonal perovskite mixed conductor Ba<sub>7</sub>Nb<sub>4</sub>MoO<sub>20</sub>: a comprehensive <i>ab initio</i> molecular dynamics study. DOI: 10.1039/d3ma00955f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of muffle furnaces in the pretreatment of medical samples? Essential for Accurate Trace Element Analysis
- What role does an industrial High-temperature Electric Furnace play? Achieve Precise Carbon Steel Standardization
- What factors affect the price range of muffle furnaces? Key Drivers for Smart Lab Investment
- Why is it necessary to use a preheating furnace for SiC and B4C? Ensure Safety and Quality in Magnesium Composites
- What are the advantages of the bottom-loading furnace configuration? Achieve High-Temp Control and Element Protection
- How is the muffle furnace designed to ensure uniform and safe heating? Discover Its Precision Engineering
- What is the role of high-temperature furnaces in 3D-printed glass debinding? Mastering the Silica Foundation
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature muffle furnace for thermal etching of ceramic samples? Expert Insights



















