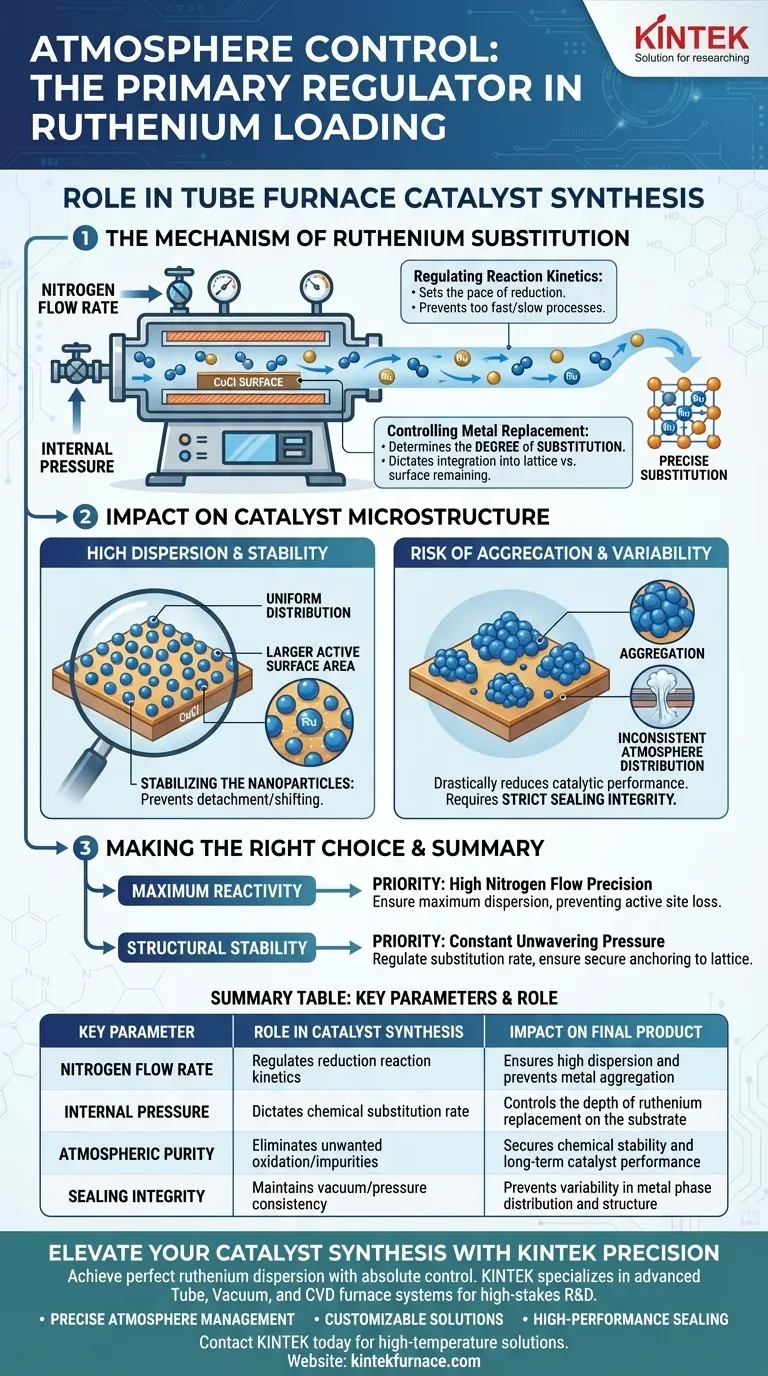
Atmosphere control functions as the primary regulator of reaction kinetics during the ruthenium loading process. Specifically, by manipulating the nitrogen flow rate and internal pressure within the tube furnace, you directly dictate the speed of the reduction reaction. This precise regulation controls the extent to which ruthenium replaces copper on the substrate, a critical step in defining the final catalyst structure.
By governing the reaction environment, atmosphere control transforms a simple heating process into a precise chemical substitution operation. It ensures ruthenium is chemically bonded and evenly dispersed rather than physically clumped, directly securing the catalyst's long-term stability and performance.
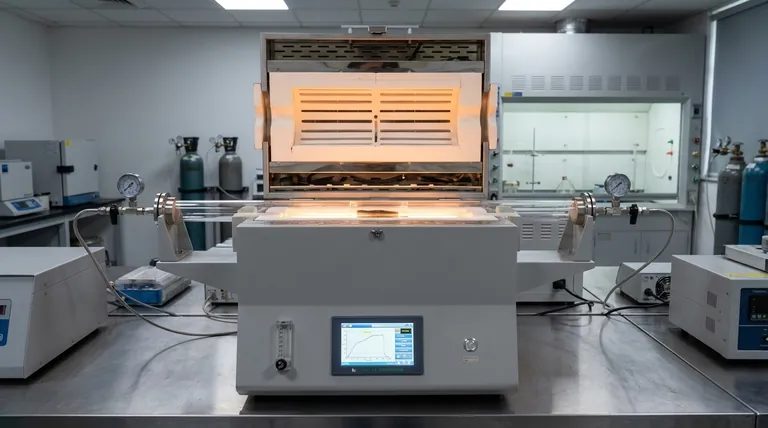

The Mechanism of Ruthenium Substitution
Regulating Reaction Kinetics
The core function of the tube furnace atmosphere is to set the pace of the reduction reaction.
By adjusting the nitrogen flow rate and pressure, you modulate the reaction environment. This control prevents the reaction from proceeding too quickly or too slowly, ensuring the chemical processes occur at a controlled, optimal rate.
Controlling Metal Replacement
The goal of this synthesis is often the replacement of copper on a CuCl surface with ruthenium.
The atmosphere does not just protect the sample; it determines the degree of substitution. Precise pressure and flow settings allow you to dictate exactly how much ruthenium integrates into the lattice structure versus how much remains on the surface or fails to react.
Impact on Catalyst Microstructure
Ensuring High Dispersion
A strictly controlled atmosphere is required to achieve a uniform distribution of active sites.
When the flow and pressure are uniform, ruthenium nanoparticles disperse evenly across the CuCl substrate. High dispersion creates a larger active surface area, which is the defining characteristic of a highly efficient catalyst.
Stabilizing the Nanoparticles
Beyond just placement, the atmosphere influences the physical stability of the metal phase.
Proper atmospheric conditions ensure that once the ruthenium is deposited, it remains stable on the substrate. This prevents the particles from detaching or shifting during subsequent use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Aggregation
The most significant risk in this process is uneven atmosphere distribution.
If the gas flow is inconsistent or the pressure fluctuates, the ruthenium metal phase will fail to disperse. Instead, it will suffer from aggregation, clumping together into larger, less effective particles that drastically reduce catalytic performance.
Sealing and Consistency
Achieving this control requires hardware capable of maintaining strict seals.
As noted in broader applications, the furnace must utilize sealing flanges (often stainless steel) to maintain vacuum or pressure integrity. Any leak or failure in the sealing mechanism compromises the atmosphere, leading to variable oxidation states or incomplete reduction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your ruthenium synthesis, align your atmospheric parameters with your specific structural targets:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Reactivity: Prioritize high nitrogen flow precision to ensure maximum dispersion of ruthenium nanoparticles, preventing active site loss through clumping.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Focus on maintaining constant, unwavering pressure to regulate the substitution rate, ensuring the ruthenium is securely anchored to the CuCl lattice.
Atmosphere control is not merely a protective measure; it is the active tool that sculpts the geometry and efficiency of your final catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Role in Catalyst Synthesis | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Flow Rate | Regulates reduction reaction kinetics | Ensures high dispersion and prevents metal aggregation |
| Internal Pressure | Dictates chemical substitution rate | Controls the depth of ruthenium replacement on the substrate |
| Atmospheric Purity | Eliminates unwanted oxidation/impurities | Secures chemical stability and long-term catalyst performance |
| Sealing Integrity | Maintains vacuum/pressure consistency | Prevents variability in metal phase distribution and structure |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect ruthenium dispersion requires more than just heat; it requires absolute control over your reaction environment. KINTEK specializes in advanced Tube, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems designed specifically for high-stakes research and development.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab furnaces offer:
- Precise Atmosphere Management: Optimized for sensitive nitrogen flow and pressure control.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored configurations to meet your unique chemical substitution and loading requirements.
- High-Performance Sealing: Ensuring consistent vacuum integrity for repeatable results.
Don't let inconsistent kinetics compromise your catalyst performance. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our customizable high-temperature solutions can refine your material synthesis.
Visual Guide
References
- Tao Chen, Qiangchun Liu. RuCu Nanorod Arrays Synergistically Promote Efficient Water-Splitting. DOI: 10.3390/catal15010098
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of using argon in furnaces? Ensure Maximum Purity and Performance
- Can atmosphere furnaces be customized for specific applications? Unlock Precision for Your Unique Processes
- What is the function of a tunnel-type controlled atmosphere annealing furnace? Restoring Ductility in Copper Tubes
- How does the experimental box type atmosphere furnace ensure accurate atmosphere control? Master Precise Gas Management for Reliable Results
- Why is a high-temperature reaction furnace with CO2 control necessary for activated carbon? Unlock Maximum Porosity
- What gases are commonly used in heat treatment furnace atmospheres? Optimize Your Process with the Right Gas Mix
- Why are retort furnaces considered versatile tools? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing Control
- What process environment does a tube atmosphere furnace provide for LMFP? Master Secondary Crystallization



















